Abstract
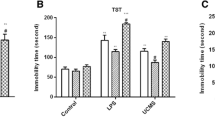
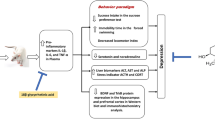
The mechanisms by which inflammation affects the different emotional moods are only partially known. Previous works have pointed to stress hormones like glucocorticoids plus the vascular factor endothelin-1 as key factors evoking stressful states especially in relation to endothelial dysfunctions. With this work, it was our intention to establish the role of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine expression variations towards depression-like behaviors and consequently the development of neurodegeneration events caused by endothelial damages in the hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). Such a rodent, which is considered a valuable animal model to test depression and anxiety states, exhibited a variety of depression-like behaviors including reduction in sucrose consumption, locomotion, and exploration (p < 0.01) following exposure to unpredictable chronic mild stress. Contextually, a tight correlation between unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced depressive states and expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines was detected as shown by marked expression levels (p < 0.01) of IL-1β and NF-kB in the hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex. Even the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 supplied notably significant (p < 0.001) expression levels in the same areas of resilient hamsters. Application of hemodynamic and endothelial functional studies pointed to altered arterial endothelial activities in depressed with respect to resilient animals. Moreover, evident damaged neuronal fields in the above areas of depressed hamsters allowed us to correlate such a behavioral phenomenon to the upregulation of IL-1β and NF-κB. Overall, the differing roles of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines on depressive states, especially in view of brain endothelial damages, may provide novel therapeutic measures against mood disorders linked to neurodegenerative diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DEP:
-
Depression
- RES:
-
Resilient
- AMY:
-
Amygdala
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- UCMS:
-
Unpredictable chronic mild stress
References
Lam RW, Malhi GS, McIntyre RS, Demyttenaere K, Gorwood P, Michalak EE et al (2013) Fatigue and occupational functioning in major depressive disorder. Aust NZJ Psychiatry 47:989–991
Krishnadas R, Cavanagh J (2012) Depression: an inflammatory illness? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:495–502
Gorska-Ciebiada, M., Saryusz-Wolska, M., Borkowska, A., Ciebiada, M., Loba, J. (2015) Adiponectin, leptin and IL-1 β in elderly diabetic patients with mild cognitive impairment. Metab Brain Dis [Epub ahead of print]
Passos IC, Vasconcelos-Moreno MP, Costa LG, Kunz M, Brietzke E, Quevedo J, Salum G, Magalhães PV, Kapczinski F, Kauer-Sant’Anna M (2015) Inflammatory markers in post-traumatic stress disorder: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Lancet Psychiatry 11:1002–1012
Hocaoglu C, Kural B, Aliyazicioglu R, Deger O, Cengiz S (2012) IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IFN-γ, TNF-α and its relationship with lipid parameters in patients with major depression. Metab Brain Dis 4:425–430
Peter J, Frey O, Stallmach A, Bruns T (2013) Attenuated antigen-specific T cell responses in cirrhosis are accompanied by elevated serum interleukin-10 levels and down-regulation of HLA-DR on monocytes. BMC Gastroenterol 27:13–37
Manji HK, Duman RS (2001) Impairments of neuroplasticity and cellular resilience in severe mood disorders: implications for the development of novel therapeutics. Psychopharmacol Bull 2:5–49
De Souza J, Jones LA, Rickards H (2010) Validation of self-report depression rating scales in Huntington’s disease. Mov Disord 1:91–96
Burgut FT, Benaur M, Hencliffe C (2006) Late-life depression: a neuropsychiatric approach. Expert Rev Neurother 1:65–72
Lavretsky H, Zheng L, Weiner MW, Mungas D, Reed B, Kramer JH, Jagust W, Chui H, Mack WJ (2008) The MRI brain correlates of depressed mood, anhedonia, apathy, and anergia in older adults with and without cognitive impairment or dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 10:1040–1050
Sakkas LI, Bogdanos DP (2016) Systemic sclerosis: new evidence re-enforces the role of B cells. Autoimmun Rev 2:155–161
Appenzeller S, Carnevalle AD, Li LM, Costallat LT, Cendes F (2006) Hippocampal atrophy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 12:1585–1589
Wichers M, Maes M (2002) The psychoneuroimmuno-pathophysiology of cytokine-induced depression in humans. Inter J Neuropsychoparmacol 5(4):375–388
Domingo AK, Asmal L, Seedat S, Esterhuizen TM, Laurence C, Volmink J (2015) Investigating the association between diabetes mellitus, depression and psychological distress in a cohort of South African teachers. S Afr Med J 12:1057–1060
Remus JL, Stewart LT, Camp RM, Novak CM, Johnson JD (2015) Interaction of metabolic stress with chronic mild stress in altering brain cytokines and sucrose preference. Behav Neurosci 129:321–330
Ji BS, Cen J, Liu L, He L (2013) In vitro and in vivo study of dolichyl phosphate on the efflux activity of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier. Int J Dev Neurosci 31:828–835
Han P, Caselli RJ, Baxter L, Serrano G, Yin J, Beach TG, Reiman EM, Shi J (2015) Association of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide with cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol 3:333–339
Hu W, Zhang Y, Wu W, Yin Y, Huang D, Wang Y, Li W, Li W (2016) Chronic glucocorticoids exposure enhances neurodegeneration in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via NLRP-1 inflammasome activation in male mice. Brain Behav Immun 52:58–70
Abelaira, H.M., Réus, G.Z., Ignácio, Z.M., Dos Santos, M.A., de Moura, A.B., Matos, D., Demo, J.P., da Silva, J.B., Danielski, L.G., Petronilho, F., Carvalho, A.F., Quevedo, J. (2016) Ketamine exhibits different neuroanatomical profile after mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition in the prefrontal cortex: the role of inflammation and oxidative stress. Mol Neurobiol (In press).
Lackner RJ, Moore MT, Minerovic J, Fresco DM (2015) Explanatory flexibility and explanatory style in treatment-seeking clients with axis I psychopathology. Cognit Ther Res 6:736–743
Bethell KD, Koyama NF (2015) Happy hamsters? Enrichment induces positive judgement bias for mildly (but not truly) ambiguous cues to reward and punishment in Mesocricetus auratus. R Soc Open Sci 7:140399
Frisbee JC, Brooks SD, Stanley SC, d’Audiffret AC (2015) An unpredictable chronic mild stress protocol for instigating depressive symptoms, behavioral changes and negative health outcomes in rodents. J Vis Exp 2:106
Jayatissa MN, Henningsen K, West MJ, Wilborg O (2009) Decreased cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus does not associate with development of anhedonic-like symptoms in rats. Brain Res 1290:133–141
Bourin M, Hascoet M (2003) The mouse light/dark box test. Eur J Pharmacol 463:55–65
Pellow S, File SE (1986) Anxiolytic and anxiogenic drug effects on exploratory activity in an elevated plus-maze: a novel test of anxiety in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:525–529
Avolio E, Alò R, Carelli A, Canonaco M (2011) Amygdalar orexinergic-GABAergic interactions regulate anxiety behaviors of the Syrian golden hamster. Behav Brain Res 218:288–295
Alò R, Mele M, Fazzari G, Avolio E, Canonaco M (2015b) Exposure to sub-chronic unpredictable stress accounts for antidepressant-like effects in hamsters treated with BDNF and CNQX. Brain Res Bull 118:65–77
Alò R, Mele M, Avolio E, Fazzari G, Canonaco M (2015a) Distinct amygdalar AMPAergic/GABAergic mechanisms promote anxiolitic-like effects in an unpredictable stress model of the hamster. J Mol Neurosci 55:541–551
Alò R, Avolio E, Mele M, Storino F, Canonaco A, Carelli A, Canonaco M (2014) Excitatory/inhibitory equilibrium of the central amygdala nucleus gates anti-depressive and anxiolytic states in the hamster. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 118:79–86
Bueno A, De Olmos S, Heimer L, De Olmos J (2003) NMDA-antagonist MK-801- induced neuronal degeneration in Wistar rat brain detected by the amino-cupric-silver method. Exp Toxicol Pathol 54:319–334
Lasselin, J., Elsenbruch, S., Lekander, M., Axelsson, J., Karshikoff, B., Grigoleit, J.S., Engler, H., Schedlowski, M., Benson, S. (2016) Mood disturbance during experimental endotoxemia: predictors of state anxiety as a psychological component of sickness behavior. Brain Behav Imm [Epub ahead of print].
Relja B, Horstmann JP, Kontradowitz K, Jurida K, Schaible A, Neunaber C, Oppermann E, Marzi I (2015) Nlrp1 inflammasome is downregulated in trauma patients. J Mol Med 12:1391–1400
Gold SM, Irwin MR (2009) Depression and immunity: inflammation and depressive symptoms in multiple sclerosis. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 2:309–320
Momeni M, Ghorban K, Dadmanesh M, Khodadadi H, Bidaki R, Kazemi Arababadi M, Kennedy D (2016) ASC provides a potential link between depression and inflammatory disorders: a clinical study of depressed Iranian medical students. Nord J Psychiatry 11:1–5
Maes M, Yirmyia R, Noraberg J, Brene S, Hibbeln J, Perini G, Kubera M, Bob P, Lerer B, Maj M (2009) The inflammatory & neurodegenerative (I&ND) hypothesis of depression: leads for future research and new drug developments in depression. az Metab Brain Dis 1:27–53
Horowitz MA, Wertz J, Zhu D, Cattaneo A, Musaelyan K, Nikkheslat N, Thuret S, Pariante CM, Zunszain PA (2014) Antidepressant compounds can be both pro- and anti-inflammatory in human hippocampal cells. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 31:18
Wuwongse S, Chang RC, Law AC (2010) The putative neurodegenerative links between depression and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 4:362–375
Murphy N, Grehan B, Lynch MA (2014) Glial uptake of amyloid beta induces NLRP3 inflammasome formation via cathepsin-dependent degradation of NLRP10. Neruomol Med 1:205–215
Hemmerle AM, Herman JP, Seroogy KB (2012) Stress, depression and Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 1:79–86
Liu, C.S., Adibfar, A., Herrmann, N., Gallagher, D., Lanctôt, K.L. (2016) Evidence for inflammation-associated depression. Curr Top Behav Neurosci (In press).
Rossetti AC, Papp M, Gruca P, Paladini MS, Racagni G, Riva MA, Molteni R (2016) Stress-induced anhedonia is associated with activation of the inflammatory system in the rat brain: restorative effect of pharmacological intervention. Pharmacol Res 103:1–12
Daniele S, Da Pozzo E, Zappelli E, Martini C (2015) Trazodone treatment protects neuronal-like cells from inflammatory insult by inhibiting NF-κB, p38 and JNK. Cell Signal 27:1609–1629
Arora V, Chopra K (2013) Possible involvement of oxido-nitrosative stress induced neuro-inflammatory cascade and monoaminergic pathway: underpinning the correlation between nociceptive and depressive behaviour in a rodent model. J Affect Disord 3:1041–1052
Pan J, Lei X, Wang J, Huang S, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Chen W, Li D, Zheng J, Cui H, Liu Q (2015) Effects of Kaixinjieyu, a Chinese herbal medicine preparation, on neurovascular unit dysfunction in rats with vascular depression. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:291
Dowling NM, Johnson SC, Gleason CE, Jagust WJ (2015) The mediational effects of FDG hypometabolism on the association between cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and neurocognitive function. NeuroImage 105:357–368
Tizabi, Y. (2015) Duality of antidepressants and neuroprotectants. Neurotox Res [Epub ahead of print].
Rosso IM, Cintron CM, Steingard RJ, Renshaw PF, Young AD, Yurgelun-Todd DA (2005) Amygdala and hippocampus volumes in pediatric major depression. Biol Psychiatry 1:21–26
Ozalay O, Calli C, Kitis O, Cagdas Eker M, Donat Eker O, Ozan E, Coburn K, Saffet Gonul A (2013) The relationship between the anterior corpus callosum size and prefrontal cortex volume in drug-free depressed patients. J Affect Disord 2:281–285
Hurley LL, Tizabi Y (2013) Neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, and depression. Neurotox Res 2:131–144
Zhang Y, Liu L, Liu YZ, Shen XL, Wu TY, Zhang T, Wang W, Wang YX, Jiang CL (2015) NLRP3 inflammasome mediates chronic mild stress-induced depression in mice via neuroinflammation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18:8
Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Senovilla L, Menger L, Chaput N, Kroemer G (2010) Immunogenic tumor cell death for optimal anticancer therapy: the calreticulin exposure pathway. Clin Cancer Res 12:3100–3104
Brown GC, Vilalta A (2015) How microglia kill neurons. Brain Res 1628:288–297
Zhu Y, Chen X, Liu Z, Peng YP, Qiu YH (2015) Interleukin-10 protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced neuro-inflammation and neurotoxicity in ventral mesencephalic cultures. Int J Mol Sci 28:17
Norden DM, Fenn AM, Dugan A, Godbout JP (2014) TGFβ produced by IL-10 redirected astrocytes attenuates microglial activation. Glia 62:881–895
Koriauli S, Natsvlishvili N, Barbakadze T, Mikeladze D (2015) Knockdown of interleukin-10 induces the redistribution of sigma1-receptor and increases the glutamate-dependent NADPH-oxidase activity in mouse brain neurons. Biol Res 9:48–55
Ge L, Liu L, Liu H, Liu S, Xue H, Wang X, Yuan L, Wang Z, Liu D (2015) Resveratrol abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior, neuroinflammatory response, and CREB/BDNF signaling in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 768:49–57
Lunnon K, Smith R, Hannon E, De Jager PL, Srivastava G, Volta M, Troakes C, Al-Sarraj S, Burrage J, Macdonald R, Condliffe D, Harries LW, Katsel P, Haroutunian V, Kaminsky Z, Joachim C, Powell J, Lovestone S, Bennett DA, Schalkwyk LC, Mill J (2014) Methylomic profiling implicates cortical deregulation of ANK1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci 17:1164–1170
Homberg JR, Molteni R, Calabrese F, Riva MA (2014) The serotonin-BDNF duo: developmental implications for the vulnerability to psychopathology. Neurosci Biobehav 43:35–47
Pham, T.H., Mendez-David, I., Defaix, C., Guiard, B.P., Tritschler, L., David, D.J., Gardier, A.M. (2016) Ketamine treatment involves medial prefrontal cortex serotonin to induce a rapid antidepressant-like activity in BALB/cJ mice. Neuropharmacol. (In press).
Xue Q, Liu Y, Qi H, Ma Q, Xu L, Chen W, Chen G, Xu X (2013) A novel brain neurovascular unit model with neurons, astrocytes and microvascular endothelial cells of rat. Int J Biol Sci 9:174–189
Ozcan ME, Gulec M, Ozerol E, Polat R, Akyol O (2004) Antioxidant enzyme activities and oxidative stress in affective disorders. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 19:89–95
Gibson SA, Korade Z, Shelton RC (2012) Oxidative stress and glutathione response in tissue cultures from persons with major depression. J Psychiatr Res 46:1326–1332
Meng XF, Yu JT, Wang HF, Tan MS, Wang C, Tan CC, Tan L (2014) Midlife vascular risk factors and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 42(4):1295–1310
Barnard KD, Skinner TC, Peveler R (2006) The prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with type 1 diabetes: systematic literature review. Diabet Med 4:445–448
Chen C, Wang Y, Zhang J, Ma L, Gu J, Ho G (2014) Contribution of neural cell death to depressive phenotypes of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Dis Model Mech 6:723–730
Hamamcioglu K, Reder AT (2007) Interferon-beta regulates cytokines and BDNF: greater effect in relapsing than in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 4:459–470
Acknowledgments
We thank the Italian University Research Ministry (MIUR), Regione of Calabria (POR, FSE-2007/2013) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avolio, E., Fazzari, G., Mele, M. et al. Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress Paradigm Established Effects of Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Cytokine on Neurodegeneration-Linked Depressive States in Hamsters with Brain Endothelial Damages. Mol Neurobiol 54, 6446–6458 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0171-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0171-1