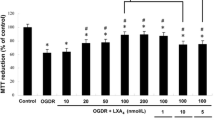
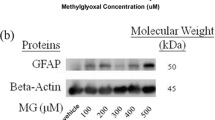
Abstract
An elevated level of glucose has been found in the blood of hyperglycemia and diabetes patients associated with several central nervous system (CNS) complications. These disorders may be due to the up-regulation of many neurotoxic mediators by host cells triggered by high glucose (HG). Moreover, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) plays a crucial role in tissue pathological changes such as brain injuries. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying HG-induced HO-1 expression in brain cells remain poorly defined. Thus, we use the rat brain astrocytes (RBA-1) as a model to investigate the signaling mechanisms of HO-1 induction by HG and its effects on neuronal cells. We demonstrated that HG induced HO-1 expression via a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent signaling pathway. NADPH oxidase (Nox)- and mitochondrion-dependent ROS generation led to activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) and then activated the downstream transcriptional factors nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and c-Fos/activator protein 1 (AP-1), respectively. Subsequently, the activated NF-κB and AP-1 turned on transcription of HO-1 gene. These results indicated that in brain astrocytes, activation of MAPK-mediated NF-κB and c-Fos/AP-1 cascades by Nox/ROS and mitoROS-dependent events is essential for HO-1 up-regulation induced by HG. Moreover, we found that HG-induced extracellular ROS increase and HO-1 expression from astrocytes resulted in neuronal apoptosis. These results offers new insights into the mechanisms and effects of the action of HG, supporting that HG may cause brain disorders in the development of diabetes- and hyperglycemia-induced CNS complications such as neurodegenerative diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomlinson DR, Gardiner NJ (2008) Glucose neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:36–45
Massengale JL, Gasche Y, Chan PH (2002) Carbohydrate source influences gelatinase production by mouse astrocytes in vitro. Glia 38:240–245
Chen J, Cui X, Zacharek A, Cui Y, Roberts C, Chopp M (2011) White matter damage and the effect of matrix metalloproteinases in type 2 diabetic mice after stroke. Stroke 42:445–452
Llewelyn JG (2003) The diabetic neuropathies: types, diagnosis and management. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74(Suppl 2):ii15–ii19
Archer AG, Watkins PJ, Thomas PK, Sharma AK, Payan J (1983) The natural history of acute painful neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:491–499
Sima AA, Bril V, Nathaniel V, McEwen TA, Brown MB, Lattimer SA, Greene DA (1988) Regeneration and repair of myelinated fibers in sural-nerve biopsy specimens from patients with diabetic neuropathy treated with sorbinil. New Engl J Med 319:548–555
Kimelberg HK (1995) Receptors on astrocytes—what possible functions? Neurochem Int 26:27–40
Hamby ME, Sofroniew MV (2010) Reactive astrocytes as therapeutic targets for CNS disorders. Neurotherapeutics 7:494–506
Verkhratsky A, Olabarria M, Noristani HN, Yeh CY, Rodriguez JJ (2010) Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 7:399–412
Yang CM, Hsieh HL, Lin CC, Shih RH, Chi PL, Cheng SE, Hsiao LD (2013) Multiple factors from bradykinin-challenged astrocytes contribute to the neuronal apoptosis: involvement of astroglial ROS, MMP-9, and HO-1/CO system. Mol Neurobiol 47:1020–1033
Syapin PJ (2008) Regulation of haeme oxygenase-1 for treatment of neuroinflammation and brain disorders. Br J Pharmacol 155:623–640
Ryter SW, Alam J, Choi AM (2006) Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: from basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol Rev 86:583–650
Cuadrado A, Rojo AI (2008) Heme oxygenase-1 as a therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases and brain infections. Curr Pharm Des 14:429–442
Schipper HM, Bennett DA, Liberman A, Bienias JL, Schneider JA, Kelly J, Arvanitakis Z (2006) Glial heme oxygenase-1 expression in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 27:252–261
Song L, Song W, Schipper HM (2007) Astroglia overexpressing heme oxygenase-1 predispose co-cultured PC12 cells to oxidative injury. J Neurosci Res 85:2186–2195
Halliwell B (2006) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J Neurochem 97:1634–1658
Chrissobolis S, Faraci FM (2008) The role of oxidative stress and NADPH oxidase in cerebrovascular disease. Trends Mol Med 14:495–502
Vallyathan V, Shi X (1997) The role of oxygen free radicals in occupational and environmental lung diseases. Environ Health Perspect 105(Suppl 1):165–177
Mehta SL, Manhas N, Raghubir R (2007) Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Res Rev 54:34–66
Park L, Anrather J, Girouard H, Zhou P, Iadecola C (2007) Nox2-derived reactive oxygen species mediate neurovascular dysregulation in the aging mouse brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1908–1918
Wang HH, Hsieh HL, Wu CY, Sun CC, Yang CM (2009) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via a p42/p44 and JNK-dependent AP-1 pathway in brain astrocytes. Glia 57:24–38
Wei W, Liu Q, Tan Y, Liu L, Li X, Cai L (2009) Oxidative stress, diabetes, and diabetic complications. Hemoglobin 33:370–377
Shanmugam N, Reddy MA, Guha M, Natarajan R (2003) High glucose-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes in monocytic cells. Diabetes 52:1256–1264
Nishikawa T, Araki E (2007) Impact of mitochondrial ROS production in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:343–353
Hsieh HL, Wang HH, Wu CY, Yang CM (2010) Reactive oxygen species-dependent c-Fos/activator protein 1 induction upregulates heme oxygenase-1 expression by bradykinin in brain astrocytes. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:1829–1844
Tung WH, Hsieh HL, Yang CM (2010) Enterovirus 71 induces COX-2 expression via MAPKs, NF-κB, and AP-1 in SK-N-SH cells: role of PGE2 in viral replication. Cell Signal 22:234–246
LeBel CP, Ischiropoulos H, Bondy SC (1992) Evaluation of the probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress. Chem Res Toxicol 5:227–231
Reinehr R, Görg B, Becker S, Qvartskhava N, Bidmon HJ, Selbach O, Haas HL, Schliess F et al (2007) Hypoosmotic swelling and ammonia increase oxidative stress by NADPH oxidase in cultured astrocytes and vital brain slices. Glia 55:758–771
Ryter SW, Choi AM (2005) Heme oxygenase-1: redox regulation of a stress protein in lung and cell culture models. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:80–91
Infanger DW, Sharma RV, Davisson RL (2006) NADPH oxidases of the brain: distribution, regulation, and function. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1583–1596
Kann O, Kovács R (2007) Mitochondria and neuronal activity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C641–C657
Shi Q, Gibson GE (2007) Oxidative stress and transcriptional regulation in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 21:276–291
Floyd RA (1999) Neuroinflammatory processes are important in neurodegenerative diseases: an hypothesis to explain the increased formation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as major factors involved in neurodegenerative disease development. Free Radic Biol Med 26:1346–1355
Wyss-Coray T (2006) Inflammation in Alzheimer disease: driving force, bystander or beneficial response? Nat Med 12:1005–1015
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2010) Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140:918–934
Wang J, Li G, Wang Z, Zhang X, Yao L, Wang F, Liu S, Yin J et al (2012) High glucose-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species in cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience 202:58–68
Bedard K, Krause KH (2007) The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87:245–313
Mohanty P, Hamouda W, Garg R, Aljada A, Ghanim H, Dandona P (2000) Glucose challenge stimulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by leucocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:2970–2973
Lee HB, Yu MR, Yang Y, Jiang Z, Ha H (2003) Reactive oxygen species-regulated signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(8 Suppl 3):S241–S245
Hsieh HL, Chi PL, Lin CC, Yang CC, Yang CM (2014) Up-regulation of ROS-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 from high-glucose-challenged astrocytes contributes to the neuronal apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol 50:520–533
Abramov AY, Jacobson J, Wientjes F, Hothersall J, Canevari L, Duchen MRL (2005) Expression and modulation of an NADPH oxidase in mammalian astrocytes. J Neurosci 25:9176–9184
Lin CC, Hsieh HL, Shih RH, Chi PL, Cheng SE, Chen JC, Yang CM (2012) NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species signal contributes to bradykinin-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and cell migration in brain astrocytes. Cell Commun Signal 10:35
He M, Pan H, Xiao C, Pu M (2013) Roles for redox signaling by NADPH oxidase in hyperglycemia-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression in the diabetic retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:4092–4101
Brown GC, Bal-Price A (2003) Inflammatory neurodegeneration mediated by nitric oxide, glutamate, and mitochondria. Mol Neurobiol 27:325–355
Bugger H, Abel ED (2010) Mitochondria in the diabetic heart. Cardiovasc Res 8:229–240
Daiber A (2010) Redox signaling (cross-talk) from and to mitochondria involves mitochondrial pores and reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta 1797:897–906
Dikalova AE, Bikineyeva AT, Budzyn K, Nazarewicz RR, McCann L, Lewis W, Harrison DG, Dikalov SI (2010) Therapeutic targeting of mitochondrial superoxide in hypertension. Circ Res 107:106–116
Gao L, Mann GE (2009) Vascular NAD(P)H oxidase activation in diabetes: a double-edged sword in redox signalling. Cardiovasc Res 82:9–20
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869
Lopes JP, Oliveira SM, Soares Fortunato J (2008) Oxidative stress and its effects on insulin resistance and pancreatic beta-cells dysfunction: relationship with type 2 diabetes mellitus complications. Acta Med Port 21:293–302
Wu WS (2006) The signaling mechanism of ROS in tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25:695–705
Park J, Min JS, Kim B, Chae UB, Yun JW, Choi MS, Kong IK, Chang KT et al (2015) Mitochondrial ROS govern the LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response in microglia cells by regulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Neurosci Lett 584:191–196
Alam J, Cook JL (2007) How many transcription factors does it take to turn on the heme oxygenase-1 gene? Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 36:166–174
Haddad JJ (2002) Oxygen-sensitive pro-inflammatory cytokines, apoptosis signaling and redox-responsive transcription factors in development and pathophysiology. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther 7:1–14
Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-κB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 336:1066–1071
Hsieh HL, Lin CC, Hsiao LD, Yang CM (2013) High glucose induces reactive oxygen species-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and cell migration in brain astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol 48:601–614
Das DK, Maulik N, Engelman RM (2004) Redox regulation of angiotensin II signaling in the heart. J Cell Mol Med 8:144–152
Cheng PY, Lee YM, Shih NL, Chen YC, Yen MH (2006) Heme oxygenase-1 contributes to the cytoprotection of alpha-lipoic acid via activation of p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1313–1322
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Taiwan, Grant Number EMRPD1E1641; Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, Grant Numbers MOST103-2321-B-182-006, MOST104-2320-B-182-010 (CMY), and NSC102-2320-B-255-005-MY3 (HLH); and Chang Gung Medical Research Foundation, Grant Numbers CMRPD1B0383, CMRPD1C0103, CMRPD1C0563, CMRPD1B0332, and CMRPD1F0021 (CMY); CMRPF1A0063, CMRPF1C0192, CMRPF1C0193, CMRPF3D0031, and CMRPF3D0032 (HLH); and CMRPG3B1093 and CMRPG3E2231 (CCL). We thank Ms. Yin-Chen Chen for her technical assistance.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, CM., Lin, CC. & Hsieh, HL. High-Glucose-Derived Oxidative Stress-Dependent Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression from Astrocytes Contributes to the Neuronal Apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol 54, 470–483 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9666-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9666-4