Abstract
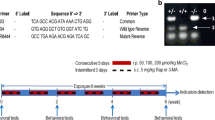
Over-exposure to manganese (Mn) has been known to induce endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress involving protein misfolding. The proper maturation and folding of native proteins rely on the activity of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI). However, the exact mechanism of Mn-induced alpha-synuclein oligomerization is unclear. To explore whether alpha-synuclein oligomerization was associated with S-nitrosylation of PDI, we made the rat brain slice model of manganism and pretreated slices with l-Canavanine, a selective iNOS inhibitor. After slices were treated with Mn (0, 25, 100, and 400 μM) for 24 h, there were dose-dependent increases in apoptotic percentage of cells, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) releases, production of NO, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity, the mRNA and protein expressions of iNOS, and PDI. Moreover, S-nitrosylated PDI and alpha-synuclein oligomerization also increased. However, there was a significant increase in the PDI activity of 25-μM Mn-treated slices. Then, PDI activity and the affinity between PDI and alpha-synuclein decreased significantly in response to Mn (100 and 400 μM), which was associated with S-nitrosylation of PDI. The results indicated that S-nitrosylated PDI could affect its activity. We use the l-Canavanine pretreatment brain slices to inhibit S-nitrosylation of PDI. The results showed that l-Canavanine pretreatment could reduce Mn-induced nerve cell injury and alpha-synuclein oligomerization. Additionally, there was a significant recovery in PDI activity in l-Canavanine-pretreated slices. The findings revealed that Mn induced nitrosative stress via the activation of iNOS and subsequent S-nitrosylation of PDI in cultured slices. Moreover, S-nitrosylation of PDI is an important signaling event in the Mn-induced alpha-synuclein oligomerization in brain slices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuschl K, Mills PB, Clayton PT (2013) Manganese and the brain. Int Rev Neurobiol 110:277–312. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-410502-7.00013-2
Gonzalez-Cuyar LF, Nelson G, Criswell SR, Ho P, Lonzanida JA, Checkoway H, Seixas N, Gelman BB, Evanoff BA, Murray J, Zhang J, Racette BA (2013) Quantitative neuropathology associated with chronic manganese exposure in South African mine workers. Neurotoxicology. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2013.12.008
Park RM (2013) Neurobehavioral deficits and parkinsonism in occupations with manganese exposure: a review of methodological issues in the epidemiological literature. Saf Health Work 4(3):123–135. doi:10.1016/j.shaw.2013.07.003
Fukushima T, Tan X, Luo Y, Kanda H (2010) Relationship between blood levels of heavy metals and Parkinson’s disease in China. Neuroepidemiology 34(1):18–24. doi:10.1159/000255462
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Aschner M (2013) Role of astrocytes in manganese mediated neurotoxicity. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 14:23. doi:10.1186/2050-6511-14-23
Martinez-Finley EJ, Gavin CE, Aschner M, Gunter TE (2013) Manganese neurotoxicity and the role of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 62:65–75. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.032
Verina T, Schneider JS, Guilarte TR (2013) Manganese exposure induces alpha-synuclein aggregation in the frontal cortex of non-human primates. Toxicol Lett 217(3):177–183. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.12.006
Vekrellis K, Rideout HJ, Stefanis L (2004) Neurobiology of alpha-synuclein. Mol Neurobiol 30(1):1–21. doi:10.1385/MN:30:1:001
Pluta R, Jablonski M, Ulamek-Koziol M, Kocki J, Brzozowska J, Januszewski S, Furmaga-Jablonska W, Bogucka-Kocka A, Maciejewski R, Czuczwar SJ (2013) Sporadic Alzheimer’s disease begins as episodes of brain ischemia and ischemically dysregulated Alzheimer’s disease genes. Mol Neurobiol 48(3):500–515. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8439-1
Lind KR, Ball KK, Cruz NF, Dienel GA (2013) The unfolded protein response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in cultured astrocytes and rat brain during experimental diabetes. Neurochem Int 62(5):784–795. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.02.009
Braakman I, Hebert DN (2013) Protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5(5):a013201. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a013201
Halloran M, Parakh S, Atkin JD (2013) The role of S-nitrosylation and S-glutathionylation of protein disulphide isomerase in protein misfolding and neurodegeneration. Int J Cell Biol 2013:797914. doi:10.1155/2013/797914
Xu B, Wang F, Wu SW, Deng Y, Liu W, Feng S, Yang TY, Xu ZF (2014) Alpha-synuclein is involved in manganese-induced ER stress via PERK signal pathway in organotypic brain slice cultures. Mol Neurobiol 49(1):399–412. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8527-2
Ohnishi M, Katsuki H, Unemura K, Izumi Y, Kume T, Takada-Takatori Y, Akaike A (2010) Heme oxygenase-1 contributes to pathology associated with thrombin-induced striatal and cortical injury in organotypic slice culture. Brain Res 1347:170–178. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.05.077
Stoppini L, Buchs PA, Muller D (1991) A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods 37(2):173–182
Xu B, Xu ZF, Deng Y (2009) Effect of manganese exposure on intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and expression of NMDA receptor subunits in primary cultured neurons. Neurotoxicology 30(6):941–949. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2009.07.011
Villalba M, Pereira R, Martinez-Serrano A, Satrustegui J (1995) Altered cell calcium regulation in synaptosomes and brain cells of the 30-month-old rat: prominent effects in hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 16(5):809–816
Wei P, Ma P, Xu QS, Bai QH, Gu JG, Xi H, Du YG, Yu C (2012) Chitosan oligosaccharides suppress production of nitric oxide in lipopolysaccharide-induced N9 murine microglial cells in vitro. Glycoconj J 29(5–6):285–295. doi:10.1007/s10719-012-9392-3
Hu SQ, Ye JS, Zong YY, Sun CC, Liu DH, Wu YP, Song T, Zhang GY (2012) S-nitrosylation of mixed lineage kinase 3 contributes to its activation after cerebral ischemia. J Biol Chem 287(4):2364–2377. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.227124
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Bernardoni P, Fazi B, Costanzi A, Nardacci R, Montagna C, Filomeni G, Ciriolo MR, Piacentini M, Di Sano F (2013) Reticulon1-C modulates protein disulphide isomerase function. Cell Death Dis 4:e581. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.113
Zhang S, Jiang C, Liu H, Guan Z, Zeng Q, Zhang C, Lei R, Xia T, Gao H, Yang L, Chen Y, Wu X, Zhang X, Cui Y, Yu L, Wang Z, Wang A (2013) Fluoride-elicited developmental testicular toxicity in rats: roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammatory response. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 271(2):206–215. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.04.033
Jin YC, Lee HG, Xu CX, Han JA, Choi SH, Song MK, Kim YJ, Lee KB, Kim SK, Kang HS, Cho BW, Shin TS, Choi YJ (2010) Proteomic analysis of endogenous conjugated linoleic acid biosynthesis in lactating rats and mouse mammary gland epithelia cells (HC11). Biochim Biophys Acta 1804(4):745–751. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.11.016
Xu LR, Liu XL, Chen J, Liang Y (2013) Protein disulfide isomerase interacts with tau protein and inhibits its fibrillization. PLoS One 8(10):e76657. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076657
Xu B, Wu SW, Lu CW, Deng Y, Liu W, Wei YG, Yang TY, Xu ZF (2013) Oxidative stress involvement in manganese-induced alpha-synuclein oligomerization in organotypic brain slice cultures. Toxicology 305:71–78. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2013.01.006
Moreno JA, Streifel KM, Sullivan KA, Hanneman WH, Tjalkens RB (2011) Manganese-induced NF-kappaB activation and nitrosative stress is decreased by estrogen in juvenile mice. Toxicol Sci 122(1):121–133. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr091
Mortimer JA, Borenstein AR, Nelson LM (2012) Associations of welding and manganese exposure with Parkinson disease: review and meta-analysis. Neurology 79(11):1174–1180. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182698ced
Rettori V, Fernandez-Solari J, Mohn C, Zorrilla Zubilete MA, de la Cal C, Prestifilippo JP, De Laurentiis A (2009) Nitric oxide at the crossroad of immunoneuroendocrine interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1153:35–47. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03968.x
Streifel KM, Moreno JA, Hanneman WH, Legare ME, Tjalkens RB (2012) Gene deletion of nos2 protects against manganese-induced neurological dysfunction in juvenile mice. Toxicol Sci 126(1):183–192. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr335
Uehara T, Nakamura T, Yao D, Shi ZQ, Gu Z, Ma Y, Masliah E, Nomura Y, Lipton SA (2006) S-nitrosylated protein-disulphide isomerase links protein misfolding to neurodegeneration. Nature 441(7092):513–517. doi:10.1038/nature04782
Honjo Y, Ito H, Horibe T, Takahashi R, Kawakami K (2011) Protein disulfide isomerase immunopositive glial cytoplasmic inclusions in patients with multiple system atrophy. Int J Neurosci 121(10):543–550. doi:10.3109/00207454.2011.585440
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 81102098).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 381 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Jin, CH., Deng, Y. et al. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomerization in Manganese-Induced Nerve Cell Injury in Brain Slices: A Role of NO-Mediated S-Nitrosylation of Protein Disulfide Isomerase. Mol Neurobiol 50, 1098–1110 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8711-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8711-z