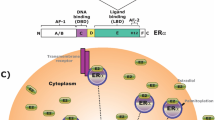
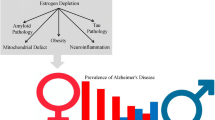
Abstract
The significantly higher incidence of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in women than in men has been attributed to loss of estrogen and a variety of related mechanisms at the molecular, cellular, and hormonal levels, which subsequently elucidate neuroprotective roles of estrogen against AD-related pathology. Recent studies have proposed that beneficial effects of estrogen on AD are directly linked to its ability to reduce amyloid-β peptides and tau aggregates, two hallmark lesions of AD. Despite high expectations, large clinical trials with postmenopausal women indicated that the beneficial effects of estrogen therapies were insignificant and, in fact, elicited adverse effects. Here, we review the current status of AD prevention and treatment using estrogens focusing on recent understandings of their biochemical links to AD pathophysiology. This review also discusses development of selective ligands that specifically target either estrogen receptor α (ERα) or ERβ isoforms, which are potentially promising strategies for safe and efficient treatment of AD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corpechot C, Robel P, Axelson M, Sjovall J, Baulieu EE (1981) Characterization and measurement of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78(8):4704–4707
Hojo Y, Murakami G, Mukai H, Higo S, Hatanaka Y, Ogiue-Ikeda M, Ishii H, Kimoto T, Kawato S (2008) Estrogen synthesis in the brain—role in synaptic plasticity and memory. Mol Cell Endocrinol 290(1–2):31–43
Wharton W, Baker LD, Gleason CE, Dowling M, Barnet JH, Johnson S, Carlsson C, Craft S, Asthana S (2011) Short-term hormone therapy with transdermal estradiol improves cognition for postmenopausal women with Alzheimer's disease: results of a randomized controlled trial. J Alzheimers Dis 26(3):495–505
Lee JH, Lee MJ (2012) Emerging roles of the ubiquitin–proteasome system in the steroid receptor signaling. Arch Pharm Res 35(3):397–407
Revankar CM, Cimino DF, Sklar LA, Arterburn JB, Prossnitz ER (2005) A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science 307(5715):1625–1630
Bunn F, Goodman C, Sworn K, Rait G, Brayne C, Robinson L, McNeilly E, Iliffe S (2012) Psychosocial factors that shape patient and carer experiences of dementia diagnosis and treatment: a systematic review of qualitative studies. PLoS Med 9(10):e1001331
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81(2):741–766
Aisen PS (2009) Alzheimer's disease therapeutic research: the path forward. Alzheimers Res Ther 1(1):2
Lee MJ, Lee JH, Rubinsztein DC (2013) Tau degradation: the ubiquitin–proteasome system versus the autophagy–lysosome system. Prog Neurobiol 105(2013):49–59
Giannakopoulos P, Herrmann FR, Bussiere T, Bouras C, Kovari E, Perl DP, Morrison JH, Gold G, Hof PR (2003) Tangle and neuron numbers, but not amyloid load, predict cognitive status in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 60(9):1495–1500
Robertson JF (2004) Selective oestrogen receptor modulators/new antioestrogens: a clinical perspective. Cancer Treat Rev 30(8):695–706
Muchmore DB (2000) Raloxifene: a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with multiple target system effects. Oncologist 5(5):388–392
Pratt WB, Toft DO (1997) Steroid receptor interactions with heat shock protein and immunophilin chaperones. Endocr Rev 18(3):306–360
Gronemeyer H, Gustafsson JA, Laudet V (2004) Principles for modulation of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(11):950–964
Rochette-Egly C (2005) Dynamic combinatorial networks in nuclear receptor-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem 280(38):32565–32568
Carroll JS, Brown M (2006) Estrogen receptor target gene: an evolving concept. Mol Endocrinol 20(8):1707–1714
Okoh V, Deoraj A, Roy D (2011) Estrogen-induced reactive oxygen species-mediated signalings contribute to breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1815(1):115–133
Bjornstrom L, Sjoberg M (2005) Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol Endocrinol 19(4):833–842
Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Frackelton AR Jr, Bland KI (2002) Estrogen action via the G protein-coupled receptor, GPR30: stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and cAMP-mediated attenuation of the epidermal growth factor receptor-to-MAPK signaling axis. Mol Endocrinol 16(1):70–84
Filice E, Recchia AG, Pellegrino D, Angelone T, Maggiolini M, Cerra MC (2009) A new membrane G protein-coupled receptor (GPR30) is involved in the cardiac effects of 17beta-estradiol in the male rat. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(4):3–10
Filardo EJ, Quinn JA, Bland KI, Frackelton AR Jr (2000) Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF. Mol Endocrinol 14(10):1649–1660
Thomas P, Pang Y, Filardo EJ, Dong J (2005) Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 146(2):624–632
Doolan CM, Condliffe SB, Harvey BJ (2000) Rapid non-genomic activation of cytosolic cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity and [Ca(2+)](i) by 17beta-oestradiol in female rat distal colon. Br J Pharmacol 129(7):1375–1386
Vasudevan N, Pfaff DW (2008) Non-genomic actions of estrogens and their interaction with genomic actions in the brain. Front Neuroendocrinol 29(2):238–257
Corder EH, Ghebremedhin E, Taylor MG, Thal DR, Ohm TG, Braak H (2004) The biphasic relationship between regional brain senile plaque and neurofibrillary tangle distributions: modification by age, sex, and APOE polymorphism. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1019:24–28
Barnes LL, Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Schneider JA, Evans DA, Bennett DA (2005) Sex differences in the clinical manifestations of Alzheimer disease pathology. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62(6):685–691
Kalesnykas G, Roschier U, Puolivali J, Wang J, Miettinen R (2005) The effect of aging on the subcellular distribution of estrogen receptor-alpha in the cholinergic neurons of transgenic and wild-type mice. Eur J Neurosci 21(5):1437–1442
Shughrue PJ, Scrimo PJ, Merchenthaler I (2000) Estrogen binding and estrogen receptor characterization (ERalpha and ERbeta) in the cholinergic neurons of the rat basal forebrain. Neuroscience 96(1):41–49
Garcia-Segura LM, Azcoitia I, DonCarlos LL (2001) Neuroprotection by estradiol. Prog Neurobiol 63(1):29–60
Watters JJ, Campbell JS, Cunningham MJ, Krebs EG, Dorsa DM (1997) Rapid membrane effects of steroids in neuroblastoma cells: effects of estrogen on mitogen activated protein kinase signalling cascade and c-fos immediate early gene transcription. Endocrinology 138(9):4030–4033
Singh M (2001) Ovarian hormones elicit phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular-signal regulated kinase in explants of the cerebral cortex. Endocrine 14(3):407–415
Singer CA, Figueroa-Masot XA, Batchelor RH, Dorsa DM (1999) The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates estrogen neuroprotection after glutamate toxicity in primary cortical neurons. J Neurosci 19(7):2455–2463
Cordey M, Gundimeda U, Gopalakrishna R, Pike CJ (2003) Estrogen activates protein kinase C in neurons: role in neuroprotection. J Neurochem 84(6):1340–1348
Yao M, Nguyen TV, Pike CJ (2007) Estrogen regulates Bcl-w and Bim expression: role in protection against beta-amyloid peptide-induced neuronal death. J Neurosci 27(6):1422–1433
Pike CJ (1999) Estrogen modulates neuronal Bcl-xL expression and beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 72(4):1552–1563
Shy H, Malaiyandi L, Timiras PS (2000) Protective action of 17beta-estradiol and tamoxifen on glutamate toxicity in glial cells. Int J Dev Neurosci 18(2–3):289–297
Spampinato SF, Merlo S, Molinaro G, Battaglia G, Bruno V, Nicoletti F, Sortino MA (2012) Dual effect of 17beta-estradiol on NMDA-induced neuronal death: involvement of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1. Endocrinology 153(12):5940–5948
Carroll JC, Rosario ER, Chang L, Stanczyk FZ, Oddo S, LaFerla FM, Pike CJ (2007) Progesterone and estrogen regulate Alzheimer-like neuropathology in female 3xTg-AD mice. J Neurosci 27(48):13357–13365
Luciani P, Deledda C, Rosati F, Benvenuti S, Cellai I, Dichiara F, Morello M, Vannelli GB, Danza G, Serio M, Peri A (2008) Seladin-1 is a fundamental mediator of the neuroprotective effects of estrogen in human neuroblast long-term cell cultures. Endocrinology 149(9):4256–4266
Yue X, Lu M, Lancaster T, Cao P, Honda S, Staufenbiel M, Harada N, Zhong Z, Shen Y, Li R (2005) Brain estrogen deficiency accelerates Abeta plaque formation in an Alzheimer's disease animal model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(52):19198–19203
Marin R, Guerra B, Morales A, Diaz M, Alonso R (2003) An ICI 182,780-sensitive, membrane-related estrogen receptor contributes to estrogenic neuroprotective actions against amyloid-beta toxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1007:108–116
Fitzpatrick JL, Mize AL, Wade CB, Harris JA, Shapiro RA, Dorsa DM (2002) Estrogen-mediated neuroprotection against beta-amyloid toxicity requires expression of estrogen receptor alpha or beta and activation of the MAPK pathway. J Neurochem 82(3):674–682
Nord LC, Sundqvist J, Andersson E, Fried G (2010) Analysis of oestrogen regulation of alpha-, beta- and gamma-secretase gene and protein expression in cultured human neuronal and glial cells. Neurodegener Dis 7(6):349–364
Zhao L, Yao J, Mao Z, Chen S, Wang Y, Brinton RD (2011) 17beta-Estradiol regulates insulin-degrading enzyme expression via an ERbeta/PI3-K pathway in hippocampus: relevance to Alzheimer's prevention. Neurobiol Aging 32(11):1949–1963
Liang K, Yang L, Yin C, Xiao Z, Zhang J, Liu Y, Huang J (2010) Estrogen stimulates degradation of beta-amyloid peptide by up-regulating neprilysin. J Biol Chem 285(2):935–942
Bao J, Cao C, Zhang X, Jiang F, Nicosia SV, Bai W (2007) Suppression of beta-amyloid precursor protein signaling into the nucleus by estrogens mediated through complex formation between the estrogen receptor and Fe65. Mol Cell Biol 27(4):1321–1333
Shi C, Zheng DD, Fang L, Wu F, Kwong WH, Xu J (2012) Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes nonamyloidgenic cleavage of APP via estrogen receptor signaling to MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(4):453–460
Bernstein HG, Ansorge S, Riederer P, Reiser M, Frolich L, Bogerts B (1999) Insulin-degrading enzyme in the Alzheimer's disease brain: prominent localization in neurons and senile plaques. Neurosci Lett 263(2–3):161–164
Kurochkin IV (2001) Insulin-degrading enzyme: embarking on amyloid destruction. Trends Biochem Sci 26(7):421–425
Kurochkin IV, Goto S (1994) Alzheimer's beta-amyloid peptide specifically interacts with and is degraded by insulin degrading enzyme. FEBS Lett 345(1):33–37
Qiu WQ, Folstein MF (2006) Insulin, insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid-beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease: review and hypothesis. Neurobiol Aging 27(2):190–198
Jayaraman A, Carroll JC, Morgan TE, Lin S, Zhao L, Arimoto JM, Murphy MP, Beckett TL, Finch CE, Brinton RD, Pike CJ (2012) 17beta-estradiol and progesterone regulate expression of beta-amyloid clearance factors in primary neuron cultures and female rat brain. Endocrinology 153(11):5467–5479
Farris W, Schutz SG, Cirrito JR, Shankar GM, Sun X, George A, Leissring MA, Walsh DM, Qiu WQ, Holtzman DM, Selkoe DJ (2007) Loss of neprilysin function promotes amyloid plaque formation and causes cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Am J Pathol 171(1):241–251
Xiao ZM, Sun L, Liu YM, Zhang JJ, Huang J (2009) Estrogen regulation of the neprilysin gene through a hormone-responsive element. J Mol Neurosci 39(1–2):22–26
Yin KJ, Cirrito JR, Yan P, Hu X, Xiao Q, Pan X, Bateman R, Song H, Hsu FF, Turk J, Xu J, Hsu CY, Mills JC, Holtzman DM, Lee JM (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases expressed by astrocytes mediate extracellular amyloid-beta peptide catabolism. J Neurosci 26(43):10939–10948
Wingrove CS, Garr E, Godsland IF, Stevenson JC (1998) 17beta-oestradiol enhances release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 from human vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1406(2):169–174
Merlo S, Sortino MA (2012) Estrogen activates matrix metalloproteinases-2 and −9 to increase beta amyloid degradation. Mol Cell Neurosci 49(4):423–429
Goodenough S, Schleusner D, Pietrzik C, Skutella T, Behl C (2005) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta links neuroprotection by 17beta-estradiol to key Alzheimer processes. Neuroscience 132(3):581–589
Zhang QG, Wang R, Khan M, Mahesh V, Brann DW (2008) Role of Dickkopf-1, an antagonist of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, in estrogen-induced neuroprotection and attenuation of tau phosphorylation. J Neurosci 28(34):8430–41
Liu XA, Zhu LQ, Zhang Q, Shi HR, Wang SH, Wang Q, Wang JZ (2008) Estradiol attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation induced by upregulation of protein kinase-A. Neurochem Res 33(9):1811–1820
Wray S, Noble W (2009) Linking amyloid and tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease: the role of membrane cholesterol in Abeta-mediated tau toxicity. J Neurosci 29(31):9665–9667
Spampinato SF, Molinaro G, Merlo S, Iacovelli L, Caraci F, Battaglia G, Nicoletti F, Bruno V, Sortino MA (2012) Estrogen receptors and type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors are interdependent in protecting cortical neurons against beta-amyloid toxicity. Mol Pharmacol 81(1):12–20
Benvenuti S, Luciani P, Vannelli GB, Gelmini S, Franceschi E, Serio M, Peri A (2005) Estrogen and selective estrogen receptor modulators exert neuroprotective effects and stimulate the expression of selective Alzheimer's disease indicator-1, a recently discovered antiapoptotic gene, in human neuroblast long-term cell cultures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(3):1775–1782
Kelly JF, Bienias JL, Shah A, Meeke KA, Schneider JA, Soriano E, Bennett DA (2008) Levels of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in frontal cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease: relationship to Mini-Mental State Examination scores. Curr Alzheimer Res 5(1):45–51
Hestiantoro A, Swaab DF (2004) Changes in estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta in the infundibular nucleus of the human hypothalamus are related to the occurrence of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(4):1912–1925
Carroll JC, Pike CJ (2008) Selective estrogen receptor modulators differentially regulate Alzheimer-like changes in female 3xTg-AD mice. Endocrinology 149(5):2607–2611
Bagheri M, Joghataei MT, Mohseni S, Roghani M (2011) Genistein ameliorates learning and memory deficits in amyloid beta(1–40) rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Learn Mem 95(3):270–276
Grimm A, Lim YA, Mensah-Nyagan AG, Gotz J, Eckert A (2012) Alzheimer's disease, oestrogen and mitochondria: an ambiguous relationship. Mol Neurobiol 46(1):151–160
Shao H, Breitner JC, Whitmer RA, Wang J, Hayden K, Wengreen H, Corcoran C, Tschanz J, Norton M, Munger R, Welsh-Bohmer K, Zandi PP (2012) Hormone therapy and Alzheimer disease dementia: new findings from the Cache County Study. Neurology 79(18):1846–1852
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by programs of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2012–0009484, 2013025964 to M.J.L., 2012R1A6A3A01039788 to J.H.L.). This work is also supported by a grant of the Korea-UK Collaborative Alzheimer's Disease Research Project) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (A111227 to M.J.L.).
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Glossary
- AC
-
Adenylyl cyclase
- ACE
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- AD
-
Alzheimer's disease
- Aβ
-
Amyloid-β peptide
- ApoE4
-
Apolipoprotein E4
- APP
-
Amyloid-β precursor protein
- CBP
-
CREB-binding protein
- CDK5
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5
- ChIP
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- DBD
-
DNA-binding domain
- DPN
-
Diarylpropionitrile
- E1
-
Estrone
- E2
-
17β-Estradiol
- E3
-
Estriol
- EBAG9
-
Estrogen receptor binding site associated antigen 9
- EDN1
-
Endothelin-converting enzyme 1
- ER
-
Estrogen receptor
- ERE
-
Estrogen-responsive element
- GPCR
-
G-protein-coupled receptor
- GPR30
-
G-protein-coupled receptor 30
- GSK3β
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
- HB-EGF
-
Heparin-binding epithermal growth factor
- HSP
-
Heat shock protein
- IDE
-
Insulin-degrading enzyme
- JNK
-
c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase
- LBD
-
Ligand-binding domain
- MAPK
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MMP
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- NFT
-
Neurofibrillary tangle
- NO
-
Nitric oxide
- PHF
-
Paired helical filament
- PI3K
-
Phosphoinositol 3-kinase
- PKA
-
Protein kinase A
- PPT
-
Propylpyrazole triol
- PRD
-
Proline-rich domain
- ROS
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SAGE
-
Serial analysis of gene expression
- Seladin-1
-
Selective AD indicator-1
- SERM
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulator
- SRC
-
Steroid receptor coactivator
- TFF1
-
Trefoil factor 1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Jiang, Y., Han, D.H. et al. Targeting Estrogen Receptors for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 49, 39–49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8484-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8484-9