Abstract
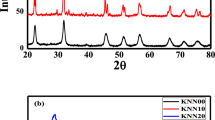
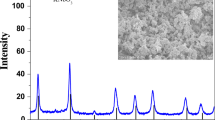
Non-toxic lead-free potassium sodium niobate (K0.5Na0.5NbO3) ceramics were manufactured by using solid-state reaction method. The influences of excessive alkali metal (Na, K) ions concentration (0–20%) on their structural and electro-optical properties have been examined systematically. The structural properties confirmed the perovskite phase having orthorhombic crystal structure without any secondary phase even on the addition of excessive quantities of (Na, K) ions. Optical properties revealed decrease in optical bandgap energy with increase in the (Na, K) ions ratio. Photoluminescence spectrum shows the emission band in the UV–visible region, which makes KNN a suitable candidate for telecommunication devices, optical storage technology and LEDs. Impedance study revealed the negative temperature coefficient of resistance and non-Debye nature of the synthesized samples.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rafiq M A, Costa M E, Tkach A and Vilarinho P M 2015 Cryst. Growth Des. 15 1289
Panda P and B Sahoo 2015 Ferroelectrics 474 128
Bell A J and O Deubzer 2018 MRS Bull. 43 581
Shandilya M and Kaur G A 2019 J. Solid State Chem. 280 120988
Kumari P, Shandilya M, Lal M and Rai R 2017 in Smart materials for smart living (New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.)
Kaur G A, Kumar S and Shandilya M 2020 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elect. 31 20303
Sharma S, Kumari S, Rai R and Sharma D K 2016 Int. Ferroelectr. 168 115
Chandrasekhar M and Kumar P 2015 Cerm. Int. 41 5574
Kumar P and Pattanaik M 2013 Cerm. Int. 39 65
Zhang Y, Li L, Shen B and Zhai J 2015 Dalt. Trans. 44 7797
Yang J, Zhang F, Yang Q, Liu Z, Li Y, Liu Y et al 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 182904
Kumar S, Shandilya M, Thakur S and Thakur N 2018 J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 88 646
Sharma S, Shandilya M and Rai R 2015 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elect. 26 9484
Zhao T, Scholl A, Zavaliche F, Lee K, Barry M, Doran A et al 2006 Nat. Mater. 5 823
Shafiee E, Chermahini M D, Doostmohammadi A, Nilforoushan M R and Zehipour B 2019 Cerm. Int. 45 22203
Shandilya M, Kaur G A and Rai R 2021 Mater. Chem. Phys. 263 124422
Chaiyo N, Muanghlua R, Wongprasert Y, Seeharaj P and Vittayakorn N 2013 Int. Ferroelectr. 149 128
Shandilya M and Verma R 2021 J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 527 167782
Wang Y, Yi Z, Li Y, Yang Q and Wang D 2007 Cerm. Int. 33 1611
Skidmore T A, Comyn T P, Bell A J, Zhu F and Milne S J 2011 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Contr. 58 1819
Kumar S, Shandilya M, Thakur S, Thakur N and Kaur G A 2019 J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 92 215
Patterson A L 1939 Phys. Rev. 56 978
Shandilya M, Thakur S and Rai R 2019 Ferroelect. Lett. Sect. 46 8
Khorrami G H, Kompany A and Zak A K 2015 Funct. Mater. Lett. 8 1550030
Kumar S and Thakur N 2019 J. Elect. Mater. 48 6203
Kumar S and Thakur N 2021 Bull. Mater. Sci. 44 51
Birey H 1978 J. Appl. Phys. 49 2898
Shi W, Feng Y, Lu T, Lu Y, Shen J, Xue J et al 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elect. 30 9
Kamal A, Rafiq M A, Rafiq M N, Usman M, Waqar M and Anwar M S 2016 Appl. Phys. A 122 1037
Hussain A, Kim J S, Rahman J U, Maqbool A, Song T K, Kim W J et al 2014 Ferroelectrics 464 107
Zhai Y, Feng Y, Du J, Xue J, Shen J, Lu Y et al 2019 J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electr. 30 4352
Acknowledgements
Shammi Kumar is grateful to Dr Pankaj Sharma and Dr Ragini Raj Singh from JUIT Waknaghat, Solan, HP, for their support to record the optical and photoluminescence spectra of the material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Shandilya, M., Kaur, G. et al. Effect of excessive amount of (Na, K) ion ratio on structural, optical and electrical properties of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramics prepared by solid-state route. Bull Mater Sci 45, 30 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02606-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02606-z