Abstract
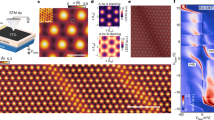
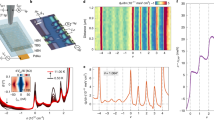
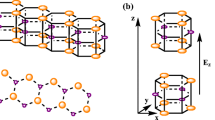
Moiré superlattices of two-dimensional (2D) materials oriented at low twist angles generate a large-scale interference pattern leading to strong interlayer coupling, which influences the band structure and introduces flatbands. Conventional electronic transport measurements have shown the effects of flatband physics, manifesting as correlated insulating states and emergent superconductivity. In this study, we probe the electronic states in a trinary hybrid of graphene and twisted bilayer (tbl) MoS2. Graphene acts as a sensing layer, which captures the electronic effects of the underlying substrate, and we observe certain anomalies in the electronic characteristics of graphene only in the presence of an underlying 58.5\(^\circ\) tbl MoS2, at low temperatures. Interestingly, graphene on tbl MoS2, with twist angle near 0\(^\circ\) or on natural bilayer MoS2, does not show any anomalies. Density functional theory calculations show several distinguishable peaks in the density of states at the conduction band edge of twisted MoS2 near 60\(^\circ\). We speculate that the anomaly appears due to fermi level pinning of graphene owing to a large density of states in the flatbands of twisted bilayer MoS2. An analysis of the energetics in the graphene-MoS2 hybrid quantitatively agree with theoretical predictions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu H, Liu G B, Tang J, Xu X and Yao W 2017 Sci. Adv. 3 e1701696
Bistritzer R and MacDonald A H 2011 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108 12233
Naik M H and Jain M 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 266401
Kundu S, Naik M H, Krishnamurthy H R and Jain M 2021 arXiv:2103.07447
Chen G, Jiang L, Wu S, Lyu B, Li H, Chittari B L et al 2018 Nat. Phys. 15 237
Jin C, Regan E C, Yan A, Utama M I B, Wang D, Zhao S et al 2019 Nature 567 76
Tran K, Moody G, Wu F, Lu X, Choi J, Kim K et al 2019 Nature 567 71
Cao Y, Luo J Y, Fatemi V, Fang S, Sanchez-Yamagishi J D, Watanabe K et al 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 116804
Cao Y, Fatemi V, Fang S, Watanabe K, Taniguchi T, Kaxiras E et al 2018 Nature 556 43
Pan H, Wu F and Sarma S D 2020 Phys. Rev. Res. 2 033087
Zhang Z, Wang Y, Watanabe K, Taniguchi T, Ueno K, Tutuc E and LeRoy B J 2019 arXiv:1910.13068
Wang L, Shih E M, Ghiotto A, Xian L, Rhodes D A et al 2020 Nat. mater. 19 861
Xu Y, Liu S, Rhodes D A, Watanabe K, Taniguchi T, Hone J et al 2020 Nature 587 214
Naik M H, Kundu S, Maity I and Jain M 2020 Phys. Rev. B 102 075413
Roy K, Padmanabhan M, Goswami S, Sai T P, Ramalingam G, Raghavan S et al 2013 Nat. Nanotech. 8 826
Mitra S, Kakkar S, Ahmed T and Ghosh A 2020 Phys. Rev. Appl. 14 064029
Ahmed T, Roy K, Kakkar S, Pradhan A and Ghosh A 2020 2D Mater. 7 025043
Kashid R, Mishra J K, Pradhan A, Ahmed T, Kakkar S, Mundada P et al 2020 APL Mater. 8 091114
Larentis S, Tolsma J R, Fallahazad B, Dillen D C, Kim K, MacDonald A H et al 2014 Nano Lett. 14 2039
Guo Y, Liu C, Yin Q, Wei C, Lin S, Hoffman T B et al 2016 ACS Nano 10 8980
Debnath R, Sett S, Biswas R, Raghunathan V and Ghosh A 2021 Nanotech. 32 455705
Dean C R, Young A F, Meric I, Lee C, Wang L, Sorgenfrei S et al 2010 Nat. Nanotech. 5 722
Bolotin K I, Sikes K J, Hone J, Stormer H L and Kim P 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 096802
Pal A N, Kochat V and Ghosh A 2012 Phys. Rev. Lett. 109 196601
Sols F, Guinea F and Neto A C 2007 Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 166803
Yan R, Zhang Q, Li W, Calizo I, Shen T, Richter C A et al 2012 Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 022105
Howell S L, Jariwala D, Wu C C, Chen K S, Sangwan V K, Kang J et al 2015 Nano Lett. 15 2278
Kunstmann J, Wendumu T B and Seifert G 2017 Phys. Status Solidi (b) 254 1600645
Mongillo M, Chiappe D, Arutchelvan G, Asselberghs I, Perucchini M, Manfrini M et al 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 233102
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge financial support from the U.S. Army International Technology Centre Pacific (ITC-PAC) and Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India, as well as the Supercomputer Education and Research Centre (SERC) at IISc, for providing computational resources. SS acknowledges Aditya Jayaraman for fruitful discussions during the development of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the special issue on ‘Quantum materials and devices’.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sett, S., Kundu, S., Kakkar, S. et al. Anomalous electrical transport in orientationally controlled trinary hybrids of graphene and twisted bilayer molybdenum disulphide. Bull Mater Sci 44, 280 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02590-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02590-4