Abstract
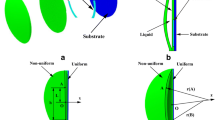
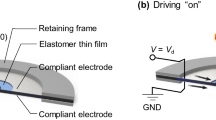
In order to simulate the auto-focusing function of human eyes, a liquid lens is proposed based on dielectric elastomer actuator (DEA). The lens could realize rapid focusing under voltages. The structure and principle of the lens are described in detail. A novel fabricating method is presented for the lens, which is inspired by the negative pressure technology. A negative pressure region is made in the centre of the dielectric elastomer (DE) membrane, and the liquid is filled. Then the other layer of membrane is covered to seal the liquid. Around the lens is the DEA coupling carbon grease electrodes. The finite element analysis and simulation of the lens deformation are carried out by using the software of Abaqus. The relationship is explored among lens diameter, volume, pretension ratio, actuating voltage and focal length. It is found that when the liquid volume is fixed in the soft lens, the larger the pre-stretching ratio is, the greater the lens deformation is. At the condition of the same lens diameter, focal-length changes are inversely proportional to the liquid volume. The correctness of built theoretical models is verified by experiments in the end.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang L, Hayakawa T and Ishikawa M 2017 Opt. Express 25 31708
Shian S, Diebold R and Clarke D 2013 Opt. Express 21 8669
Wang Q, Cao Y J, Wang Y N, Liu J C and Xie Y X 2018 Mech. Based Des. Struct. 46 800
Faye A, Rodriguez-Martinez J A and Volokh K Y 2017 Int. J. Non-lin. Mech. 92 118
Ren H W and Wu S T 2018 Appl. Sci. 8 1085
Jin B, Lee J H, Zhou Z, Zhang G, Lee G B, Ren H et al 2016 Opt. Eng. 55 017107
Choi D S, Jeong J, Shin E J and Kim S Y 2017 Opt. Express 25 20133
Rasti P, Hous H, Schlaak H F, Kiefer R and Anbarjafari G 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 9976
Maffli L, Rosset S, Ghilardi M, Carpi F and Shea H 2015 Adv. Funct. Mater. 25 1656
Zhang H, Dai M and Zhang Z S 2019 Optik 178 841
Acknowledgement
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 51775108) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant Number BK20190375).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Xia, Z. & Zhang, Z. Focus-tunable imaging analyses of the liquid lens based on dielectric elastomer actuator. Bull Mater Sci 44, 148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02466-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02466-7