Abstract
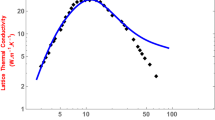
Lattice thermal conductivity (LTC) of Si bulk and nanowires (NWs) with diameter 22, 37, 50, 56, 98 and 115 nm was investigated in the temperature range 3–300 K using a modified Callaway model that contains both longitudinal and transverse modes. Using proper equations, mean bond length, lattice parameter, unit cell volume, mass density, melting temperature, longitudinal and transverse Debye temperature and group velocity for all transverse and longitudinal modes were calculated for each NW diameter mentioned. Surface roughness, Gruneisen parameter and impurity were used as adjustable parameters to fit theoretical results with experimental curves. In addition, values of electron concentration and dislocation density were determined. There are some phonon scattering mechanisms assumed, which are Umklapp and normal processes, imperfections, phonon confinement, NW boundaries, electrons scattering and dislocation. Dislocation density less than 10\(^{{14}}\) m\(^{{-2}}\) for NWs and 10\(^{{12}}\) m\(^{{-2}}\) for bulk has no effect on LTC. Also, electron concentration less than 10\(^{{22}}\) m\(^{{-3}}\) for NWs and 10\(^{{16}}\) m\(^{{-3}}\) for the bulk has no effect. On increasing dislocation density and electron concentration, LTC comparably decreases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lundstrom M 2003 Science 299 210
Tian B, Zheng X, Kempa T J, Fang Y, Yu N, Yu G et al 2007 Nature 449 885
Cohen G, Reuter M C, Wacaser B A and Khayyat M M 2012 Production scale fabrication method for high resolution AFM tips Google Patents
Balandin A and Wang K L 1998 Phys. Rev. B 58 1544
Zou J and Balandin A 2001 J. Appl. Phys. 89 2932
Li D, Wu Y, Kim P, Shi L, Yang P and Majumdar A 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 2934
Hochbaum A I, Chen R, Delgado R D, Liang W, Garnett E C, Najarian M et al 2008 Nature 451 163
Zou J 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 034324
Mingo N 2003 Phys. Rev. B 68 113308
Yang R, Chen G and Dresselhaus M S 2005 Phys. Rev. B 72 125418
Lacroix D, Joulain K, Terris D and Lemonnier D 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 103104
Bera C 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 112 074323
Omar M and Taha H 2010 Sadhana 35 177
Huang M-J, Chong W-Y and Chang T-M 2006 J. Appl. Phys. 99 114318
Callaway J 1959 Phys. Rev. 113 1046
Khitun A, Balandin A and Wang K 1999 Superlattices Microstruct. 26 181
Morelli D, Heremans J and Slack G 2002 Phys. Rev. B 66 195304
Asen-Palmer M, Bartkowski K, Gmelin E, Cardona M, Zhernov A, Inyushkin A et al 1997 Phys. Rev. B 56 9431
Holland M 1963 Phys. Rev. 132 2461
Mamand S, Omar M and Muhammad A 2012 Mater. Res. Bull. 47 1264
Herring C 1954 Phys. Rev. 95 954
Omar M 2007 Mater. Res. Bull. 42 319
Omar M 2016 Int. J. Thermophys. 37 1
Klemens P 1955 Proc. Phys. Soc. Sec. A 68 1113
Pudalov V, Gershenson M, Kojima H, Butch N, Dizhur E, Brunthaler G et al 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 196404
Casimir H 1938 Physica 5 495
Vandersande J 1977 Phys. Rev. B 15 2355
Omar M and Taha H 2009 Phys. B Condens. Matter 404 5203
Omar M 2012 Mater. Res. Bull. 47 3518
Liang L and Li B 2006 Phys. Rev. B 73 153303
Dash J 1999 Rev. Mod. Phys. 71 1737
Post E 1953 Can. J. Phys. 31 112
Martin P, Aksamija Z, Pop E and Ravaioli U 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 102 125503
Ziman J M 1960 Electrons and phonons: the theory of transport phenomena in solids (Oxford: Oxford University Press)
Vandersande J and Wood C 1986 Contemp. Phys. 27 117
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Faculty of Science, University of Raparin in Rania/Sulaimani, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq (IB16), and S M Mamand, N M Saeed and Jawameer R Hama for their scientific explanation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qader, I.N., Omar, M.S. Carrier concentration effect and other structure-related parameters on lattice thermal conductivity of Si nanowires. Bull Mater Sci 40, 599–607 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1393-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1393-1