Abstract
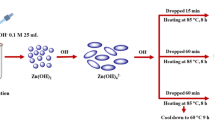
Three different precipitating agents (NaOH, \(\hbox {NH}_{4}(\hbox {H})\hbox {CO}_{3}\) and \(\hbox {CO}(\hbox {NH}_{2})_{2}\)) have been applied for the hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO powder materials, aiming at obtaining various types of porosity and surface species on ZnO. The synthesis procedures were carried out in the presence and in the absence of tri-block copolymer Pluronic (P123, EO20PO70EO20). These materials were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM)–energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), BET method and TG–differential thermal analysis (DTA) method, and their photocatalytic activities were tested in the removal azo dye Reactive Black 5 (RB5). The urea precipitant yields spongy-like surface forms and the greatest share of mesopores. It has the highest specific surface area, highest degree of crystallinity of wurtzite ZnO phase and largest content of surface OH groups in comparison with the other two precipitants. The zinc hydroxycarbonate intermediate phase is missing in the case of NaOH as precipitating agent; therefore, it manifests poorer textural characteristics. The morphology of P123-modified sample is different and consists of needle-shaped particles. The urea-precipitated samples display superior performance in the photocatalytic oxidation reaction, compared with the other precipitated samples. The other two precipitating agents are inferior in regard to their photocatalytic activity due to greater share of micropores (not well-illuminated inner surface) and different surface morphologies.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakthivel S, Neppolian B, Shankar M V, Arabindoo B, Palanichamy M and Murugesan V 2003 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 77 65
Kiomarsipour N, Razavi R S, Ghani K and Kioumarsipour M 2013 Appl. Surf. Sci. 270 33
Stambolova I, Blaskov M, Shipochka M, Vassilev S, Dushkin C and Dimitriev Y 2010 Mater. Chem. Phys. 121 447
de Lima J F, Martins R F and Serra O A Opt. Mater. 35 56
Stambolova I, Blaskov V, Kaneva N, Shipochka M, Vassilev S, Dimitrov O et al 2014 Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 25 244
Suwanboon S and Amornpitoksuk P 2011 Ceram. Int. 37 3515
Athma P V, Martinez A I, Johns N, Safeera T A, Reshmi R and Anila E I 2015 Superlattices Microstruct. 85 379
Khalil M I, Al-Qunaibit M M, Al-zahem A M and Labis J P 2014 Arab. J. Chem. 7 1178
Nishizawa H, Tani T and Matsuoka K 1984 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 67 c98
Pudukudy M and Yaakob Z 2014 Solid State Ion. 30 78
Chen C C, Liu P and Lu C 2008 Chem. Eng. J. 144 509
Zhang Y, Dai J Y, Ong H C, Wang N, Chan H L W and Choy C L 2004 Chem. Phys. Lett. 393 17
Abdel Aal N, Al-Hazmi F, Al-Ghamdi A A, Al-Ghamdi A A, El-Tantawy F and Yakuphanoglu F 2015 Spectrochim. Acta Part A 135 871
Wang J M and Gao L 2004 Solid State Commun. 132 269
Ni Y H, Wei X W, Hong J M and Ye Y 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 121 42
Eliyas A, Stambolova I, Blaskov V, Stoyanova D, Milenova K, Dimitrov L et al 2015 Bulg. Chem. Commun. 47 94
Stambolova I, Blaskov V, Stoyanova D, Dimitrov L, Milenova K, Eliyas A et al 2015 C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 68 463
Hussain S, Liu T, Miao B, Kashif M, Aslam N, Rashad M et al 2015 Ceram. Int. 41 4861
Liu I-H and Chen P 2010 Ceram. Int. 36 1289
Miao Y, Zhang H, Yuan S, Jiao Z and Zhu X 2016 J. Colloid Interface Sci. 462 9
Zhang Z and Mu J 2007 J. Colloid Interface Sci. 307 79
Zheng J H, Jiang Q and Lian J S 2011 Appl. Surf. Sci. 257 5083
Moulder J F, Stickle W F, Sobol P E and Bomben K D 1992 In Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy J Chastain (ed) (Eden Prairie: Perkin-Elmer Corporation) p 89
Das J, Pradhan S K, Sahu D R, Mishra D K, Sarangi S N, Nayak B B et al 2010 Phys. B 405 2492
Wang H H and Xie C S 2008 Phys. E 40 2724
Wang H H, Baek S H, Song J J, Lee J H and Lim S W 2008 Nanotechnology 19 art. no. 075607
Al-Gaashani R, Radiman S, Daud A R, Tabet N and Al-Douri Y 2013 Ceram. Int. 39 2283
Hu S-H, Chen Y-C, Hwang C-C, Peng C-H and Gong D-C 2010 J. Mater. Sci. 45 5309
Lamba R, Umar A, Mehta S K and Kansal S K 2015 Talanta 131 490
Baruah S, Mahmood M A, Myint M I Z, Bora T and Dutta J 2010 Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 1 14
Bacsa R R and Kiwi J 1998 Appl. Catal. B 16 19
Li D and Haneda H 2003 Chemosphere 51 129
Yu J C, Yu J and Zhao J 2002 Appl. Catal. B Environ. 36 31
Hoffmann M R, Martin S T, Choi W and Bahnemann D 1995 Chem. Rev. 95 69
Yang C, Li Q, Tang L, Xin K, Bai A and Yu Y 2015 Appl. Surf. Sci. 357 1928
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to EBR SANI for the financial support through the contract ‘Development of advanced catalytic systems applicable to chemical and photochemical processes for neutralization of environmental pollutions’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stambolova, I., Blaskov, V., Stoyanova, D. et al. Dependence of the textural properties and surface species of ZnO photocatalytic materials on the type of precipitating agent used in the hydrothermal synthesis. Bull Mater Sci 40, 483–492 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1389-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1389-x