Abstract
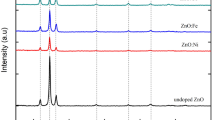
ZnO thin films have been prepared using zinc acetate precursor by spray pyrolytic decomposition of zinc acetate on glass substrates at 450 °C. Effect of precursor concentration on structural and optical properties has been investigated. ZnO films are polycrystalline with (002) plane as preferential orientation. The optical transmission spectrum shows that transmission increases with decrease in the concentration and the maximum transmission in visible region is about 95% for ZnO films prepared with 0·1 M. The direct bandgap value decreases from 3·37 to 3·19 eV, when the precursor concentration increases from 0·1 to 0·4 M. Photoluminescence spectra at room temperature show an ultraviolet (UV) emission at 3·26 eV and two visible emissions at 2·82 and 2·38 eV. Lowest resistivity is obtained at 2·09 Ω cm for 0·3 M. The current– voltage characteristic of the ZnO thin films were measured in dark and under UV illumination. The values of photocurrent and photoresponsivity at 5 V are increased with increase in precursor concentration and reaches to maximum value of 1148 μA and 0·287 A/W, respectively which is correlated to structural properties of ZnO thin films.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alver, U., T. Kilinc, E. Bacaksiz, T. Kucukomeroglu, S. Nezir, I.H. Mutlu, and F. Aslan. 2007. Thin Solid Films 515: 3448.
Ashour, A., M.A. Kaid, N.Z. El-Sayed, and A.A. Ibrahim. 2006. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252: 7844.
Basak, D., G. Amin, B. Mallik, G.K. Paul, and S.K. Sen. 2003. J. Cryst. Growth 256: 73.
Brinker, C.J., and G.W. Scherer. 1975. Sol–gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol–gel processing, 87. New York: Academic Press.
Cao, H., J.Y. Xu, E.W. Seelig, and R.P.H. Chang. 2000. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76: 2997.
Cullity, B.D., and S.R. Stock. 2001. Elements of X-ray diffraction. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Djurisic, A.B., and Y.H. Leung. 2006. Small 2: 944.
Dong, L., Y.C. Liu, Y.H. Tong, and Z.Y. Xiao. 2005. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 283: 380.
Dutta, M., S. Mridha, and D. Basak. 2008. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254: 2743.
Fay, S., U. Kroll, C. Bucher, E. Vallat-Sauvain, and A. Shah. 2005. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 86: 385.
Fortunato, E., A. Goncalves, A. Pimentel, P. Barquinha, G. Goncalves, L. Pereira, I. Ferreira, and R. Martins. 2009. Appl. Phys. A 96: 197.
Ghosh, R., D. Basak, and S. Fujihara. 2004. J. Appl. Phys. 96: 2689.
Girtan, M., G.G. Rusu, S. Dabos-Seignon, and M. Rusu. 2008. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254: 4179.
Huang, B., G. He, and H. Yang. 2010. Physica B 405: 4101.
Hupkes, J., B. Rech, O. Kluth, T. Repmann, B. Zwayagardt, J. Muller, R. Drese, and M. Wutting. 2006. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90: 3054.
Leary, D.J., J.O. Bornes, and A.G. Jordon. 1982. J. Electrochem. Soc. 129: 1382.
Liu, A., J. Zhang, and Q. Wang. 2011. Chem. Eng. Comm. 198: 494.
Liu, C.Y., B.P. Zhang, W. Lu, N.T. Binh, K. Wakatsuki, Y. Segawa, and R. Mu. 2009. J. Mater. Sci. 20: 197.
Liu, J.M., Y.B. Xia, L.J. Wanga, Q.F. Su, and W.M. Shi. 2007. J. Cryst. Growth 300: 353.
Lokhande, B.J., and M.D. Uplane. 2000. Appl. Surf. Sci. 167: 243.
Luo, L., Y. Zhang, S.S. Mao, and L. Lin. 2006. Sens. Actuators A 127: 201.
Martins, R., E. Fortunato, P. Nunes, I. Ferreira, and A. Marques. 2004. J. Appl. Phys. 96: 1398.
Mishra, D., K.C. Dubey, R.K. Shukla, A. Srivastava, and A. Srivastava. 2009. Sens. Trans. J. 105: 119.
Monroy, E., F. Omnes, and F. Calle. 2003. Semicond. Sci. Tech. 18: 33.
Mridha, S., and D. Basak. 2006. Chem. Phys. Lett. 427: 62.
Mridha, S., and D. Basak. 2007. Mater. Res. Bull. 42: 875.
Nunes, P., E. Fortunato, A. Lopes, and R. Martins. 2001. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 3: 1129.
Nunes, P., A. Malik, B. Fernandes, E. Fortunato, P. Vilarinho, and R. Martins. 1999. Vacuum 52: 45.
Pankove J I 1971 Optical processes in semiconductors (New York: Dover Publication) Ch. 2, p. 22
Prasada Rao, T., and M.C. Santhoshkumar. 2009. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255: 4579.
Rozati, S.M., F. Zarenejad, and N. Memarian. 2011. Thin Solid Films 520: 1259.
Saito, N., H. Haneda, T. Sekiguchi, N. Ohashi, I. Sakaguchi, and K. Koumoto. 2002. Adv. Mater. 14: 418.
Salvatori, S., E. Pace, M.C. Rossi, and F. Galluzzi. 1997. Diam. Relat. Mater. 6: 361.
Schroder, D.K. 1998. Semiconductor material and device characterization. New York: Wiley.
Sharma, P., K. Sreenivas, and K.V. Rao. 2003. J. Appl. Phys. 93: 3963.
Srikant, V., and D.R. Clarke. 1997. J. Appl. Phys. 81: 6357.
Suhail, A.M., E.K. Hassan, S.S. Ahmed, and M.K.M. Alnoori. 2010. J. Electr. Dev. 8: 268.
Vanheusden, K., W.L. Warren, C.H. Seager, D.R. Tallant, J.A. Voigt, and B.E. Gnade. 1996. J. Appl. Phys. 79: 7983.
Wu, Y., E. Girgis, V. Strom, W. Voit, L. Belova, and K.V. Rao. 2011. Phys. Status Solidi A 208: 206.
Xingwen, Z., L. Yongqiang, L. Ye, L. Yingwei, and X. Yiben. 2006. Vacuum 81: 502.
Yim, J.H., et al. 2003. Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 766: E8.10.1.
Zahedi, F., and R.S. Dariani. 2012. Thin Solid Films 520: 2132.
Zahedi, F., R.S. Dariani, and S.M. Rozati. 2013. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16: 245.
Zaier, A., F. OumElaz, F. Lakfif, A. Kabir, S. Boudjadar, and M.S. Aida. 2009. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 12: 207.
Zhang, H.Z., X.C. Sun, R.M. Wang, and D.P. Yu. 2004. J. Cryst. Growth 269: 464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahedi, F., Dariani, R.S. & Rozati, S.M. Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis: Effect of Precursor Concentration. Bull Mater Sci 37, 433–439 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-014-0696-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-014-0696-8