Abstract
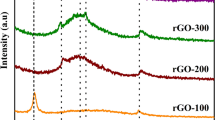
In this paper, the influence of temperature and voltage on direct electrochemical reduction were discussed in detail. Reduced graphene oxide is characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD), fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT–IR) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE–SEM). It is found that the reduction degree of graphene oxide (GO) decreases gradually with the increase of applied temperature. The optimal applied temperature found in our experiment is 20 °C; Meanwhile, as the applied voltage increases from 0·1 to 12·5 V, the reduction degree of graphene oxide increases gradually. However, above 2·5 V, increasing voltage has little effect on the reduction degree of graphene oxide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhavan O and Ghaderi E 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C113 20214
Balandin A A, Ghosh S, Bao W Z, Calizo I, Teweldebrhan D, Miao Feng and Lau C N 2008 Nano Lett. 8 902
Buchsteiner A, Lerf A and Pieper J 2006 J. Phys. Chem. B110 22328
Cai W W et al 2008 Science 321 1815
Chae H K et al 2004 Nature 427 523
Guo H L et al 2009 ACS Nano 3 2653
Jeong H K et al 2008 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 1362
Lee C, Wei X and Kysar J W 2008 Science 321 3858
Lei Z B, Christov N and Zhao X S 2011 Energy & Environ. Sci. 26 1039
Liu S et al 2012 Appl. Surf. Sci. 258 5299
Muszynski R B, Seger and Kamat P V 2008 J. Phys. Chem. C112 5263
Sung J A and Yan W Z 2010 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1 1259
Wang Z J et al 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C113 14071
Williams G, Seger B and Kamat P V 2008 ACS Nano 2 1487
Yang J et al 2012 Appl. Surf. Sci. 258 5056
Zhang T Y and Zhang D 2011 Bull. Mater. Sci. 34 25
Zhu P Y, Zhang D, Xiao S H and Shen M 2011 Phys. BConden. Matter 406 498
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhang, D., Zhu, P. et al. Influence of temperature and voltage on electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide. Bull Mater Sci 37, 629–634 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-014-0684-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-014-0684-z