Abstract
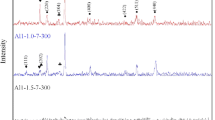
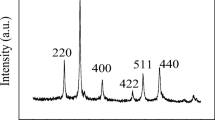
The barium ferrite particles were prepared using a self-propagating low-temperature combustion method using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a fuel. The process was investigated with simultaneous thermo-gravimetric-differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA). The crystalline structure, morphology and the magnetic properties of the barium ferrite particles were studied by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and SQUID susceptometer. The results show that the ignition temperature of PEG is lower compared with other combustion methods and gives nanocrystalline barium ferrite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barb D, Diamandescu L and Rusi A 1986 J. Mater. Sci. 21 1118
Basavaraja S, Vijayananad H, Venkataraman A, Deshpande U P and Shripathi T 2007 Synth. React. Inorg. Met-Org. Nano-Metal Chem. 37 409
Benito G, Morales M P, Requena J, Raposo V, Vazquez M and Moya J S 2001 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 234 65
Cornell R M and Schwertmann U 1996 The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrence and uses (VCH: Weinheim)
Hun X, Zhaohui L, Xuxu W and Xianzhi F 2007 Mater. Lett. 61 347
Jacobo S E, Blesa M A, Domingo-Pascual C and Rodpiguez-Clemente R 1997 J. Mater. Sci. 32 1025
Kojima H and Wohlfarth E P 1982 Ferromagnetic materials (Amsterdam: North Holland) p. 305
Kubo O, Ido T and Yokoyama H 1982 IEEE Trans. Magn. 18 1122
Lagashetty A, Havanoor V, Basavaraja S and Venkataraman S 2005 Bull. Mater. Sci. 28 477
Liu X, Wang J, Gan L M, Ng S C and Ding J 1998 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 184 344
Lucchini E, Meriani S and Slokar G 1983 J. Mater. Sci. 18 1331
Patil K C, Aruna S T and Ekambaram S 1997 Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2 158
Qiu J X, Liang L and Gu M Y 2005 Mater. Sci. Eng. A393 361
Roos W 1980 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 63 601
Shirk B T and Buessem W R 1970 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 53 192
Stablin H and Wohlfarth E P 1982 Ferromagnetic materials (North-Holland, Amsterdam) Vol. 3, Ch. 7
Surig C, Hempel K A and Bonnenberg D 1994 IEEE Trans. Magn. 30 4092
Venkataraman A, Hiremath V A, Date S K and Kulkarni S D 2001 Bull. Mater. Sci. 24 617
Zheng Z, Guo B and Mei X 1989 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 78 73
Zhong W, Ding W, Zhang N, Hong J, Yan Q and Du Y 1997 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 198 196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prithviraj Swamy, P.M., Basavaraja, S., Havanoor, V. et al. Barium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by self-propagating low-temperature combustion method and its characterization. Bull Mater Sci 34, 1319–1323 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-011-0322-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-011-0322-y