Abstract
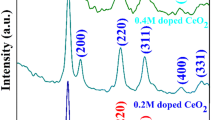
Mn-doped CeO2 nanorods have been prepared from CeO2 particles through a facile composite-hydroxide-mediated (CHM) approach. The products were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The analysis from the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy indicates that the manganese doped in CeO2 exists as Mn4 + . The responses to humidity for static and dynamic testing proved doping Mn into CeO2 can improve the humidity sensitivity. For the sample with Mn% about 1·22, the resistance changes from 375·3 to 2·7MΩ as the relative humidity (RH) increases from 25 to 90%, indicating promising applications of the Mn-doped CeO2 nanorods in environmental monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson J H and Parks G A 1968 J. Phys. Chem. 72 3362
Blanco G, Cauqui M A, Delgado J J and Galtayries A 2004 Surf. Interface Anal. 36 752
Burroughs P, Hamnett A, Orchard A F and Thornton G 1976 J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1686
Chen Z and Lu C 2005 Sensor Lett. 3 274
Chou K S, Lee T K and Liu F J 1999 Sensors Actuators B56 106
Corma A, Atienzar P and Garc H 2004 Nature Mater. 3 394
Fu Q, Deng W and Saltsburg H 2006 Appl. Catal. B56 57
Fu X Q, Wang C, Yu H C, Wang Y G and Wang T H 2007 Nanotechnology 18 145503
Goi D, Leitenburg C, Dolcetti G and Trovarelli A 2004 Environ. Technol. 25 1397
Hu C G, Liu H, Lao C S, Zhang L Y, Davidovic D and Wang Z L 2006 J. Phys. Chem. B110 14050
Kang CH Y, Kusaba H, Yahiro H, Sasaki K and Teraoka Y 2006 Solid State Ionics 177 1799
Kim C H and Thompson L T 2006 J. Catal. 244
Kosynkin V D, Arzgatkina A A, Ivanov E N and Chtoutsa M G 2000 J. Alloys Compd 39 1023
Leandro G R, Jose M S A and Miguel L H 2009 Nano Lett. 9 1395
Machida M, Uto M, Kurogi D and Kijima T 2000 Chem. Mater. 12 3158
Parvatikar N, Jain S, Bhoraskar S V and Ambika Prasad M V N 2006 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102 5533
Pokhrel S and Nagaraja K S 2003 Sensors Actuators B92 144
Sears W M 2000 Sensors Actuators B67 161
Shan W J, Ma N, Yang J L, Dong X W, Liu C and Wei L L 2010 J. Nat. Gas Chem. 19 86
Stefanik T S and Tuller H L 2001 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21 1967
Teraoka T, Matsumura Y, Asakura K and Kagawa S 1999 Electrochem. Soc. Proc. 99 131
Wang N, Hu C G, Xia C H, Feng B, Zhang Z W and Xi Y 2007 Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 163111
Wu X D, Qing L, Duan W, Jun F and Rui R 2007 Catal. Today 126 430
Zhang D S, Fu H X, Shi L Y, Fang J H and Qiang L 2007 J. Solid State Chem. 180 654
Zhang Z W, Hu C G, Xiong Y F, Yang R S and Wang Z L 2007 Nanotechnology 18 465504
Zhao J, Bulduml A, Han J and Lu J P 2002 Nanotechnology 13 195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HU, C.H., XIA, C.H., WANG, F. et al. Synthesis of Mn-doped CeO2 nanorods and their application as humidity sensors. Bull Mater Sci 34, 1033–1037 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-011-0129-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-011-0129-x