Abstract
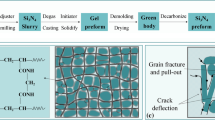
Green bodies of porous Si3N4 ceramics were shaped by extrusion technique using different organic additives as binder during extrusion molding. Different porosity, microstructures and mechanical properties after the extrusion, drying, debinding and sintering stages were investigated. The solid slurry content of 70–75% and extrusion pressure of 0.5–1.0 MPa had played a decisive role in the smooth realization of extrusion molding. The porous Si3N4 ceramics were obtained with excellent properties using 4% hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) as binder and polyethylene glycol (PEG) of molecular weight, 1000, as plasticizer with a density of 1.91 g cm−3, porosity of 41.70%, three-point bending strength of 166.53 ± 20 MPa, fracture toughness of 2.45 ± 0.2 MPa m1/2 and Weibull modulus (m) of 20.75.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazant Z P 2004 Prob. Eng. Mech. 19 307
Corbin S F, Lee J and Qiao X 2001 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84 41
Haslam J J, Beroth K E and Lange F F 2000 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 20 607
Isobe T, Tomita T, Kameshima Y, Nakajima A and Okada K 2006 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26 957
Isobe T, Kameshima Y, Nakajima A and Okada K 2007 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27 61
Kawai C and Yamakawa A 1997 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80 2705
Kaya C and Butler E G 2002 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22 1917
Lper A M 1995 Phase diagrams on advanced ceramics: chemical and metallurgical products II [C] (ed.) Y T Tseng (PA: Towanda) pp 127–128
Oh S T, Tajima K I, Ando M and Ohji T 2000 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83 1314
Raupp-Pereira F, Ribeiro M J, Segadaes A M and Labrincha J A 2007 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27 2333
Shigegaki Y, Brito M E, Hirao K, Toriyama M and Kanzaki S 1997 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80 495
Tarì G, Ferreira J M F and Lyckfeldt O 1998a J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 18 386
Tarì G, Fonseca A T and Ferreira J M F 1998b Br. Ceram. Trans. 97 259
Treischel C C and Emrich E W 1946 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 29 129
Weibull W 1951 J. Appl. Mech. 18 293
Yang J, Yang J F, Shan S Y and Gao J Q 2006 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89 3843
Yang J F, Ohji T and Niihara K 2000 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83 2094
Yang J F, Ohji T, Kanzaki S, Díaz A and Hampshire S 2002 J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85 1512
Yang J F, Deng Z Y and Ohji T 2003a J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23 371
Yang J F, Zeng Y P, Ohji T, Kanzaki S and Zhang G J 2003b J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn 111 758
Yu F L, Yang J F, Xue Y H, Gao J Q and Jin Z H 2008 J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 36 1037
Zeng L K, Wang H and Luo M H 2006 Preparation and application of porous functional ceramics (Beijing: Chemical Industry Publishers) p. 95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, F., Wang, H., Yang, J. et al. Effects of organic additives on microstructure and mechanical properties of porous Si3N4 ceramics. Bull Mater Sci 33, 285–291 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0044-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-010-0044-6