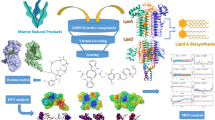
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) is a gram-negative biofilm-forming opportunistic human pathogen whose vital mechanism is biofilm formation for better survival. PelA and PelB proteins of the PEL operon are essential for bacterial-synthesized pellicle polysaccharide (PEL), which is a vital structural component of the biofilm. It helps in adherence of biofilm on the surface and maintenance of cell-to-cell interactions and with other matrix components. Here, in-silico molecular docking and simulation studies were performed against PelA and PelB using ten natural bioactive compounds, individually [podocarpic acids, ferruginol, scopadulcic acid B, pisiferic acid, metachromin A, Cytarabine (cytosine arabinoside; Ara-C), ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, maslinic acid, and betulinic acid], those have already been established as anti-infectious compounds. The results obtained from AutoDock and Glide-Schordinger stated that a marine-derived cytosine arabinoside (Ara-C) among the ten compounds binds active sites of PelA and PelB, exhibiting strong binding affinity [Trp224 (hydrogen), Ser219 (polar), Val234 (hydrophobic) for PelA; Leu365 and Glu389 (hydrogen), Gln366 (polar) for PelB] with high negative binding energy − 5.518 kcal/mol and − 6.056 kcal/mol, respectively. The molecular dynamic and simulation studies for 100 ns showed the MMGBSA binding energy scores are − 16.4 kcal/mol (Ara-C with PelA), and − 22.25 kcal/mol (Ara-C with PelB). Further, ADME/T studies indicate the IC50 values of AraC are 6.10 mM for PelA and 18.78 mM for PelB, which is a comparatively very low dose. The zero violation of Lipinski’s Rule of Five further established that Ara-C is a good candidate for drug development. Thus, Ara-C could be considered a potent anti-biofilm compound against PEL operon-dependent biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed of the current study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors via email request.
References
Haque, M., Sartelli, M., McKimm, J., & Bakar, M. A. (2018). Health care-associated infections - an overview. Infection and Drug Resistance, 11, 2321–2333.
Roy, D. N., & Ahmad, I. (2022). Combating biofilm of ESKAPE pathogens from ancient plant-based therapy to modern nanotechnological combinations. A complete guidebook on biofilm study (pp. 59–94). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Datta, S., Nag, S., & Roy, D. N. (2024). Biofilm-producing antibiotic-resistant bacteria in Indian patients: a comprehensive review. Current Medical Research and Opinion. https://doi.org/10.1080/03007995.2024.2305241
Majumdar, M., Misra, T. K., & Roy, D. N. (2020). In vitro anti-biofilm activity of 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide from Andrographis paniculata against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 51, 15–27.
Majumdar, M., Khan, S. A., Biswas, S. C., Roy, D. N., Panja, A. S., & Misra, T. K. (2020). In vitro and in silico investigation of anti-biofilm activity of Citrus macroptera fruit extract mediated silver nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 302, 112586.
Pal, A., Goswami, R., & Roy, D. N. (2021). A critical assessment on biochemical and molecular mechanisms of toxicity developed by emerging nanomaterials on important microbes. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 16, 100485.
Whitfield, G. B., Marmont, L. S., Ostaszewski, A., Rich, J. D., Whitney, J. C., Parsek, M. R., Harrison, J. J., & Howell, P. L. (2020). Pel Polysaccharide biosynthesis requires an inner membrane complex comprised of PelD, PelE, PelF, and PelG. Journal of Bacteriology, 202, e00684-e719.
Marmont, L. S., Whitfield, G. B., Rich, J. D., Yip, P., Giesbrecht, L. B., Stremick, C. A., Whitney, J. C., Parsek, M. R., Harrison, J. J., & Howell, P. L. (2017). PelA and PelB proteins form a modification and secretion complex essential for Pel polysaccharide-dependent biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 292, 19411–19422.
Friedman, L., & Kolter, R. (2004). Genes involved in matrix formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 biofilms. Molecular microbiology, 51, 675–690.
Jennings, L. K., Storek, K. M., Ledvina, H. E., Coulon, C., Marmont, L. S., Sadovskaya, I., Secor, P. R., Tseng, B. S., Scian, M., & Filloux, A. (2015). Pel is a cationic exopolysaccharide that cross-links extracellular DNA in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112, 11353–11358.
Sakuragi, Y., & Kolter, R. (2007). Quorum-sensing regulation of the biofilm matrix genes (pel) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of bacteriology, 189, 5383–5386.
Colvin, K. M., Gordon, V. D., Murakami, K., Borlee, B. R., Wozniak, D. J., Wong, G. C., & Parsek, M. R. (2011). The pel polysaccharide can serve a structural and protective role in the biofilm matrix of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathogens, 7, e1001264.
Mahizan, N. A., Yang, S.-K., Moo, C.-L., Song, A.A.-L., Chong, C.-M., Chong, C.-W., Abushelaibi, A., Lim, S.-H.E., & Lai, K.-S. (2019). Terpene derivatives as a potential agent against antimicrobial resistance (AMR) pathogens. Molecules, 24, 2631.
Majumdar, M., & Roy, D. N. (2019). Terpenoids: the biological key molecules. Terpenoids against human diseases (pp. 39–60). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Roy, D. N. (2019). Terpenoids against human diseases. Boca Raton: CRC Pres.
Majumdar, M., Singh, V., Misra, T. K., & Roy, D. N. (2022). In silico studies on structural inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease Mpro by major secondary metabolites of Andrographis paniculata and Cinchona officinalis. Biologia, 77, 1373–1389.
Majumdar, M., Dubey, A., Goswami, R., Misra, T. K., & Roy, D. N. (2020). In vitro and in silico studies on the structural and biochemical insight of anti-biofilm activity of andrograpanin from Andrographis paniculata against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 36, 1–18.
Roy, D. N., Sen, G., Chowdhury, K. D., & Biswas, T. (2011). Combination therapy with andrographolide and d-penicillamine enhanced therapeutic advantage over monotherapy with d-penicillamine in attenuating fibrogenic response and cell death in the periportal zone of liver in rats during copper toxicosis. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 250, 54–68.
Roy, D., Mandal, S., Sen, G., Mukhopadhyay, S., & Biswas, T. (2010). 14-Deoxyandrographolide desensitizes hepatocytes to tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis through calcium-dependent tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A release via the NO/cGMP pathway. British Journal of Pharmacology, 160, 1823–1843.
Sarfaraj, H. M., Sheeba, F., Saba, A., & Khan, M. (2012). Marine natural products: A lead for Anti-cancer. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 18, 180–187.
Karthikeyan, A., Joseph, A., & Nair, B. G. (2022). Promising bioactive compounds from the marine environment and their potential effects on various diseases. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 20, 1–38.
Das, R., Rauf, A., Mitra, S., Emran, T. B., Hossain, M. J., Khan, Z., Naz, S., Ahmad, B., Meyyazhagan, A., & Pushparaj, K. (2022). Therapeutic potential of marine macrolides: An overview from 1990 to 2022. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 365, 110072.
Mamada, S. S., Nainu, F., Masyita, A., Frediansyah, A., Utami, R. N., Salampe, M., Emran, T. B., Lima, C. M. G., Chopra, H., & Simal-Gandara, J. (2022). Marine macrolides to tackle antimicrobial resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Marine Drugs, 20, 691.
Kabir, M. T., Uddin, M. S., Jeandet, P., Emran, T. B., Mitra, S., Albadrani, G. M., Sayed, A. A., Abdel-Daim, M. M., & Simal-Gandara, J. (2021). Anti-Alzheimer’s molecules derived from marine life: Understanding molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Marine Drugs, 19, 251.
Bahbah, E. I., Ghozy, S., Attia, M. S., Negida, A., Emran, T. B., Mitra, S., Albadrani, G. M., Abdel-Daim, M. M., Uddin, M. S., & Simal-Gandara, J. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of astaxanthin as a potential neurotherapeutic agent. Marine drugs, 19, 201.
Zinatloo-Ajabshir, Z., & Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S. (2019). Preparation and characterization of Curcumin niosomal nanoparticles via a simple and eco-friendly route. Journal of Nanostructures, 9, 784–790.
Taheri Qazvini, N., & Zinatloo, S. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of gelatin nanoparticles using CDI/NHS as a non-toxic cross-linking system. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 22, 63–69.
Zinatloo, A. S., & Taheri, Q. N. (2015). Effect of some synthetic parameters on size and polydispersity index of gelatin nanoparticles cross-linked by CDI/NHS System. Journal of Nanostructures, 5, 137–144.
Hamzeh, S., Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H., Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S., Amiri, M., & Nasab, S. A. R. (2024). Eco-friendly synthesis of mesoporous praseodymium oxide nanoparticles for highly efficient electrochemical sensing of carmoisine in food samples. Food Chemistry, 433, 137363.
Zinatloo-Ajabshir, S., & Salavati-Niasari, M. (2019). Preparation of magnetically retrievable CoFe2O4@ SiO2@ Dy2Ce2O7 nanocomposites as novel photocatalyst for highly efficient degradation of organic contaminants. Composites Part B: Engineering, 174, 106930.
Morris, G. M., Huey, R., Lindstrom, W., Sanner, M. F., Belew, R. K., Goodsell, D. S., & Olson, A. J. (2009). AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. Journal of computational chemistry, 30, 2785–2791.
Gasteiger, J., & Marsili, M. (1980). Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron, 36, 3219–3228.
Dubey, A., Marabotti, A., Ramteke, P. W., & Facchiano, A. (2016). Interaction of human chymase with ginkgolides, terpene trilactones of Ginkgo biloba investigated by molecular docking simulations. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 473, 449–454.
Olsson, M. H., Søndergaard, C. R., Rostkowski, M., & Jensen, J. H. (2011). PROPKA3: consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical pKa predictions. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 7, 525–537.
Shan, Y., Klepeis, J. L., Eastwood, M. P., Dror, R. O., & Shaw, D. E. (2005). Gaussian split Ewald: A fast Ewald mesh method for molecular simulation. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 122, 54101.
Madhavi Sastry, G., Adzhigirey, M., Day, T., Annabhimoju, R., & Sherman, W. (2013). Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design, 27, 221–234.
Halgren, T. A., Murphy, R. B., Friesner, R. A., Beard, H. S., Frye, L. L., Pollard, W. T., & Banks, J. L. (2004). Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 47, 1750–1759.
Hayes, J. M., & Archontis, G. (2012). Molecular dynamics-studies of synthetic and biological macromolecules. In Molecular dynamics-studies of synthetic and biological macromolecules (pp. 171–190). IntechOpen Press.
Bowers, K. J., Chow, E., Xu, H., Dror, R. O., Eastwood, M. P., Gregersen, B. A., Klepeis, J. L., Kolossvary, I., Moraes, M. A. and Sacerdoti, F. D. (2006). Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters, in Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing, 84-es.
Combrouse, T., Sadovskaya, I., Faille, C., Kol, O., Guerardel, Y., & Midelet-Bourdin, G. (2013). Quantification of the extracellular matrix of the Listeria monocytogenes biofilms of different phylogenic lineages with optimization of culture conditions. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 114, 1120–1131.
Vasanthakumari, D., Vadakkethil Lalithabhai, P., & Kanthimathi Bahuleyan, M. (2019). An in silico approach to discover the best molecular modeling strategy for designing novel CDK4 inhibitors. Chemical Biology & Drug Design, 93, 556–569.
Zhou, P., Huang, J., & Tian, F. (2012). Specific noncovalent interactions at protein-ligand interface: Implications for rational drug design. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 19, 226–238.
Chouhan, M., Tiwari, P. K., Moustafa, M., Chaubey, K. K., Gupta, A., Kumar, R., Sahoo, A. K., Azhar, E. I., Dwivedi, V. D., & Kumar, S. (2024). Inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis resuscitation-promoting factor B (RpfB) by microbially derived natural compounds: A computational study. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 42, 948–959.
Pingali, M. S., Singh, A., Singh, V., Sahoo, A. K., Varadwaj, P. K., & Samanta, S. K. (2023). Docking and molecular dynamics simulation for therapeutic repurposing in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients infected with COVID-19. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 41, 16–25.
Burlingham, B. T., & Widlanski, T. S. (2003). An intuitive look at the relationship of K-i and IC50: A more general use for the Dixon plot. Journal of Chemical Education, 80, 214–218.
Lipinski, C. A., Lombardo, F., Dominy, B. W., & Feeney, P. J. (1997). Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 23, 3–25.
Anjum, K., Abbas, S. Q., Shah, S. A. A., Akhter, N., Batool, S., & Ul Hassan, S. S. (2016). Marine sponges as a drug treasure. Biomolecules & Therapeutics, 24, 347–362.
Capizzi, R. L. (1996). Curative chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia: The development of high-dose ara-C from the laboratory to bedside. Investigational New Drugs, 14, 249–256.
Kufe, D. W., Major, P., Egan, E., & Beardsley, G. (1980). Correlation of cytotoxicity with incorporation of ara-C into DNA. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 255, 8997–9000.
Razvi, E., DiFrancesco, B. R., Wasney, G. A., Morrison, Z. A., Tam, J., Auger, A., Baker, P., Alnabelseya, N., Rich, J. D., & Sivarajah, P. (2023). Small molecule inhibition of an exopolysaccharide modification enzyme is a viable strategy to block Pseudomonas aeruginosa pel biofilm formation. Microbiology Spectrum, 11, e00296-e1223.
Colvin, K. M., Alnabelseya, N., Baker, P., Whitney, J. C., Howell, P. L., & Parsek, M. R. (2013). PelA deacetylase activity is required for Pel polysaccharide synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology, 195, 2329–2339.
Ghosh, S., Roy, K., & Pal, C. (2019). Terpenoids against infectious diseases. Terpenoids against human diseases (pp. 187–208). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Roa-Linares, V. C., Brand, Y. M., Agudelo-Gomez, L. S., Tangarife-Castaño, V., Betancur-Galvis, L. A., Gallego-Gomez, J. C., & González, M. A. (2016). Anti-herpetic and anti-dengue activity of abietane ferruginol analogues synthesized from (+)-dehydroabietylamine. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 108, 79–88.
Alangari, A., Mateen, A., Alqahtani, M. S., Shahid, M., Syed, R., Shaik, M. R., Khan, M., Adil, S. F., & Kuniyil, M. (2023). Antimicrobial, anticancer, and biofilm inhibition studies of highly reduced graphene oxide (HRG): In vitro and in silico analysis. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 11, 1149588.
Poulin, M. B., & Kuperman, L. L. (2021). Regulation of biofilm exopolysaccharide production by cyclic di-guanosine monophosphate. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 730980.
Dai, L., Wu, T.-Q., Xiong, Y.-S., Ni, H.-B., Ding, Y., Zhang, W.-C., Chu, S.-P., Ju, S.-Q., & Yu, J. (2019). Ibuprofen-mediated potential inhibition of biofilm development and quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life sciences, 237, 116947.
Acknowledgements
SD is grateful to the Nationa Institute of Technology-Agartala for providing the PhD fellowship. All authors express their profound gratitude to Dr. Amaresh Kumar Sahoo, Department of Applied Sciences, Indian Institute of Information Technology-Allahabad, for providing the dry laboratory facilities to accomplish this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interest would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Ethical Approval
No human or non-human animal was used for the current study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Datta, S., Singh, V., Nag, S. et al. Marine-Derived Cytosine Arabinoside (Ara-C) Inhibits Biofilm Formation by Inhibiting PEL Operon Proteins (Pel A and Pel B) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An In Silico Approach. Mol Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01169-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01169-8