Abstract
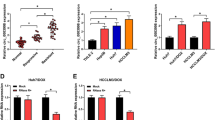
Sorafenib (SOR) is the first-line chemotherapeutic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment, but SOR resistance is a key factor affecting the therapeutic effect. Emerging studies have suggested that circular RNAs (circRNAs) play an important role in the development of drug resistance in HCC cells. This paper aimed to elucidate the potential role and molecular mechanism of circRNA Scm polycomb group protein homolog 1 (circSCMH1) in SOR-resistant HCC cells. CircSCMH1, microRNA-485-5p (miR-485-5p), and hematological and neurological expressed 1 (HN1) contents were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) assay was adopted to detect the SOR sensitivity of cells. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis were assessed using colony formation, 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (EdU), transwell, and flow cytometry assays. Glucose metabolism was analyzed using commercial kits. HN1, B cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), and Bcl-2-associated X (Bax) protein levels were assessed using western blot. Binding between miR-485-5p and circSCMH1 or HN1 was verified using a dual-luciferase reporter. Xenograft tumor model was used to explore the function of circSCMH1 in vivo. CircSCMH1 expression and HN1 abundances were increased, but the miR-485-5p level was reduced in SOR-resistant HCC tissues and cells. Deficiency of circSCMH1 enhanced SOR sensitivity by suppressing cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glucose metabolism and inducing cell apoptosis in SOR-resistant HCC cell lines (Huh7/SOR and Hep3B/SOR). Mechanistically, circSCMH1 sponged miR-485-5p to positively regulate HN1 expression. Importantly, circSCMH1 depletion inhibited tumor growth and increased SOR sensitivity in vivo. CircSCMH1 promoted SOR resistance in HCC cells at least partly through upregulating HN1 expression by sponging miR-485-5p. These findings elucidated a new regulatory pathway of chemo-resistance in SOR-resistant HCC cells and provided a possible circRNA-targeted therapy for HCC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The analyzed datasets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Heimbach, J. K., Kulik, L. M., Finn, R. S., Sirlin, C. B., Abecassis, M. M., Roberts, L. R., Zhu, A. X., Murad, M. H., & Marrero, J. A. (2018). AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 67(1), 358–380.
Diaz-Gonzalez, A., Reig, M., & Bruix, J. (2016). Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Digestive Diseases, 34(5), 597–602.
Colecchia, A., Schiumerini, R., Cucchetti, A., Cescon, M., Taddia, M., Marasco, G., & Festi, D. (2014). Prognostic factors for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 20(20), 5935–5950.
Fujiwara, N., Friedman, S. L., Goossens, N., & Hoshida, Y. (2018). Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. Journal of Hepatology, 68(3), 526–549.
Adnane, L., Trail, P. A., Taylor, I., & Wilhelm, S. M. (2006). Sorafenib (BAY 43–9006, Nexavar), a dual-action inhibitor that targets RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in tumor cells and tyrosine kinases VEGFR/PDGFR in tumor vasculature. Methods in Enzymology, 407, 597–612.
Hosseinzadeh, F., et al. (2022). The effects of Sorafenib and Natural killer cell co-injection in combinational treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma; an in vivo approach. Pharmacological reports : PR, 74(2), 379–391.
Xia, S., Pan, Y., Liang, Y., Xu, J., & Cai, X. (2020). The microenvironmental and metabolic aspects of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. eBioMedicine, 51, 102610.
Li, W., et al. (2019). LncRNA SNHG1 contributes to sorafenib resistance by activating the Akt pathway and is positively regulated by miR-21 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research : CR, 38(1), 183.
Hsu, C. H., Shen, Y. C., Shao, Y. Y., Hsu, C., & Cheng, A. L. (2014). Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future perspectives. Journal of hepatocellular carcinoma, 1, 85–99.
Li, J. F., & Song, Y. Z. (2017). Circular RNA GLI2 promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting miR-125b-5p. Tumour Biology, 39(7), 1010428317709991.
Liang, H. F., Zhang, X. Z., Liu, B. G., Jia, G. T., & Li, W. L. (2017). Circular RNA circ-ABCB10 promotes breast cancer proliferation and progression through sponging miR-1271. American Journal of Cancer Research, 7(7), 1566–1576.
Yao, Z., et al. (2017). ZKSCAN1 gene and its related circular RNA (circZKSCAN1) both inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth, migration, and invasion but through different signaling pathways. Molecular Oncology, 11(4), 422–437.
Zhao, L., Ma, N., Liu, G., Mao, N., Chen, F., & Li, J. (2021). Lidocaine Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development by Modulating circ_ITCH/miR-421/CPEB3 Axis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 66(12), 4384–4397.
Wei, Y., et al. (2020). A Noncoding Regulatory RNAs Network Driven by Circ-CDYL Acts Specifically in the Early Stages Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology, 71(1), 130–147.
Yu, J., et al. (2018). Circular RNA cSMARCA5 inhibits growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Hepatology, 68(6), 1214–1227.
Cao, S., Wang, G., Wang, J., Li, C., & Zhang, L. (2019). Hsa_circ_101280 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-375/JAK2. Immunology and Cell Biology, 97(2), 218–228.
Sun, R., Li, H., Li, J., Shen, S., Cui, G., & Dong, G. (2020). CircRNA circ-0038718 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through sponging miR-139-3p. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 533(4), 845–852.
Ren, L., Zhai, H., Wang, X. L., Li, J. Z., & Xia, Y. H. (2020). Hsa_circ_0011946 promotes the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing EMT process. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 24(3), 1108–1115.
Catalanotto, C., Cogoni, C., Zardo, G.: MicroRNA in control of gene expression: an overview of nuclear functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17(10) (2016)
Lv, L., & Wang, X. (2018). MicroRNA-296 targets specificity protein 1 to suppress cell proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer. Oncology Research, 26(5), 775–783.
Shi, D. M., et al. (2018). miR-296-5p suppresses EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma via attenuating NRG1/ERBB2/ERBB3 signaling. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 37(1), 294.
Zhou, S. L., Tang, Q. L., Zhou, S. X., & Ren, R. Z. (2019). MiR-296-5p suppresses papillary thyroid carcinoma cell growth via targeting PLK1. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 23(5), 2084–2091.
Liu, S., Wang, H., Mu, J., Wang, H., Peng, Y., Li, Q., Mao, D., & Guo, L. (2020). MiRNA-211 triggers an autophagy-dependent apoptosis in cervical cancer cells: regulation of Bcl-2. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s archives of pharmacology, 393(3), 359–370.
Hua, F. F., Liu, S. S., Zhu, L. H., Wang, Y. H., Liang, X., Ma, N., & Shi, H. R. (2017). MiRNA-338-3p regulates cervical cancer cells proliferation by targeting MACC1 through MAPK signaling pathway. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 21(23), 5342–5352.
Sun, X., Liu, Y., Li, M., Wang, M., & Wang, Y. (2015). Involvement of miR-485-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma progression targeting EMMPRIN. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 72, 58–65.
Laughlin, K. M., Luo, D., Liu, C., Shaw, G., Warrington, K. H., Jr., Qiu, J., Yachnis, A. T., & Harrison, J. K. (2009). Hematopoietic- and neurologic-expressed sequence 1 expression in the murine GL261 and high-grade human gliomas. Pathology Oncology Research, 15(3), 437–444.
Zhou, G., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhong, C., Ni, J., Wang, L., Guo, J., Zhang, K., Yu, L., & Zhao, S. (2004). Cloning, expression and subcellular localization of HN1 and HN1L genes, as well as characterization of their orthologs, defining an evolutionarily conserved gene family. Gene, 331, 115–123.
Petroziello, J., Yamane, A., Westendorf, L., Thompson, M., McDonagh, C., Cerveny, C., Law, C. L., Wahl, A., & Carter, P. (2004). Suppression subtractive hybridization and expression profiling identifies a unique set of genes overexpressed in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene, 23(46), 7734–7745.
Zhang, C., Xu, B., Lu, S., Zhao, Y., & Liu, P. (2017). HN1 contributes to migration, invasion, and tumorigenesis of breast cancer by enhancing MYC activity. Molecular Cancer, 16(1), 90.
Alkan, A. H., & Akgül, B. (2022). Endogenous miRNA Sponges. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ), 2257, 91–104.
Hansen, T. B., Jensen, T. I., Clausen, B. H., Bramsen, J. B., Finsen, B., Damgaard, C. K., & Kjems, J. (2013). Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature, 495(7441), 384–388.
Liu, C., Wu, J., Chang, Z.: Trends and age-period-cohort effects on the prevalence, incidence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma from 2008 to 2017 in Tianjin, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18(11) (2021)
Liu, Z., Jiang, Y., Yuan, H., Fang, Q., Cai, N., Suo, C., Jin, L., Zhang, T., & Chen, X. (2019). The trends in incidence of primary liver cancer caused by specific etiologies: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 and implications for liver cancer prevention. Journal of Hepatology, 70(4), 674–683.
Roxburgh, P., & Evans, T. R. (2008). Systemic therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: are we making progress? Advances in Therapy, 25(11), 1089–1104.
Kim, D. W., Talati, C., & Kim, R. (2017). Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): beyond sorafenib-chemotherapy. J Gastrointest Oncol, 8(2), 256–265.
Aishanjiang, K., et al. (2021). Circular RNAs and hepatocellular carcinoma: new epigenetic players with diagnostic and prognostic roles. Frontiers in oncology, 11, 653717.
Li, P., et al. (2022). circMRPS35 promotes malignant progression and cisplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Molecular Therapy : The Journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy, 30(1), 431–447.
Xu, J., et al. (2020). CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 5(1), 298.
Zhou, J., Zhang, W. W., Peng, F., Sun, J. Y., He, Z. Y., & Wu, S. G. (2018). Downregulation of hsa_circ_0011946 suppresses the migration and invasion of the breast cancer cell line MCF-7 by targeting RFC3. Cancer Management and Research, 10, 535–544.
Wei, H., Li, J., Xie, C., & Dong, H. (2022). Circular RNA hsa_circ_0011946 promotes the malignant process of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma by downregulating miR-1205 expression. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 23(4), 295.
Qiu, F., Qiao, B., Zhang, N., Fang, Z., Feng, L., Zhang, S., & Qiu, W. (2021). Blocking circ-SCMH1 (hsa_circ_0011946) suppresses acquired DDP resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells both in vitro and in vivo by sponging miR-338-3p and regulating LIN28B. Cancer Cell International, 21(1), 412.
Panda, A. C. (2018). Circular RNAs Act as miRNA sponges. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1087, 67–79.
Liu, H., Hu, G., Wang, Z., Liu, Q., Zhang, J., Chen, Y., Huang, Y., Xue, W., Xu, Y., & Zhai, W. (2020). circPTCH1 promotes invasion and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma via regulating miR-485-5p/MMP14 axis. Theranostics, 10(23), 10791–10807.
Wang, X., Zhou, X., Zeng, F., Wu, X., & Li, H. (2020). miR-485-5p inhibits the progression of breast cancer cells by negatively regulating MUC1. Breast cancer (Tokyo, Japan), 27(4), 765–775.
Pan, Y., Qin, J., Sun, H., Xu, T., Wang, S., & He, B. (2020). MiR-485-5p as a potential biomarker and tumor suppressor in human colorectal cancer. Biomarkers in Medicine, 14(3), 239–248.
Yang, L., Deng, W. L., Zhao, B. G., Xu, Y., Wang, X. W., Fang, Y., & Xiao, H. J. (2022). FOXO3-induced lncRNA LOC554202 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the miR-485-5p/BSG axis. Cancer Gene Therapy, 29(3–4), 326–340.
Tu, J., Zhao, Z., Xu, M., Chen, M., Weng, Q., Ji, J.: LINC00460 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development through sponging miR-485-5p to up-regulate PAK1. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 118, 109213 (2019)
Gao, J., Dai, C., Yu, X., Yin, X. B., & Zhou, F. (2020). microRNA-485-5p inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through blocking the WBP2/Wnt signaling pathway. Cellular Signalling, 66, 109466.
Feng, J., Liu, Y., Fang, T., Zhu, J., Wang, G., & Li, J. (2023). Hematological and neurological expressed 1 (HN1) activates c-Myc signaling by inhibiting ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of c-Myc in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biology International, 47(3), 560–572.
Chen, J. J., Sun, X., Mao, Q. Q., Jiang, X. Y., Zhao, X. G., Xu, W. J., & Zhong, L. (2020). Increased expression of hematological and neurological expressed 1 (HN1) is associated with a poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and its knockdown inhibits cell growth and migration partly by down-regulation of c-Met. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences, 36(3), 196–205.
Wang, R., Fu, Y., Yao, M., Cui, X., Zhao, Y., Lu, X., Li, Y., Lin, Y., & He, S. (2022). The HN1/HMGB1 axis promotes the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma and attenuates the chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin. The FEBS Journal, 289(20), 6400–6419.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
This work was supported by Deep Science and Technology Innovation [2014] 109 .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XP and HX: Conceptualization and Methodology. HX and LX: Formal analysis and Data curation. ML and XP Validation and Investigation. ML, XP and HX: Writing—original draft preparation and Writing—review and editing of the manuscript. All authors: Approval of final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University Health Science Center. Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients.
Consent for publication
Patients agree to participate in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Pang, X., Xu, H. et al. CircSCMH1 Accelerates Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating HN1 Expression via miR-485-5p. Mol Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01054-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-024-01054-4