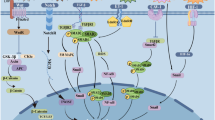
Abstract
Cancer is one of the diseases, which it is not still completely curable; the existing treatments are associated with many complications, that double its complexity. One of the causes of cancer cell metastasis is Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT). Recently study demonstrated that EMT cause cardiotoxicity and heart diseases such as heart failure, hypertrophy and fibrosis. This study evaluated molecular and signaling pathway, which lead to cardiotoxicity via EMT. It was demonstrated that the processes of inflammation, oxidative stress and angiogenesis were involved in EMT and cardiotoxicity. The pathways related to these processes act as a double-edged sword. In relation to inflammation and oxidative stress, molecular pathways caused apoptosis of cardiomyocytes and cardiotoxicity induction. While the angiogenesis process inhibits cardiotoxicity despite the progression of EMT. On the other hand, some molecular pathways such as PI3K/mTOR despite causing the progression of EMT lead to the proliferation of cardiomyocytes and prevent cardiotoxicity. Therefore, it was concluded that the identification of molecular pathways can help in designing therapeutic and preventive strategies to increase patients' survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This is a review study, and it is not an original. Data availability is corresponding author responsibility.
Change history
30 March 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00730-1
References
Darwish, M. M., Riad, A. Y., Salem, D. A., Essa, A. E., Shakweer, M. M., & Sherif, D. E. M. (2021). Prognostic implication of PD-L1 expression and associated tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in metastatic breast cancer. Immunopathologia Persa, 8(1), e18–e18.
van der Valk, M. J. M., Marijnen, C. A. M., van Etten, B., Dijkstra, E. A., Hilling, D. E., Kranenbarg, E. M., Putter, H., Roodvoets, A. G. H., Bahadoer, R. R., Fokstuen, T., Ten Tije, A. J., Capdevila, J., Hendriks, M. P., Edhemovic, I., Cervantes, A. M. R., de Groot, D. J. A., Nilsson, P. J., Glimelius, B., van de Velde, C. J. H., & Hospers, G. A. P. (2020). Compliance and tolerability of short-course radiotherapy followed by preoperative chemotherapy and surgery for high-risk rectal cancer–results of the international randomized RAPIDO-trial. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 147, 75–83.
Hao, W., Shi, Y. Y., Qin, Y. N., Sun, C. P., Chen, L. Y., Wu, C. Y., Bao, Y. J., & Liu, S. (2022). Cardioprotective effect of Chinese herbal medicine for anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in cancer patients: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Medicine (Baltimore), 101(30), e29691.
Rottapel, R. E., Hudson, L. B., & Folta, S. C. (2021). Cardiovascular health and African-American women: A qualitative analysis. American Journal of Health Behavior, 45(4), 735–745.
Leman, M. A., Claramita, M., & Rahayu, G. R. (2021). Predicting factors on modeling health behavior: A systematic review. American Journal of Health Behavior, 45(2), 268–278. https://doi.org/10.5993/AJHB.45.2.7
Alagal, R. I., AlFaris, N. A., Alshammari, G. M., ALTamimi, J. Z., AlMousa, L. A., & Yahya, M. A. (2023). The protection afforded by Berberine against chemotherapy-mediated nephropathy in rats involves regulation of the antioxidant axis. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology, 132(1), 98–110.
Dadras, F., Sheikh, V., & Khoshjou, F. (2018). Epithelial and endothelial mesenchymal transition and their role in diabetic kidney disease. Journal of Renal Injury Prevention, 7(1), 1–6.
Seo, J., Ha, J., Kang, E., & Cho, S. (2021). The role of epithelial–mesenchymal transition-regulating transcription factors in anti-cancer drug resistance. Archives of pharmacal research, 44, 281–292.
Zhong, W., & Sun, T. (2023). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) as a therapeutic target in cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 13, 119.
Ashrafizadeh, M., Mirzaei, S., Hashemi, F., Zarrabi, A., Zabolian, A., Saleki, H., Sharifzadeh, S. O., Soleymani, L., Daneshi, S., Hushmandi, K., Khan, H., Kumar, A. P., Aref, A. R., & Samarghandian, S. (2021). New insight towards development of paclitaxel and docetaxel resistance in cancer cells: EMT as a novel molecular mechanism and therapeutic possibilities. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 141, 111824.
Sanjaya, A. (2022). microRNA-379 as a Candidate Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Childhood Active and Latent Tuberculosis.
Efentakis, P., Gavriatopoulou, M., Choustoulaki, E., Georgoulis, A., Tsekenis, G., Chakim, Z., Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I., Dimopoulos, M. A., Terpos, E., & Andreadou, I. (2022). 33P Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced cardiotoxicity is driven through inflammation, autophagy and stress. Annals of Oncology, 33, S556.
Quagliariello, V., Paccone, A., Iovine, M., Cavalcanti, E., Berretta, M., Maurea, C., Canale, M. L., & Maurea, N. (2021). Interleukin-1 blocking agents as promising strategy for prevention of anticancer drug-induced cardiotoxicities: Possible implications in cancer patients with COVID-19. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 25(21), 6797–6812.
Ichikawa, M. K., Endo, K., Itoh, Y., Osada, A. H., Kimura, Y., Ueki, K., Yoshizawa, K., Miyazawa, K., & Saitoh, M. (2022). Ets family proteins regulate the EMT transcription factors Snail and ZEB in cancer cells. FEBS Open Bio, 12(7), 1353–1364.
Al-Obaidi, Z. M. J., Abdul-Rasheed, O. F., Mahdi, M. F., & Raauf, A. M. (2019). Biological evaluation of newly synthesized spebrutinib analogues: Potential candidates with enhanced activity and reduced toxicity profiles. International Journal of Drug Delivery Technology, 9(03), 339–346.
Liu, J., Wu, Z., Han, D., Wei, C., Liang, Y., Jiang, T., Chen, L., Sha, M., Cao, Y., Huang, F., Geng, X., Yu, J., Shen, Y., Wang, H., Feng, L., Wang, D., Fang, S., Wang, S., & Shen, Y. (2020). Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor inhibits liver cancer through small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)ylation-related suppression of NF-kappaB/snail signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hepatology, 71(4), 1262–1278. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30917
Jafari, M., Dadras, F., Ghadimipour, H. R., Rabiei, M. A. S., & Khoshjou, F. (2017). Tempol effect on epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by hyperglycemia. Journal of Nephropathology, 6(1), 1.
Suarez-Carmona, M., Lesage, J., Cataldo, D., & Gilles, C. (2017). EMT and inflammation: Inseparable actors of cancer progression. Molecular Oncology, 11(7), 805–823. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12095
Grande, M. T., Sanchez-Laorden, B., Lopez-Blau, C., De Frutos, C. A., Boutet, A., Arevalo, M., & Nieto, M. A. (2015). Snail1-induced partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition drives renal fibrosis in mice and can be targeted to reverse established disease. Nature Medicine, 21(9), 989–997. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3901
Sun, Z., Ji, N., Ma, Q., Zhu, R., Chen, Z., Wang, Z., Qian, Y., Wu, C., Hu, F., Huang, M., & Zhang, M. (2020). Epithelial-Mesenchymal transition in asthma airway remodeling is regulated by the IL-33/CD146 Axis. Frontiers in Immunology, 11, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01598
Liu, J., Mao, W., Ding, B., & Liang, C. S. (2008). ERKs/p53 signal transduction pathway is involved in doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells and cardiomyocytes. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 295(5), H1956-1965. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00407.2008
Zhang, D. X., Ma, D. Y., Yao, Z. Q., Fu, C. Y., Shi, Y. X., Wang, Q. L., & Tang, Q. Q. (2016). ERK1/2/p53 and NF-kappaB dependent-PUMA activation involves in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 20(11), 2435–2442.
El-Agamy, D. S., El-Harbi, K. M., Khoshhal, S., Ahmed, N., Elkablawy, M. A., Shaaban, A. A., & Abo-Haded, H. M. (2019). Pristimerin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and fibrosis through modulation of Nrf2 and MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathways. Cancer Manag Res, 11, 47–61. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S186696
Imam, F., Al-Harbi, N. O., Khan, M. R., Qamar, W., Alharbi, M., Alshamrani, A. A., Alhamami, H. N., Alsaleh, N. B., & Alharbi, K. S. (2020). Protective effect of RIVA against Sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated inflammation: probable role of TGF-beta and smad signaling. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 20(3), 281–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-019-09551-8
Kabel, A. M., & Elkhoely, A. A. (2017). Targeting proinflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, TGF-beta1 and STAT-3 by rosuvastatin and ubiquinone to ameliorate trastuzumab cardiotoxicity. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 93, 17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.033
Fuxe, J., & Karlsson, M. C. (2012). TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A link between cancer and inflammation. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 22(5–6), 455–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.05.004
Alaaeldin, R., Ali, F. E., Bekhit, A. A., Zhao, Q.-L., & Fathy, M. (2022). Inhibition of NF-kB/IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells by azilsartan. Molecules, 27(22), 7825.
Poursani, E. M., Mercatelli, D., Raninga, P., Bell, J. L., Saletta, F., Kohane, F. V., Zheng, Y., Rouaen, J., Jue, T. R., Michniewicz, F. T., & Kasiou, E. (2022). Copper chelation inhibits TGF-β pathways and suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. biorxiv, 9(2), 112.
Wang, F., Wang, L., Jiao, Y., & Wang, Z. (2020). Qishen Huanwu capsule reduces pirarubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Annals of Palliative Medicine, 9(5), 3453–3461. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-20-1746
Wang, X., Wang, Q., Li, W., Zhang, Q., Jiang, Y., Guo, D., Sun, X., Lu, W., Li, C., & Wang, Y. (2020). TFEB-NF-kappaB inflammatory signaling axis: A novel therapeutic pathway of Dihydrotanshinone I in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 39(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01595-x
Amiri, M. (2018). Oxidative stress and free radicals in liver and kidney diseases; an updated short-review. Journal of Nephropathology, 7, 3.
Phan, T. H. G., Paliogiannis, P., Nasrallah, G. K., Giordo, R., Eid, A. H., Fois, A. G., Zinellu, A., Mangoni, A. A., & Pintus, G. (2021). Emerging cellular and molecular determinants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 78(5), 2031–2057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03693-7
Kartini, D., Taher, A., Panigoro, S. S., Setiabudy, R., Jusman, S. W., Haryana, S. M., Murdani, A., Rustamadji, P., Karisyah, A., & Rasyid, S. H. (2021). Melatonin effect on hypoxia inducible factor-1α and clinical response in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Carcinogenesis. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcar.JCar_19_20
Lage, R., Cebro-Marquez, M., Rodriguez-Manero, M., Gonzalez-Juanatey, J. R., & Moscoso, I. (2019). Omentin protects H9c2 cells against docetaxel cardiotoxicity. PLoS One, 14(2), e0212782. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212782
Giannoni, E., Parri, M., & Chiarugi, P. (2012). EMT and oxidative stress: A bidirectional interplay affecting tumor malignancy. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 16(11), 1248–1263. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2011.4280
Shete, M. V., Deshmukh, R. S., Kulkarni, T., Shete, A. V., Karande, P., & Hande, P. (2020). Myofibroblasts as important diagnostic and prognostic indicators of oral squamous cell carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study in normal oral mucosa, epithelial dysplasia, and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Carcinogenesis. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcar.JCar_3_20
Chatterjee, R., & Chatterjee, J. (2020). ROS and oncogenesis with special reference to EMT and stemness. Eur J Cell Biol, 99(2–3), 151073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2020.151073
Kong, D., Zhang, Z., Chen, L., Huang, W., Zhang, F., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Cao, P., & Zheng, S. (2020). Curcumin blunts epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocytes to alleviate hepatic fibrosis through regulating oxidative stress and autophagy. Redox Biol, 36, 101600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101600
Arjuna, S., Chakraborty, G., Venkataram, R., Dechamma, P. N., & Chakraborty, A. (2020). Detection of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation by allele-specific loop mediated isothermal amplification. Journal of Carcinogenesis, 19.
Huang, G., Yang, L., Zhou, W., Tang, X., Wang, Y., Ma, Z., Gao, S., & Gao, Y. (2018). Study on cardiotoxicity and mechanism of “Fuzi” extracts based on metabonomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113506
Gondo, H. K. (2021). The effect of spirulina on apoptosis through the caspase-3 pathway in a Preeclamptic Wistar rat model. Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine, 12(3), 280–284.
Yarmohammadi, F., Hayes, A. W., & Karimi, G. (2021). Natural compounds against cytotoxic drug-induced cardiotoxicity: A review on the involvement of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 35(3), e22683. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22683
Zhao, D., Yang, J., & Yang, L. (2017). Insights for oxidative stress and mTOR signaling in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury under diabetes. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2017, 6437467. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6437467
Song, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, J., You, Z., Hu, T., Shao, G., Zhang, Z., Xu, Z., & Yu, X. (2021). TWIST2 inhibits EMT and induces oxidative stress in lung cancer cells by regulating the FGF21-mediated AMPK/mTOR pathway. Experimental cell research, 405(1), 112661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112661
Chan, B. Y. H., Roczkowsky, A., Cho, W. J., Poirier, M., Sergi, C., Keschrumrus, V., Churko, J. M., Granzier, H., & Schulz, R. (2021). MMP inhibitors attenuate doxorubicin cardiotoxicity by preventing intracellular and extracellular matrix remodelling. Cardiovascular Research, 117(1), 188–200. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaa017
Rabinovich-Nikitin, I., Love, M., & Kirshenbaum, L. A. (2021). Inhibition of MMP prevents doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by attenuating cardiac intracellular and extracellular matrix remodelling. Cardiovascular Research, 117(1), 11–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvaa198
Baroroh, H. N., Nugroho, A. E., Lukitaningsih, E., & Nurrochmad, A. (2021). Immune-enhancing effect of bengkoang (Pachyrhizus erosus (L.) Urban) fiber fractions on mouse peritoneal macrophages, lymphocytes, and cytokines. Journal of Natural Science, Biology and Medicine, 12(1), 84–92.
Kang, M. K., Kim, S. I., Oh, S. Y., Na, W., & Kang, Y. H. (2020). Tangeretin ameliorates glucose-induced podocyte injury through blocking epithelial to mesenchymal transition caused by oxidative stress and hypoxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228577
Das, N. A., Carpenter, A. J., Belenchia, A., Aroor, A. R., Noda, M., Siebenlist, U., Chandrasekar, B., & DeMarco, V. G. (2020). Empagliflozin reduces high glucose-induced oxidative stress and miR-21-dependent TRAF3IP2 induction and RECK suppression, and inhibits human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Signal, 68, 109506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109506
Chen, Q. M., & Maltagliati, A. J. (2018). Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection. Physiological Genomics, 50(2), 77–97. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00041.2017
Tonelli, C., Chio, I. I. C., & Tuveson, D. A. (2018). Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 29(17), 1727–1745. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2017.7342
Wang, J., Zhu, H., Huang, L., Zhu, X., Sha, J., Li, G., Ma, G., Zhang, W., Gu, M., & Guo, Y. (2019). Nrf2 signaling attenuates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Experimental and Molecular Pathology, 111, 104296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104296
Jin, M., Wang, J., Ji, X., Cao, H., Zhu, J., Chen, Y., Yang, J., Zhao, Z., Ren, T., & Xing, J. (2019). MCUR1 facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via the mitochondrial calcium dependent ROS/Nrf2/Notch pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 38(1), 136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1135-x
Feng, R., Morine, Y., Ikemoto, T., Imura, S., Iwahashi, S., Saito, Y., & Shimada, M. (2018). Nrf2 activation drive macrophages polarization and cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition during interaction. Cell Communication and Signaling: CCS, 16(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-018-0262-x
Zhao, L., Qi, Y., Xu, L., Tao, X., Han, X., Yin, L., & Peng, J. (2018). MicroRNA-140-5p aggravates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by promoting myocardial oxidative stress via targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2. Redox Biology, 15, 284–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.12.013
Jiang, B. H., & Liu, L. Z. (2008). PI3K/PTEN signaling in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1784(1), 150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.09.008
Mashouri, L., Yousefi, H., Aref, A. R., Ahadi, A. M., Molaei, F., & Alahari, S. K. (2019). Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0991-5
Mohammadi, H., & Ashari, S. (2021). Mechanistic insight into toxicity of phthalates, the involved receptors, and the role of Nrf2, NF-kappaB, and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 28(27), 35488–35527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14466-5
Cheng, S., Zhang, X., Feng, Q., Chen, J., Shen, L., Yu, P., Yang, L., Chen, D., Zhang, H., Sun, W., & Chen, X. (2019). Astragaloside IV exerts angiogenesis and cardioprotection after myocardial infarction via regulating PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Life Sciences, 227, 82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.040
Chung, C. (2020). From oxygen sensing to angiogenesis: Targeting the hypoxia signaling pathway in metastatic kidney cancer. American Journal of Health System Pharmacy, 77(24), 2064–2073. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/zxaa308
Soni, H., Pandya, G., Patel, P., Acharya, A., Jain, M., & Mehta, A. A. (2011). Beneficial effects of carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-2 (CORM-2) on acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in mice: Role of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 253(1), 70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.03.013
Ma, W., Zhang, X., & Liu, Y. (2021). miR-124 promotes apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation of vessel endothelial cells through P38/MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways, making it a potential mechanism of vessel endothelial injury in acute myocardial infarction. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 22(6), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10819
Bi, Q. R., Hou, J. J., Qi, P., Ma, C. H., Feng, R. H., Yan, B. P., Wang, J. W., Shi, X. J., Zheng, Y. Y., Wu, W. Y., & Guo, D. A. (2016). TXNIP/TRX/NF-kappaB and MAPK/NF-kappaB pathways involved in the cardiotoxicity induced by Venenum Bufonis in rats. Science and Reports, 6, 22759. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22759
Cao, Y., Ruan, Y., Shen, T., Huang, X., Li, M., Yu, W., Zhu, Y., Man, Y., Wang, S., & Li, J. (2014). Astragalus polysaccharide suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating the PI3k/Akt and p38MAPK pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/674219
Gallego, I., Beaumont, J., López, B., Ravassa, S., Gómez-Doblas, J. J., Moreno, M. U., Valencia, F., de Teresa, E., Díez, J., & González, A. (2016). Potential role of microRNA-10b down-regulation in cardiomyocyte apoptosis in aortic stenosis patients. Clinical Science (London, England), 130(23), 2139–2149. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20160462
Kalantary-Charvadeh, A., Sanajou, D., Hemmati-Dinarvand, M., Marandi, Y., Khojastehfard, M., Hajipour, H., Mehran, M. A., Leila, R., & Ahmad, N. S. (2019). Micheliolide protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-kB signaling pathway. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 19(4), 297–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-019-09511-2
Hassanein, E. H. M., Abd El-Ghafar, O. A. M., Ahmed, M. A., Sayed, A. M., Gad-Elrab, W. M., Ajarem, J. S., & Mahmoud, A. M. (2020). Edaravone and acetovanillone upregulate Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and prevent cyclophosphamide cardiotoxicity in rats. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 14, 5275–5288. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S281854
Sun, L., Wang, H., Xu, D., Yu, S., Zhang, L., & Li, X. (2022). Lapatinib induces mitochondrial dysfunction to enhance oxidative stress and ferroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocytes via inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Bioengineered, 13(1), 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2004980
Yu, W., Qin, X., Zhang, Y., Qiu, P., Wang, L., Zha, W., & Ren, J. (2020). Curcumin suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via a PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent manner. Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy, 10(4), 752–769. https://doi.org/10.21037/cdt-19-707
Scheau, C., Badarau, I. A., Costache, R., Caruntu, C., Mihai, G. L., Didilescu, A. C., Constantin, C., & Neagu, M. (2019). The role of matrix metalloproteinases in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma. Analytical Cellular Pathology (Amsterdam), 2019, 9423907. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9423907
Schanza, L. M., Seles, M., Stotz, M., Fosselteder, J., Hutterer, G. C., Pichler, M., & Stiegelbauer, V. (2017). MicroRNAs associated with von hippel-lindau pathway in renal cell carcinoma: a comprehensive review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112495
Skala, M., Hanouskova, B., Skalova, L., & Matouskova, P. (2019). MicroRNAs in the diagnosis and prevention of drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Archives of Toxicology, 93(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2356-z
Pan, J. A., Tang, Y., Yu, J. Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, J. F., Wang, C. Q., & Gu, J. (2019). miR-146a attenuates apoptosis and modulates autophagy by targeting TAF9b/P53 pathway in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cell Death & Disease, 10(9), 668. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1901-x
Vosgha, H., Ariana, A., Smith, R. A., & Lam, A. K. (2018). miR-205 targets angiogenesis and EMT concurrently in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 25(3), 323–337. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-17-0497
Chakraborti, S., Pramanick, A., Saha, S., Roy, S. S., Chaudhuri, A. R., Das, M., Ghosh, S., Stewart, A., & Maity, B. (2018). Atypical G protein beta5 promotes cardiac oxidative stress, apoptosis, and fibrotic remodeling in response to multiple cancer chemotherapeutics. Cancer Research, 78(2), 528–541. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1280
Iqubal, A., Iqubal, M. K., Sharma, S., Ansari, M. A., Najmi, A. K., Ali, S. M., Ali, J., & Haque, S. E. (2019). Molecular mechanism involved in cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity: Old drug with a new vision. Life Sciences, 218, 112–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.12.018
Ren, X., Zhao, B., Chang, H., Xiao, M., Wu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2018). Paclitaxel suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis through regulation of ROS and the AKT/MAPK signaling pathway in canine mammary gland tumor cells. Molecular Medicine Reports, 17(6), 8289–8299. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.8868
Oh, E. T., Kim, C. W., Kim, S. J., Lee, J. S., Hong, S. S., & Park, H. J. (2016). Docetaxel induced-JNK2/PHD1 signaling pathway increases degradation of HIF-1α and causes cancer cell death under hypoxia. Science and Reports, 6, 27382. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27382
Zhang, X., Shao, J., Li, X., Cui, L., & Tan, Z. (2019). Docetaxel promotes cell apoptosis and decreases SOX2 expression in CD133expressing hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells by suppressing the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncology Reports, 41(2), 1067–1074. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6891
Sadek, K. M., Mahmoud, S. F. E., Zeweil, M. F., & Abouzed, T. K. (2021). Proanthocyanidin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury by inhibiting NF-kB pathway and modulating oxidative stress, cell cycle, and fibrogenesis. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 35(4), e22716. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22716
Xu, J., Liu, D., Niu, H., Zhu, G., Xu, Y., Ye, D., Li, J., & Zhang, Q. (2017). Resveratrol reverses Doxorubicin resistance by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through modulating PTEN/Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 36(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0487-8
Kitani, T., Ong, S. G., Lam, C. K., Rhee, J. W., Zhang, J. Z., Oikonomopoulos, A., Ma, N., Tian, L., Lee, J., Telli, M. L., Witteles, R. M., Sharma, A., Sayed, N., & Wu, J. C. (2019). Human-induced pluripotent stem cell model of trastuzumab-induced cardiac dysfunction in patients with breast cancer. Circulation, 139(21), 2451–2465. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037357
Roukos, D. H. (2011). Trastuzumab and beyond: Sequencing cancer genomes and predicting molecular networks. The Pharmacogenomics Journal, 11(2), 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2010.81
Huang, Z., Hu, Z., Ouyang, J., & Huang, C. (2019). Electroacupuncture regulates the DREAM/NF-kappaB signalling pathway and ameliorates cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression in mice. Acupuncture in Medicine, 37(5), 292–300. https://doi.org/10.1136/acupmed-2017-011593
Chen, X., Wei, W., Li, Y., Huang, J., & Ci, X. (2019). Hesperetin relieves cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by mitigating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 308, 269–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.05.040
Ma, W., Wei, S., Zhang, B., & Li, W. (2020). Molecular mechanisms of cardiomyocyte death in drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Front Cell Dev Biol, 8, 434. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00434
Zhang, P., Yi, L. H., Meng, G. Y., Zhang, H. Y., Sun, H. H., & Cui, L. Q. (2017). Apelin-13 attenuates cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity through inhibition of ROS-mediated DNA damage and regulation of MAPKs and AKT pathways. Free Radical Research, 51(5), 449–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2017.1313414
Li, J.-P., Liu, Y.-J., Zeng, S.-H., Gao, H.-J., Chen, Y.-G., & Zou, X. (2022). Identification of COX4I2 as a hypoxia-associated gene acting through FGF1 to promote EMT and angiogenesis in CRC. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 27(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-022-00380-2
Li, P., Liu, X., Xing, W., Qiu, H., Li, R., Liu, S., & Sun, H. (2022). Exosome-derived miR-200a promotes esophageal cancer cell proliferation and migration via the mediating Keap1 expression. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 477(4), 1295–1308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04353-z
Xia, W., Chen, H., Xie, C., & Hou, M. (2020). Long-noncoding RNA MALAT1 sponges microRNA-92a-3p to inhibit doxorubicin-induced cardiac senescence by targeting ATG4a. Aging (Albany NY), 12(9), 8241–8260. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103136
Gallo, S., Sala, V., Gatti, S., & Crepaldi, T. (2015). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of HGF/Met in the cardiovascular system. Clinical Science (London, England), 129(12), 1173–1193. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20150502
Jiao, D., Wang, J., Lu, W., Tang, X., Chen, J., Mou, H., & Chen, Q. Y. (2016). Curcumin inhibited HGF-induced EMT and angiogenesis through regulating c-Met dependent PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in lung cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics, 3, 16018. https://doi.org/10.1038/mto.2016.18
Chen, J., Yuan, W., Wu, L., Tang, Q., Xia, Q., Ji, J., Liu, Z., Ma, Z., Zhou, Z., Cheng, Y., & Shu, X. (2017). PDGF-D promotes cell growth, aggressiveness, angiogenesis and EMT transformation of colorectal cancer by activation of Notch1/Twist1 pathway. Oncotarget., 8(6), 9961–9973. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14283
Mansour, H. H., El Kiki, S. M., Ibrahim, A. B., & Omran, M. M. (2021). Effect of l-carnitine on cardiotoxicity and apoptosis induced by imatinib through PDGF/ PPARγ /MAPK pathways. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 704, 108866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2021.108866
Gonzalez-Moreno, O., Lecanda, J., Green, J. E., Segura, V., Catena, R., Serrano, D., & Calvo, A. (2010). VEGF elicits epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in prostate intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN)-like cells via an autocrine loop. Experimental Cell Research, 316(4), 554–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.11.020
Räsänen, M., Degerman, J., Nissinen, T. A., Miinalainen, I., Kerkelä, R., Siltanen, A., Backman, J. T., Mervaala, E., Hulmi, J. J., Kivelä, R., & Alitalo, K. (2016). VEGF-B gene therapy inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by endothelial protection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(46), 13144–13149. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1616168113
Shen, X., Hu, X., Mao, J., Wu, Y., Liu, H., Shen, J., Yu, J., & Chen, W. (2020). The long noncoding RNA TUG1 is required for TGF-β/TWIST1/EMT-mediated metastasis in colorectal cancer cells. Cell death & disease, 11(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2254-1
Xu, Y., Zhou, J., Lv, G., Liu, Y., Zhao, X., Li, X., Ye, D., Qu, X., & Huang, X. (2020). Effect of Pilose Antler peptide on doxorubicin-induced H9c2 cells Injury via TGF-β/Smad/ERK signaling pathway. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 52(5), 1787.
Liu, C., Xue, J., Xu, B., Zhang, A., Qin, L., Liu, J., & Yang, Y. (2021). Exosomes derived from miR-146a-5p-enriched mesenchymal stem cells protect the cardiomyocytes and myocardial tissues in the polymicrobial sepsis through regulating MYBL1. Stem Cells Int, 2021, 1530445. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1530445
Meng, Q., Liang, C., Hua, J., Zhang, B., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Wei, M., Yu, X., Xu, J., & Shi, S. (2020). A miR-146a-5p/TRAF6/NF-kB p65 axis regulates pancreatic cancer chemoresistance: Functional validation and clinical significance. Theranostics, 10(9), 3967–3979. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.40566
Hu, X., Liu, H., Wang, Z., Hu, Z., & Li, L. (2019). miR-200a Attenuated doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through upregulation of Nrf2 in mice. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2019, 1512326. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1512326
Chen, C., Zhou, Y., Ding, P., & He, L. (2021). miR-1 targeted downregulation of Bcl-2 increases chemosensitivity of lung cancer cells. Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers, 25(8), 540–545. https://doi.org/10.1089/gtmb.2021.0009
Wu, J., Sun, C., Wang, R., Li, J., Zhou, M., Yan, M., Xue, X., & Wang, C. (2018). Cardioprotective effect of paeonol against epirubicin-induced heart injury via regulating miR-1 and PI3K/AKT pathway. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 286, 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.035
Wu, Y., Pu, N., Su, W., Yang, X., & Xing, C. (2020). Downregulation of miR-1 in colorectal cancer promotes radioresistance and aggressive phenotypes. Journal of Cancer, 11(16), 4832–4840. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.44753
Lin, F., Yin, H. B., Li, X. Y., Zhu, G. M., He, W. Y., & Gou, X. (2020). Bladder cancer cellsecreted exosomal miR21 activates the PI3K/AKT pathway in macrophages to promote cancer progression. International Journal of Oncology, 56(1), 151–164. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4933
Tong, Z., Jiang, B., Wu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Gao, M., Jiang, Y., Lv, Q., & Xiao, X. (2015). MiR-21 protected cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by targeting BTG2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(7), 14511–14525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160714511
Guo, D., Guo, J., Li, X., & Guan, F. (2018). Enhanced motility and proliferation by miR-10b/FUT8/p-AKT axis in breast cancer cells. Oncology Letters, 16(2), 2097–2104. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8891
Lin, C. C., Yang, T. Y., Lu, H. J., Wan, C. K., Hsu, S. L., & Wu, C. C. (2021). Attenuating role of withaferin A in the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells via a p53-miR-27a/miR-10b pathway. Oncology Letters, 21(3), 232. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2021.12493
Bian, W. S., Shi, P. X., Mi, X. F., Sun, Y. Y., Yang, D. D., Gao, B. F., Wu, S. X., & Fan, G. C. (2018). MiR-210 protects cardiomyocytes from OGD/R injury by inhibiting E2F3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 22(3), 743–749. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201802_14305
Yang, F., Yan, Y., Yang, Y., Hong, X., Wang, M., Yang, Z., Liu, B., & Ye, L. (2020). MiR-210 in exosomes derived from CAFs promotes non-small cell lung cancer migration and invasion through PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Signal, 73, 109675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109675
Acknowledgements
We wish thank you of all our colleague in IRAN university of medical science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MMA: has conceived the manuscript and revised it. AB and AJ: wrote the manuscript. AK and AB: revise the manuscript. SG: edited manuscript English language.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kardooni, A., Bahrampour, A., Golmohammadi, S. et al. The Role of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Pathogenesis of Cardiotoxicity: Diagnostic & Prognostic Approach. Mol Biotechnol 65, 1403–1413 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00697-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00697-z