Abstract
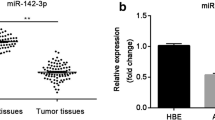
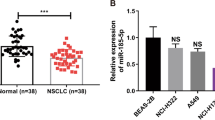
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), a prevalent form of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), has a high incidence and mortality rate. However, its molecular regulatory mechanisms have yet to be fully understood. The purpose of this study was to look into how NADPH quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1) and it miR-485-5p and affected LUAD cells. The levels of miR-485-5p and NQO1 expression in LUAD cells and tissues were determined by means of quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. The viability, proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of LUAD cells were assessed using cell counting Kit-8, 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine, transwell, and caspase-3 assays, respectively. Western blot experiments were used to examine the relative protein expression of matrix metallopeptidase 2 and matrix metallopeptidase 9, as well as the phosphorylation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (Akt) in LUAD cells. Luciferase and RNA pull-down experiments were also conducted for the verification of miR-485-5p’s underlying relationship with NQO1. In our study, we found that LUAD cells and tissues had miR-485-5p downregulation and NQO1 upregulation. The experimental outcomes indicated that miR-485-5p overexpression in LUAD cells reduced their malignant behaviors, suppressed PI3K and Akt phosphorylation, and facilitated apoptosis. The results also revealed that NQO1 was a direct miR-485-5p target, and that NQO1 could reverse miR-485-5p’s inhibitory effect on the malignant phenotype of LUAD cells. Furthermore, it was also observed that through targeting NQO1, miR-485-5p could suppress LUAD cell migration and proliferation, further blocking the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt and inducing apoptosis among LUAD cells. In conclusion, the miR-485-5/NQO1 axis regulates LUAD progression through the PI3K/Akt pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study can be found in below websites. One mRNA microarrays (GSE118370) from GEO DataSets (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gds) were used to screen the genes. GEPIA (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/), miRDB (http://mirdb.org/), starBase (https://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/) and TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/vert_80/) were used to predict the binding sites.
Abbreviations
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- NQO1:
-
NADPH quinone oxidoreductase-1
- LUAD:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- GEPIA:
-
Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- MMP2:
-
Metallopeptidase 2
- MMP9:
-
Matrix metallopeptidase 9
- CCK-8:
-
Cell Counting kit-8
- BrdU:
-
5′-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma
- 3′UTR:
-
3′Untranslated region
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- STR :
-
Short tandem repeat
- U6:
-
Uracil6
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- Ac-DEVD-pNA:
-
Glu-Val-Asp-chromophore p-nitroaniline
- RIPA:
-
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sulfate-polyacrylamidegel electrophoresis
- ECL:
-
Chemiluminescence
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
References
Zappa, C., & Mousa, S. A. (2016). Non-small cell lung cancer: Current treatment and future advances. Translational Lung Cancer Research, 5, 288–300.
Hutchinson, B. D., Shroff, G. S., Truong, M. T., & Ko, J. P. (2019). Spectrum of lung adenocarcinoma. Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MR, 40, 255–264.
Wang, D., Luo, Y., Shen, D., Yang, L., Liu, H. Y., & Che, Y. Q. (2019). Clinical features and treatment of patients with lung adenocarcinoma with bone marrow metastasis. Tumori, 105, 388–393.
Song, Q., Shang, J., Yang, Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, C., Chen, J., & Wu, X. (2019). Identification of an immune signature predicting prognosis risk of patients in lung adenocarcinoma. Journal of Translational Medicine, 17, 70.
Denisenko, T. V., Budkevich, I. N., & Zhivotovsky, B. (2018). Cell death-based treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death & Disease, 9, 117.
Reuter, J. A., Spacek, D. V., & Snyder, M. P. (2015). High-throughput sequencing technologies. Molecular Cell, 58, 586–597.
Tsai, Y. M., Wu, K. L., Chang, Y. Y., Chang, W. A., Huang, Y. C., Jian, S. F., Tsai, P. H., Lin, Y. S., Chong, I. W., Hung, J. Y., & Hsu, Y. L. (2020). Upregulation of Thr/Tyr kinase increases the cancer progression by neurotensin and dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 in lung cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21, 1640.
de Aberasturi, A. L., Redrado, M., Villalba, M., Larzabal, L., Pajares, M. J., Garcia, J., Evans, S. R., Garcia-Ros, D., Bodegas, M. E., Lopez, L., Montuenga, L., & Calvo, A. (2016). TMPRSS4 induces cancer stem cell-like properties in lung cancer cells and correlates with ALDH expression in NSCLC patients. Cancer Letters, 370, 165–176.
Zheng, Y. W., Li, Z. H., Lei, L., Liu, C. C., Wang, Z., Fei, L. R., Yang, M. Q., Huang, W. J., & Xu, H. T. (2020). FAM83A promotes lung cancer progression by regulating the Wnt and Hippo signaling pathways and indicates poor prognosis. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 180.
Wang, G., Li, X., Yao, Y., Jiang, Z., Zhou, H., Xie, K., Luo, J., & Shen, Y. (2021). FAM83A and FAM83A‑AS1 both play oncogenic roles in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncology Letters, 21, 297.
Xu, L., Lu, C., Huang, Y., Zhou, J., Wang, X., Liu, C., Chen, J., & Le, H. (2018). SPINK1 promotes cell growth and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma and acts as a novel prognostic biomarker. BMB Reports, 51, 648–653.
Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Jin, T., Men, J., Lin, Z., Qi, P., Piao, Y., & Yan, G. (2015). NQO1 protein expression predicts poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancers. BMC Cancer, 15, 207.
Siegel, D., Yan, C., & Ross, D. (2012). NAD (P) H: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) in the sensitivity and resistance to antitumor quinones. Biochemical Pharmacology, 83, 1033–1040.
Madajewski, B., Boatman, M. A., Chakrabarti, G., Boothman, D. A., & Bey, E. A. (2016). Depleting tumor-NQO1 potentiates anoikis and inhibits growth of NSCLC depleting tumor-NQO1 levels inhibits NSCLC growth. Molecular Cancer Research: MCR, 14, 14–25.
Bey, E. A., Reinicke, K. E., Srougi, M. C., Varnes, M., Anderson, V. E., Pink, J. J., Li, L. S., Patel, M., Cao, L., Moore, Z., Rommel, A., Boatman, M., Lewis, C., Euhus, D. M., Bornmann, W. G., Buchsbaum, D. J., Spitz, D. R., Gao, J., & Boothman, D. A. (2013). Catalase abrogates β-lapachone–induced PARP1 hyperactivation–directed programmed necrosis in NQO1-positive breast cancers catalase confers resistance to β-lapachone cell death. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 12, 2110–2120.
Silvers, M. A., Deja, S., Singh, N., Egnatchik, R. A., Sudderth, J., Luo, X., Beg, M. S., Burgess, S. C., DeBerardinis, R. J., Boothman, D. A., & Merritt, M. E. (2017). The NQO1 bioactivatable drug, β-lapachone, alters the redox state of NQO1+ pancreatic cancer cells, causing perturbation in central carbon metabolism. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 292, 18203–18216.
Motea, E. A., Huang, X., Singh, N., Kilgore, J. A., Williams, N. S., Xie, X. J., Gerber, D. E., Beg, M. S., Bey, E. A., & Boothman, D. A. (2019). NQO1-dependent, tumor-selective radiosensitization of non-small cell lung cancers NQO1-dependent radiosensitization of NSCLCs. Clinical Cancer Research, 25, 2601–2609.
Zhang, X., Han, K., Yuan, D. H., & Meng, C. Y. (2017). Overexpression of NAD (P) H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and induced apoptosis by activating AMPK/PGC-1α pathway. DNA and Cell Biology, 36, 256–263.
Bayoumi, A. S., Sayed, A., Broskova, Z., Teoh, J. P., Wilson, J., Su, H., Tang, Y. L., & Kim, I. M. (2016). Crosstalk between long noncoding RNAs and microRNAs in health and disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17, 356.
Lu, T. X., & Rothenberg, M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 141, 1202–1207.
Raitoharju, E., Seppälä, I., Oksala, N., Lyytikäinen, L. P., Raitakari, O., Viikari, J., Ala-Korpela, M., Soininen, P., Kangas, A. J., Waldenberger, M., Klopp, N., Illig, T., Leiviskä, J., Loo, B. M., Hutri-Kähönen, N., Kähönen, M., Laaksonen, R., & Lehtimäki, T. (2014). Blood microRNA profile associates with the levels of serum lipids and metabolites associated with glucose metabolism and insulin resistance and pinpoints pathways underlying metabolic syndrome: the cardiovascular risk in Young Finns Study. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 391, 41–49.
Orso, F., Quirico, L., Dettori, D., Coppo, R., Virga, F., Ferreira, L. C., Paoletti, C., Baruffaldi, D., Penna, E., & Taverna, D. (2020). Role of miRNAs in tumor and endothelial cell interactions during tumor progression. Seminars in Cancer Biology, 60, 214–224.
Hu, X. X., Xu, X. N., He, B. S., Sun, H. L., Xu, T., Liu, X. X., Chen, X. X., Zeng, K. X., Wang, S. K., & Pan, Y. Q. (2018). microRNA-485-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer cells by targeting CD147. Journal of Cancer, 9, 2603–2611.
Lin, X. J., He, C. L., Sun, T., Duan, X. J., Sun, Y., & Xiong, S. J. (2017). hsa-miR-485-5p reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition and promotes cisplatin-induced cell death by targeting PAK1 in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 40, 83–89.
Wu, J., Li, J., Ren, J., & Zhang, D. (2017). MicroRNA-485-5p represses melanoma cell invasion and proliferation by suppressing Frizzled7. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 90, 303–310.
Mou, X., & Liu, S. (2016). MiR-485 inhibits metastasis and EMT of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting Flot2. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 477, 521–526.
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods (San Diego Calif.), 25, 402–408.
Wang, S., Li, P., Jiang, G., Guan, J., Chen, D., & Zhang, X. (2020). Long non-coding RNA LOC285194 inhibits proliferation and migration but promoted apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells via targeting miR-211/PUMA and TGF-β1/S100A4 signal. Bioengineered, 11, 718–728.
Zhao, J. T., Chi, B. J., Sun, Y., Chi, N. N., Zhang, X. M., Sun, J. B., Chen, Y., & Xia, Y. (2020). LINC00174 is an oncogenic lncRNA of hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates miR‐320/S100A10 axis. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 38, 859–869.
Liu, Z. F., Liang, Z. Q., Li, L., Zhou, Y. B., Wang, Z. B., Gu, W. F., Tu, L. Y., & Zhao, J. (2016). MiR-335 functions as a tumor suppressor and regulates survivin expression in osteosarcoma. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 20, 1251–1257.
Zhang, N., & Liu, J. F. (2020). MicroRNA (MiR)-301a-3p regulates the proliferation of esophageal squamous cells via targeting PTEN. Bioengineered, 11, 972–983.
Awan, H. M., Shah, A., Rashid, F., Wei, S., Chen, L., & Shan, G. (2018). Comparing two approaches of miR-34a target identification, biotinylated-miRNA pulldown vs miRNA overexpression. RNA Biology, 15, 55–61.
Chen, L., Zhu, Q., Lu, L., & Liu, Y. (2020). MiR-132 inhibits migration and invasion and increases chemosensitivity of cisplatin-resistant oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting TGF-β1. Bioengineered, 11, 91–102.
Huang, Y., & Feng, G. (2021). MiR‐423‐5p aggravates lung adenocarcinoma via targeting CADM1. Thoracic Cancer, 12, 210–217.
Zhou, L. Y., Zhang, F. W., Tong, J., & Liu, F. (2020). MiR-191-5p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma by repressing SATB1 to inhibit Wnt pathway. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine, 8, e1043.
Jiang, P., Xu, C., Chen, L., Chen, A., Wu, X., Zhou, M., Haq, I. U., Mariyam, Z., & Feng, Q. (2018). Epigallocatechin‐3‐gallate inhibited cancer stem cell-like properties by targeting hsa‐mir‐485‐5p/RXRα in lung cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 119, 8623–8635.
Huang, R. S., Zheng, Y. L., Li, C., Ding, C., Xu, C., & Zhao, J. (2018). MicroRNA-485-5p suppresses growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting IGF2BP2. Life Sciences, 199, 104–111.
Li, W., Zheng, Y., Mao, B., Wang, F., Zhong, Y., & Cheng, D. (2020). SNHG17 upregulates WLS expression to accelerate lung adenocarcinoma progression by sponging miR-485–5p. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 533, 1435–1441.
Gao, F., Wu, H., Wang, R., Guo, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, T., Zhang, G., Liu, C., & Liu, J. (2019). MicroRNA-485-5p suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of small cell lung cancer cells by targeting flotillin-2. Bioengineered, 10, 1–12.
Plotnikova, O., Baranova, A., & Skoblov, M. (2019). Comprehensive analysis of human microRNA–mRNA interactome. Frontiers in Genetics, 10, 933.
Kiyohara, C., Yoshimasu, K., Takayama, K., & Nakanishi, Y. (2005). NQO1, MPO, and the risk of lung cancer: a HuGE review. Genetics in Medicine, 7, 463–478.
Park, S. Y., Lee, S. J., Han, J. H., & Koh, Y. W. (2019). Association between 18F-FDG uptake in PET/CT, Nrf2, and NQO1 expression and their prognostic significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasma, 66, 619–626.
Liang, J., Li, H., Han, J., Jiang, J., Wang, J., Li, Y., Feng, Z., Zhao, R., Sun, Z., Lv, B., & Tian, H. (2020). Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death & Disease, 11, 614.
Sun, B., Hu, N., Cong, D., Chen, K., & Li, J. (2021). MicroRNA-25-3p promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) through adjusting PTEN/PI3K/AKT route. Bioengineered, 12, 3219–3228.
Liu, Q., Wang, Z., Zhou, X., Tang, M., Tan, W., Sun, T., Wang, Y., & Deng, Y. (2020). miR-485-5p/HSP90 axis blocks Akt1 phosphorylation to suppress osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration via PI3K/AKT pathway. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry, 76, 279–290.
Dimri, M., Humphries, A., Laknaur, A., Elattar, S., Lee, T. J., Sharma, A., Kolhe, R., & Satyanarayana, A. (2020). Nqo1 ablation inhibits activation of the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways and blocks metabolic adaptation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD), 71, 549–568.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
Funding information is not available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YPC and LW executed the experiments and analyzed the data. YPC devised and designed the study. MB acquired the data. YPC, LW, and MB analyzed and interpreted the data. All authors have read and approved this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
The Ethics Committee of Wuhan No.1 Hospital (Wuhan, China) granted approval to this study. The processing of clinical tissue samples had been in strict compliance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients signed a written informed consent.
Patient Consent for Publication
All patients signed a written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wu, L. & Bao, M. MiR-485-5p Suppress the Malignant Characteristics of the Lung Adenocarcinoma via Targeting NADPH Quinone Oxidoreductase-1 to Inhibit the PI3K/Akt. Mol Biotechnol 65, 794–806 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00577-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00577-y