Abstract
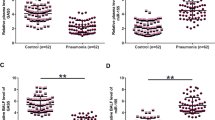
Long non-coding RNA Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 16 (SNHG16) has been reported to participate in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory pathway, which contributes to pneumonia. This study was therefore conducted to explore the role of SNHG16 in pneumonia. In this study, expression of SNHG16 and microRNA (miR)-210 in pneumonia plasma samples (n = 56) and control samples (n = 60) was detected by RT-qPCR. The potential crosstalk between SNHG16 and miR-210 was analyzed by performing overexpression experiments. MSP was performed to study the role of SNHG16 in methylation of miR-210 gene. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by cell apoptosis assay. Decreased expression levels of SNHG16 and increased expression levels of miR-210 were observed in pneumonia. SNHG16 showed an inverse correlation to miR-210. LPS treatment led to downregulated SNHG16 and upregulated miR-210 in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (HBEpCs). In HBEpCs, SNHG16 downregulated miR-210 and increased miR-210 DNA gene methylation. Moreover, SNHG16 suppressed the role of miR-210 in cell apoptosis under LPS treatment. In conclusion, SNHG16 is downregulated in pneumonia, and it downregulates miR-210 possibly through methylation to promote lung cell apoptosis induced by LPS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quinton, L. J., Walkey, A. J., & Mizgerd, J. P. (2018). Integrative physiology of pneumonia. Physiological Reviews, 98, 1417–1464.
Jain, S., Williams, D. J., Arnold, S. R., Ampofo, K., Bramley, A. M., Reed, C., Stockmann, C., Anderson, E. J., Grijalva, C. G., Self, W. H., Zhu, Y., Patel, A., Hymas, W., Chappell, J. D., Kaufman, R. A., Kan, J. H., Dansie, D., Lenny, N., Hillyard, D. R., … CDC EPIC Study Team. (2015). Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among US children. New England Journal of Medicine, 372, 835–845.
Abers, M. S., & Musher, D. M. (2014). Clinical prediction rules in community-acquired pneumonia: Lies, damn lies and statistics. QJM, 107, 595–596.
Egelund, G. B., Jensen, A. V., Andersen, S. B., Petersen, P. T., Lindhardt, B. Ø., von Plessen, C., Rohde, G., & Ravn, P. (2017). Penicillin treatment for patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Denmark: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 17, 66.
Ramirez, J. A., Wiemken, T. L., Peyrani, P., Arnold, F. W., Kelley, R., Mattingly, W. A., Nakamatsu, R., Pena, S., Guinn, B. E., Furmanek, S. P., Persaud, A. K., Raghuram, A., Fernandez, F., Beavin, L., Bosson, R., Fernandez-Botran, R., Cavallazzi, R., Bordon, J., Valdivieso, C., … University of Louisville Pneumonia Study Group. (2017). Adults hospitalized with pneumonia in the United States: incidence, epidemiology, and mortality. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 65, 1806–1812.
Fazylov, R., Peyko, V., & Burney, S. (2017). Prospective evaluation of a novel treatment algorithm for health care-associated pneumonia. Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice, 25, 82–87.
Scheraga, R. G., Abraham, S., Grove, L. M., Southern, B. D., Crish, J. F., Perelas, A., McDonald, C., Asosingh, K., Hasday, J. D., & Olman, M. A. (2020). TRPV4 protects the lung from bacterial pneumonia via MAPK molecular pathway switching. Journal of Immunology, 204, 1310–1321.
Liu, Z., Yu, H., & Guo, Q. (2018). MicroRNA-20a promotes inflammation via the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in pediatric pneumonia. Molecular Medicine Reports, 17, 612–617.
Ottosen, J., & Evans, H. (2014). Pneumonia: Challenges in the definition, diagnosis, and management of disease. Surgical Clinics of North America, 94, 1305–1317.
Esteller, M. (2011). Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12, 861–874.
Huang, S., Feng, C., Chen, L., Huang, Z., Zhou, X., Li, B., Wang, L. L., Chen, W., Lv, F. Q., & Li, T. S. (2016). Identification of potential key long non-coding RNAs and target genes associated with pneumonia using long non-coding RNA sequencing (lncRNA-Seq): A preliminary study. Medical Science Monitor, 22, 3394–3408.
Wang, W., Lou, C., Gao, J., Zhang, X., & Du, Y. (2018). LncRNA SNHG16 reverses the effects of miR-15a/16 on LPS-induced inflammatory pathway. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 106, 1661–1667.
Qi, J., Qiao, Y., Wang, P., Li, S., Zhao, W., & Gao, C. (2012). microRNA-210 negatively regulates LPS-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines by targeting NF-kB1 in murine macrophages. FEBS Let, 586, 1201–1207.
Yang, M., & Wei, W. (2019). SNHG16: A novel long-non coding rna in human cancers. Oncotargets and Therapy, 12, 11679–11690.
Shokri, S., Nabavi, M., Hirschmugl, T., Aghamohammadi, A., Arshi, S., Bemanian, M. H., Fallahpour, M., Molatefi, R., Rekabi, M., Eslami, N., Ahmadian, J., Darabi, K., Sedighi, G. R., Monajemzadeh, M., Modaresi, M., Parvaneh, N., Boztug, K., & Rezaei, N. (2016). LPS-responsive beige-like anchor gene mutation associated with possible bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia associated with hypogammaglobulinemia and normal IgM phenotype and low number of B cells. Acta Medica Iranica, 54, 620–623.
Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Guo, Y., Hu, L., Xiao, Z., Liu, X., Wang, J., Xu, Q., & Tong, X. (2019). Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by targeting miR-497-5p/PIM1 axis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 23, 7395–7405.
Zhou, Z., Zhu, Y., Gao, G., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 targets miR-146a-5p/CCL5 to regulate LPS-induced WI-38 cell apoptosis and inflammation in acute pneumonia. Life Sciences, 22, 189–197.
Zhang, J., Mao, F., Zha, G., Wang, H., Yan, X., & Zhang, Q. (2020). Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 promotes lipopolysaccharides-induced acute pneumonia in A549 cells via targeting miR-370-3p/IGF2 axis. International Immunopharmacology, 78, 106065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12033_2022_545_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 The role of overexpression of SNHG16 and miR-210 in regulating the expression of SNHG16 and miR-210 in medium. Culture medium of HBEpCs was collected at 48-h post-transfection to detect circulating miR-210 (A) and SNHG16 (B). *, p < 0.05 (TIF 92 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, P., Wang, J., Jiang, M. et al. LncRNA SNHG16 is Downregulated in Pneumonia and Downregulates miR-210 to Promote LPS-Induced Lung Cell Apoptosis. Mol Biotechnol 65, 446–452 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00545-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00545-6