Abstract
Objective
To seek out the mechanism by which C1QTNF6 mediates lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Methods
Differentially expressed mRNAs and miRNAs in LUAD were analyzed using bioinformatics. In LUAD cells, C1QTNF6 mRNA and miR-184 expression were evaluated with qRT-PCR, and C1QTNF6 protein level was assessed by western blot. Cellular behaviors were assessed by colony formation, CCK-8, Transwell, and wound healing methods. The binding ability of miR-184 to C1QTNF6 was observed by dual-luciferase assay.
Results
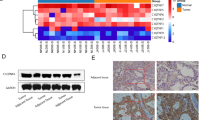
High expression of C1QTNF6 in LUAD stimulated cancer cellular behaviors. MiR-184 was lowly expressed in LUAD and downregulated C1QTNF6 expression. MiR-184 restrained LUAD cell processes by targeting C1QTNF6.
Conclusion
MiR-184 repressed LUAD cell processes via mediating C1QTNF6. MiR-184 and C1QTNF6 are expected to be indicators for LUAD treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article. The data and materials in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians., 68, 394–424.
Siegel, R., Naishadham, D., & Jemal, A. (2013). Cancer statistics, 2013. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 63, 11–30.
Yang, S., Liu, T., Sun, Y., & Liang, X. (2019). The long noncoding RNA LINC00483 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by sponging miR-204-3p. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 24, 70.
Herbst, R. S., Morgensztern, D., & Boshoff, C. (2018). The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature, 553, 446–454.
Hughes, P. E., Caenepeel, S., & Wu, L. C. (2016). Targeted therapy and checkpoint immunotherapy combinations for the treatment of cancer. Trends in Immunology., 37, 462–476.
Lin, J. J., & Shaw, A. T. (2016). Resisting resistance: Targeted therapies in lung cancer. Trends in Cancer., 2, 350–364.
Thomas, A., Liu, S. V., Subramaniam, D. S., & Giaccone, G. (2015). Refining the treatment of NSCLC according to histological and molecular subtypes. Nature reviews. Clinical Oncology, 12, 511–526.
Pakkala, S., & Ramalingam, S. S. (2018). Personalized therapy for lung cancer: striking a moving target. JCI Insight, 3.
Hirsch, F. R., Scagliotti, G. V., Mulshine, J. L., Kwon, R., Curran, W. J., Jr., Wu, Y. L., & Paz-Ares, L. (2017). Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet (London, England)., 389, 299–311.
Vargas, A. J., & Harris, C. C. (2016). Biomarker development in the precision medicine era: Lung cancer as a case study. Nature reviews. Cancer, 16, 525–537.
Stroikova, V., Fischer, A., Bockstahler, M., Muller, A. M., Katus, H. A., & Kaya, Z. (2019). Adiponectin deficiency has no effect in murine autoimmune myocarditis. Cytokine, 116, 139–149.
Le Poole, I. C., & Luiten, R. M. (2008). Autoimmune etiology of generalized vitiligo. Current Directions in Autoimmunity, 10, 227–243.
Qu, H. X., Cui, L., Meng, X. Y., Wang, Z. J., Cui, Y. X., Yu, Y. P., Wang, D., & Jiang, X. J. (2019). C1QTNF6 is overexpressed in gastric carcinoma and contributes to the proliferation and migration of gastric carcinoma cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 43, 621–629.
Han, M., Wang, B., Zhu, M., & Zhang, Y. (2019). C1QTNF6 as a novel biomarker regulates cellular behaviors in A549 cells and exacerbates the outcome of lung adenocarcinoma patients. In vitro cellular & developmental biology. Animal, 55, 614–621.
Lin, W., Chen, X., Chen, T., Liu, J., Ye, Y., Chen, L., Qiu, X., Chia-Hsien Cheng, J., Zhang, L., Wu, J., & Qiu, S. (2020). C1QTNF6 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. DNA and Cell Biology, 39, 1000–1011.
Wang, C., Gao, C., Zhuang, J. L., Ding, C., & Wang, Y. (2012). A combined approach identifies three mRNAs that are down-regulated by microRNA-29b and promote invasion ability in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 138, 2127–2136.
Zhou, Y., Li, S., Li, J., Wang, D., & Li, Q. (2017). Effect of microRNA-135a on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and tumor angiogenesis through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 42, 1431–1446.
Li, W., Li, X., Li, X., Li, M., Yang, P., Wang, X., Li, L., & Yang, B. (2020). Lamin B1 overexpresses in lung adenocarcinoma and promotes proliferation in lung cancer cells via AKT pathway. Oncotargets and Therapy, 13, 3129–3139.
Xu, L., Sun, H. B., Xu, Z. N., Han, X. L., Yin, Y. Y., Zheng, Y., Zhao, Y., & Wang, Z. X. (2019). MicroRNA-218 regulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to suppress lung adenocarcinoma progression by directly targeting BMI-1. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 23, 7978–7988.
An, J. C., Shi, H. B., Hao, W. B., Zhu, K., & Ma, B. (2019). miR-944 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by targeting STAT1 interaction. Oncology Letters, 17, 3790–3798.
Wang, J., Yao, S., Diao, Y., Geng, Y., Bi, Y., & Liu, G. (2020). miR-15b enhances the proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting BCL2. Thoracic Cancer, 11, 1396–1405.
Zhao, H., Zheng, C., Wang, Y., Hou, K., Yang, X., Cheng, Y., Che, X., Xie, S., Wang, S., Zhang, T., Kang, J., Liu, Y., Pan, D., Qu, X., Hu, X., & Fan, Y. (2020). miR-1323 promotes cell migration in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting Cbl-b and is an early prognostic biomarker. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 181.
Yu, C., Tian, F., Liu, J., Su, M., Wu, M., Zhu, X., & Qian, W. (2019). Circular RNA cMras inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression via modulating miR-567/PTPRG regulatory pathway. Cell Proliferation, 52, 12–610.
Takeuchi, T., Adachi, Y., & Nagayama, T. (2011). Expression of a secretory protein C1qTNF6, a C1qTNF family member, in hepatocellular carcinoma. Analytical Cellular Pathology (Amsterdam), 34, 113–121.
Zhang, H. J., Tao, J., Sheng, L., Hu, X., Rong, R. M., Xu, M., & Zhu, T. Y. (2016). Twist2 promotes kidney cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating ITGA6 and CD44 expression in the ECM-receptor interaction pathway. OncoTargets and Therapy., 9, 1801–1812.
Rahimian, P., & He, J. J. (2016). HIV-1 Tat-shortened neurite outgrowth through regulation of microRNA-132 and its target gene expression. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 13, 247.
Huntzinger, E., & Izaurralde, E. (2011). Gene silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12, 99–110.
Cheng, Z., Wang, H. Z., Li, X., Wu, Z., Han, Y., Li, Y., Chen, G., Xie, X., Huang, Y., Du, Z., & Zhou, Y. (2015). MicroRNA-184 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion, and specifically targets TNFAIP2 in Glioma. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 34, 27.
Gao, B., Gao, K., Li, L., Huang, Z., & Lin, L. (2014). miR-184 functions as an oncogenic regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 68, 143–148.
Su, Z., Chen, D., Li, Y., Zhang, E., Yu, Z., Chen, T., Jiang, Z., Ni, L., Yang, S., Gui, Y., Ye, J., & Lai, Y. (2015). microRNA-184 functions as tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 9, 961–966.
Wan, X., Zheng, C., & Dong, L. (2019). Inhibition of CTRP6 prevented survival and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma through inactivating the AKT signaling pathway. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry., 120, 17059–17066.
Dong, X., Hu, H., Fang, Z., Cui, J., & Liu, F. (2018). CTRP6 inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 103, 844–850.
Hamamdzic, D., Fenning, R. S., Patel, D., Mohler, E. R., 3rd., Orlova, K. A., Wright, A. C., Llano, R., Keane, M. G., Shannon, R. P., Birnbaum, M. J., & Wilensky, R. L. (2010). Akt pathway is hypoactivated by synergistic actions of diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolemia resulting in advanced coronary artery disease. American Journal of Physiology Heart and Circulatory Physiology., 299, H699-706.
Derrick, T., Last, A. R., Burr, S. E., Roberts, C. H., Nabicassa, M., Cassama, E., Bailey, R. L., Mabey, D. C., Burton, M. J., & Holland, M. J. (2016). Inverse relationship between microRNA-155 and -184 expression with increasing conjunctival inflammation during ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection. BMC Infectious Diseases., 16, 60.
Qin, C. Z., Lou, X. Y., Lv, Q. L., Cheng, L., Wu, N. Y., Hu, L., & Zhou, H. H. (2015). MicroRNA-184 acts as a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker in epithelial ovarian cancer and regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation. Die Pharmazie., 70, 668–673.
Foley, N. H., Bray, I. M., Tivnan, A., Bryan, K., Murphy, D. M., Buckley, P. G., Ryan, J., O’Meara, A., O’Sullivan, M., & Stallings, R. L. (2010). MicroRNA-184 inhibits neuroblastoma cell survival through targeting the serine/threonine kinase AKT2. Molecular Cancer, 9, 83.
Liu, C., Teng, Z. Q., Santistevan, N. J., Szulwach, K. E., Guo, W., Jin, P., & Zhao, X. (2010). Epigenetic regulation of miR-184 by MBD1 governs neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell, 6, 433–444.
Yu, J., Ryan, D. G., Getsios, S., Oliveira-Fernandes, M., Fatima, A., & Lavker, R. M. (2008). MicroRNA-184 antagonizes microRNA-205 to maintain SHIP2 levels in epithelia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America., 105, 19300–19305.
Weitzel, R. P., Lesniewski, M. L., Haviernik, P., Kadereit, S., Leahy, P., Greco, N. J., & Laughlin, M. J. (2009). microRNA 184 regulates expression of NFAT1 in umbilical cord blood CD4+ T cells. Blood, 113, 6648–6657.
Misono, S., Seki, N., Mizuno, K., Yamada, Y., Uchida, A., Sanada, H., Moriya, S., Kikkawa, N., Kumamoto, T., Suetsugu, T., & Inoue, H. (2019). Molecular pathogenesis of gene regulation by the mir-150 duplex: miR-150–3p regulates TNS4 in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancers., 11, 601.
Jiang, H., Xu, S., & Chen, C. (2020). A ten-gene signature-based risk assessment model predicts the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer, 20, 782.
Zhang, M., Lan, X., & Chen, Y. (2021). MiR-133b suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting SKA3. Cancer Biology & Therapy., 22, 571–578.
Han, J., Rong, Y., & Gao, X. (2021). Multiomic analysis of the function of SPOCK1 across cancers: An integrated bioinformatics approach. The Journal of International Medical Research., 49, 300060520962659.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to submit the manuscript for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, X., Lu, Y. C1QTNF6 Targeted by MiR-184 Regulates the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Mol Biotechnol 64, 1279–1287 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00495-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00495-z