Abstract
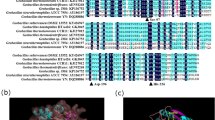
Bacillus subtilis E9 was identified as a potential strain producing esterase. The gene coding esterase from B. subtilis E9 was amplified using esterase-specific primers and the sequence was translated in silico. The presence of conserved catalytic triad amino acid residues (His-Ser-Asp/Glu) confirmed the functional nature of the esterase enzyme. Docking studies conducted with modeled protein and the ligand p-nitrophenyl acetate showed that the amino acid residues interacting with the ligand were Ser77, His76, and Gly103. The gene coding for esterase from B. subtilis E9 was cloned into an assembled vector having Tac promoter (pTac), pUC origin of replication, Ni-Histidine residues, ampicillin cassette, and T7 terminator using Golden gate DNA assembly method. The generated pTac Bs-est (4598 bp) recombinant plasmid was transformed and heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) strain. The tagged recombinant protein was purified to yield 43.4% pure protein with specific activity of 772 U/mg. The purified recombinant protein was subjected to peptide sequencing and the identity was confirmed as esterase by peptide tandem mass fragmentation method using the LC-MS/MS analysis. The purified recombinant esterase was found to be organic solvent stable and tolerant up to 5 days retaining around 95% residual activity in 30–90% v/v Acetone. The recombinant esterase expressed in our study was found to exhibit better organic solvent stability and tolerance than compared to the original bacterial esterase from B. subtilis E9, a property which could be explored in the biocatalytic and synthetic transformation reactions for industrial applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh, R., Kumar, M., Mittal, A., & Mehta, P. K. (2016). Microbial enzymes: industrial progress in 21st century. 3 Biotech, 6(2), 174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0485-8
Adıgüzel, A. O. (2020). Production and characterization of thermo-, halo- and solvent-stable esterase from Bacillus mojavensis TH309. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 38(3), 210–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/10242422.2020.1715370
Romano, D., Bonomi, F., Mattos, M., Fonseca, T., de Oliveira, M. C. F., & Molinari, F. (2015). Esterases as stereoselective biocatalysts. Biotechnology Advances. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.01.006
Baath, J. A., Mazurkewich, S., Poulsen, J. C. N., Olsson, L., Lo Leggio, L., & Larsbrink, J. (2019). Structure-function analyses reveal that a glucuronoyl esterase from Teredinibacter turnerae interacts with carbohydrates and aromatic compounds. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 294(16), 6635–6644. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.007831
Littlechild, J. A. (2017). Improving the ‘tool box’ for robust industrial enzymes. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 44(4–5), 711–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1920-5
Wu, S., Snajdrova, R., Moore, J. C., Baldenius, K., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2021). Biocatalysis: Enzymatic synthesis for industrial applications. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 60, 88–119. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202006648
Chakraborty, K., & Raj, R. P. (2008). An extra-cellular alkaline metallolipase from Bacillus licheniformisMTCC 6824: Purification and biochemical characterization. Food Chemistry, 109(4), 727–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.026
Soumya, P., & Kochupurackal, J. (2020). Pineapple Peel Extract as an Effective Substrate for Esterase Production from Bacillus subtilis E9. Current Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02073-5
Jiang, X., Huo, Y., Cheng, H., Zhang, X., Zhu, X., & Wu, M. (2012). Cloning, expression and characterization of a halotolerant esterase from a marine bacterium Pelagibacterium halotolerans B2T. Extremophiles: Life Under Extreme Conditions, 16, 427–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-012-0442-3
Gangola, S., Sharma, A., Bhatt, P., Khati, P., & Chaudhary, P. (2018). Presence of esterase and laccase in Bacillus subtilis facilitate biodegradation and detoxification of cypermethrin. Scientific Reports, 8, 12755.
Sanchez-Villeda, H., Schroeder, S., Flint-Garcia, S., Guill, K. E., Yamasaki, M., & McMullen, M. D. (2008). DNAAlignEditor: DNA alignment editor tool. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 154. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-154
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2011). MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28(10), 2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Arnold, N. S., Rees, W. G., Hodson, A. J., & Kohler, J. (2006). Topographic controls on the surface energy balance of a high Arctic valley glacier. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 111(2), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JF000426
Lovell, S. C., Davis, I. W., Arendall, W. B., III., de Bakker, P. I. W., Word, J. M., Prisant, M. G., & Richardson, D. C. (2003). Structure validation by Cα geometry: ϕ, ψ and Cβ deviation. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 50(3), 437–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.10286
Halgren, R. G. (2001). Assessment of clone identity and sequence fidelity for 1189 IMAGE cDNA clones. Nucleic Acids Research, 29(2), 582–588. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.2.582
Lozano-Terol, G., Gallego-Jara, J., Sola Martínez, R. A., Cánovas-Díaz, M., & de Diego-Puente, T. (2019). Engineering protein production by rationally choosing a carbon and nitrogen source using E. coli BL21 acetate metabolism knockout strains. Microbial Cell Factories, 18(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1202-1
Wang, X., Li, Z.-M., Li, Q., Shi, M., Bao, L., Xu, D., & Li, Z. (2019). Purification and biochemical characterization of FrsA protein from Vibrio vulnificus as an esterase. PLoS ONE, 14(4), e0215084. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0215084
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227(5259), 680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Dherbécourt, J., Falentin, H., Canaan, S., & Thierry, A. (2008). A genomic search approach to identify esterases in Propionibacterium freudenreichii involved in the formation of flavour in Emmental cheese. Microbial Cell Factories, 7, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-7-16
Kademi, A., Ait-Abdelkader, N., Fakhreddine, L., & Baratti, J. (2000). Purification and characterization of a thermostable esterase from the moderate thermophile Bacillus circulans. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 54(2), 173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000353
Zhang, Y. J., Chen, C. S., Liu, H. T., Chen, J. L., Xia, Y., & Wu, S. J. (2019). Purification, identification and characterization of an esterase with high enantioselectivity to (S)-ethyl indoline-2-carboxylate. Biotechnology Letters, 41, 1223–1232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02727-w
Masomian, M., Rahaman, R., Salleh, A., & Basri, M. (2016). Analysis of comparative sequence and genomic data to verify phylogenetic relationship and explore a new subfamily of bacterial lipases. PLoS ONE, 11(3), e0149851. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149851
Vinay Kumar, D., Lee, C., & Jang, S.-H. (2018). Organic solvent-tolerant esterase from Sphingomonas glacialis based on amino acid compositionanalysis: cloning and characterization of EstSP2. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28, 1502–1510. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1806.06032
Bourne, P. C., Isupov, M. N., & Littlechild, J. A. (2000). The atomic-resolution structure of a novel bacterial esterase. Structure, 8, 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00090-3
Dröge, M. J., Bos, R., & Quax, W. J. (2001). Paralogous gene analysis reveals a highly enantioselective 1,2-O-isopropylideneglycerol caprylate esterase of Bacillus subtilis. European Journal of Biochemistry, 268(11), 3332–3338. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2001.02238.x
Schmidt, M., Henke, E., Heinze, B., Kourist, R., Hidalgo, A., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2007). A versatile esterase from Bacillus subtilis: Cloning, expression characterization, and its application in biocatalysis. Biotechnology Journal, 2(2), 249–253. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.200600174
Fazaeli, A., Golestani, A., Lakzaei, M., Rasi Varaei, S. S., & Aminian, M. (2019). Expression optimization, purification, and functional characterization of cholesterol oxidase from Chromobacterium sp. DS1. PLoS ONE, 14(2), e0212217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212217
Rosano, G. L., & Ceccarelli, E. A. (2014). Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
Olusesan, A. T., Azura, L. K., Forghani, B., Bakar, F. A., Mohamed, A. K. S., Radu, S., & Saari, N. (2011). Purification, characterization and thermal inactivation kinetics of a non-regioselective thermostable lipase from a genotypically identified extremophilic Bacillus subtilis NS 8. New Biotechnology, 28(6), 738–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2011.01.002
Calo-Mata, P., Böhme, K., Carrera, M., Caamaño-Antelo, S., Gallardo, J., Barros-Velázquez, J., & Cañas, B. (2016). Bacterial identification by LC-ESI-IT-MS/MS. In Microbes in the spotlight: Recent progress in the understanding of beneficial and harmful microorganisms (pp. 160–164). Universal Publishers.
Ghori, I., Iqbal, M., & Hameed, A. (2011). Characterization of a novel lipase from Bacillus sp. isolated from tannery wastes. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology Publication of the Brazilian Society for Microbiology, 42, 22–29. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822011000100003
Noby, N., Hussein, A., Saeed, H., & Embaby, A. M. (2020). Recombinant cold-adapted halotolerant, organic solvent-stable esterase (estHIJ) from Bacillus halodurans. Analytical Biochemistry, 591, 113554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.113554
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funding from Department of Science and Technology (DST) under INSPIRE Fellowship scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The implementation of work and preparation of the manuscript was done by ‘First author.’ The design of the work plan and correction of the manuscript were done by ‘Corresponding author.’
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Research Involving Human/Animal Participants
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soumya, P., Kochupurackal, J. An Esterase with Increased Acetone Tolerance from Bacillus subtilis E9 over Expressed in E. coli BL21 Using pTac Bs-est Vector. Mol Biotechnol 64, 814–824 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00458-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00458-4