Abstract
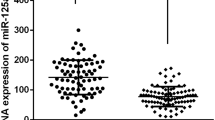
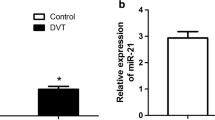
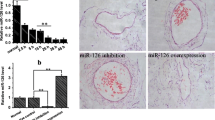
Lower extremity deep venous thrombosis (LEDVT) is a venous reflux disorder caused by abnormal coagulation of blood. LEDVT can obstruct the lumen and LEDVT is the third vascular disease after cerebrovascular diseases and coronary artery diseases. miRNAs are associated with thrombosis, and miR-185 was reported to affect the proliferation and apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells by regulating receptor of advanced glycation end products (RAGE). However, no study has reported the effect of miR-185 on LEDVT. Here, we studied the effects of miR-185 on the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in the LEDVT cells. The results showed that miR-185 promotes cell proliferation through activating the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways and then inhibits tissue factor and fibrin expression to reduce thrombosis. In short, our study provides new ideas and a theoretical basis for research on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of LEDVT.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Patterson, B., Hinchliffe, R., Loftus, I., Thompson, M., & Holt, P. (2010). Indications for catheter-directed thrombolysis in the management of acute proximal deep venous thrombosis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 30, 669–674.
Avila, L., Amiri, N., De, R., Vincelli, J., Pullenayegum, E., Williams, S., & Brandao, L. (2021). Characteristics of upper and lower extremity deep vein thrombosis and predictors of post-thrombotic syndrome in children. Blood Advances. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004727
Suzuki, K., Shibasaki, S., Nakauchi, M., Nakamura, K., Akimoto, S., Tanaka, T., Kikuchi, K., Inaba, K., Uyama, I., & Suda, K. (2021). Impact of routine preoperative sonographic screening with early intervention for deep venous thrombosis in lower extremities on preventing postoperative venous thromboembolism in patients with gastric cancer scheduled for minimally invasive surgery. Langenbeck’s Archives of Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02315-5
Long, B., & Koyfman, A. (2017). Best clinical practice: Controversies in outpatient management of acute pulmonary embolism. The Journal of Emergency Medicine, 52, 668–679.
Hisada, Y., & Mackman, N. (2017). Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis. Blood, 130, 1499–1506.
Sun, S., Chai, S., Zhang, F., & Lu, L. (2020). Overexpressed microRNA-103a-3p inhibits acute lower-extremity deep venous thrombosis via inhibition of CXCL12. IUBMB Life, 72, 492–504.
Sun, Y., Wu, R., Liu, W., & Huang, J. (2008). Analysis of the dynamic change of TF, TFPI and IL-1beta in plasma of patients with acute leukemia. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 16, 493–496.
Unruh, D., Sagin, F., Adam, M., Van Dreden, P., Woodhams, B., Hart, K., Lindsell, C., Ahmad, S., & Bogdanov, V. (2015). Levels of alternatively spliced tissue factor in the plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer may help predict aggressive tumor phenotype. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 22, S1206-1211.
Liu, H., Sun, N., Huang, Y., Su, X., Deng, D., & Cheng, P. (2018). Clinical significance of detecting tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in thalassemia patients. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 26, 1471–1476.
Winckers, K., ten Cate, H., & Hackeng, T. (2013). The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in atherosclerosis and arterial thrombosis. Blood Reviews, 27, 119–132.
Ziegenhain, C., Vieth, B., Parekh, S., Reinius, B., Guillaumet-Adkins, A., Smets, M., Leonhardt, H., Heyn, H., Hellmann, I., & Enard, W. (2017). Comparative analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing methods. Molecular Cell, 65, 631-643.e634.
Hosen, M., Li, Q., Liu, Y., Zietzer, A., Maus, K., Goody, P., Uchida, S., Latz, E., Werner, N., Nickenig, G., & Jansen, F. (2021). PUNISHERCAD increases the long noncoding RNA in small extracellular vesicles and regulates endothelial cell function via vesicular shuttling. Molecular Therapy. Nucleic Acids, 25, 388–405.
Abe, H., Kunita, A., Otake, Y., Kanda, T., Kaneda, A., Ushiku, T., & Fukayama, M. (2021). Virus–host interactions in carcinogenesis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma: Potential roles of lost ARID1A expression in its early stage. PLoS ONE, 16, e0256440.
Saravanan, S., Thirugnanasambantham, K., Hanieh, H., Karikalan, K., Sekar, D., Rajagopalan, R., & Hairul Islam, V. (2015). miRNA-24 and miRNA-466i-5p controls inflammation in rat hepatocytes. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 12, 113–115.
Wen, Z., Zhang, J., Tang, P., Tu, N., Wang, K., & Wu, G. (2018). Overexpression of miR-185 inhibits autophagy and apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons by regulating the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Molecular Medicine Reports, 17, 131–137.
Zhang, Q., Chen, B., Liu, P., & Yang, J. (2018). XIST promotes gastric cancer (GC) progression through TGF-β1 via targeting miR-185. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 119, 2787–2796.
He, J., Tian, N., Yang, Y., Jin, L., Feng, X., Hua, J., Lin, S., Wang, B., Li, H., & Wang, J. (2017). miR-185 enhances the inhibition of proliferation and migration induced by ionizing radiation in melanoma. Oncology Letters, 13, 2442–2448.
Jiang, H., Zhang, J., Du, Y., Jia, X., Yang, F., Si, S., Wang, L., & Hong, B. (2015). microRNA-185 modulates low density lipoprotein receptor expression as a key posttranscriptional regulator. Atherosclerosis, 243, 523–532.
Liu, X., Wang, D., Yang, X., & Lei, L. (2018). Huayu Tongmai Granules protects against vascular endothelial dysfunction via up-regulating miR-185 and down-regulating RAGE. Bioscience Reports, 38, 674.
Ni, W., Xia, Y., Bi, Y., Wen, F., Hu, D., & Luo, L. (2019). FoxD2-AS1 promotes glioma progression by regulating miR-185-5P/HMGA2 axis and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Aging, 11, 1427–1439.
Allaqaband, S., Solis, J., Kazemi, S., & Bajwa, T. (2006). Endovascular treatment of peripheral vascular disease. Current Problems in Cardiology, 31, 711–760.
Fink, E. (2015). Health behavior from the gender perspective–The concept of “doing genders” and the perspective of intersectionality as an explanation. Gesundheitswesen (Bundesverband der Arzte des Offentlichen Gesundheitsdienstes (Germany)), 77, 880.
Pande, M., Bondy, M., Do, K., Sahin, A., Ying, J., Mills, G., Thompson, P., & Brewster, A. (2014). Association between germline single nucleotide polymorphisms in the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, obesity, and breast cancer disease-free survival. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 147, 381–387.
Xu, N., Lao, Y., Zhang, Y., & Gillespie, D. (2012). Akt: A double-edged sword in cell proliferation and genome stability. Journal of Oncology, 12, 951724.
Kaidanovich-Beilin, O., & Woodgett, J. (2011). GSK-3: Functional insights from cell biology and animal models. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 4, 40.
Beurel, E., Grieco, S., & Jope, R. (2015). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 148, 114–131.
Liang, M., Liu, J., Ji, H., Chen, M., Zhao, Y., Li, S., Zhang, X., & Li, J. (2015). A Aconitum coreanum polysaccharide fraction induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells via pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 (PTTG1)-mediated suppression of the P13K/Akt and activation of p38 MAPK signaling pathway and displays antitumor activity in vivo. Tumour Biology, 36, 7085–7091.
Gonzalez-Robayna, I., Falender, A., Ochsner, S., Firestone, G., & Richards, J. (2000). Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates phosphorylation and activation of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) and serum and glucocorticoid-lnduced kinase (Sgk): evidence for A kinase-independent signaling by FSH in granulosa cells. Molecular Endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.), 14, 1283–1300.
Dogra, C., Changotra, H., Wergedal, J., & Kumar, A. (2006). Regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathways in dystrophin-deficient skeletal muscle in response to mechanical stretch. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 208, 575–585.
Wenzel, S., Tyurina, Y., Zhao, J., StCroix, C., Dar, H., Mao, G., Tyurin, V., Anthonymuthu, T., Kapralov, A., Amoscato, A., Mikulska-Ruminska, K., Shrivastava, I., Kenny, E., Yang, Q., Rosenbaum, J., Sparvero, L., Emlet, D., Wen, X., Minami, Y., … Kagan, V. (2017). PEBP1 wardens ferroptosis by enabling lipoxygenase generation of lipid death signals. Cell, 171, 628–641.
Atkinson, J., Rank, K., Zeng, Y., Capen, A., Yadav, V., Manro, J., Engler, T., & Chedid, M. (2015). Activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway for the treatment of melanoma-application of LY2090314, a novel selective inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3. PLoS ONE, 10, e0125028.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Research Projects Fund in Colleges and Universities of Anhui Province (Grant No. KJ2019A0327).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All experimental protocols were conducted in accordance with the principles and procedures outlined in the “Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory animals” and approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, R., Zhu, W., Sun, H. et al. Study on the Effect and Mechanism of miR-185 on Lower Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis. Mol Biotechnol 64, 330–337 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00412-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00412-w