Abstract
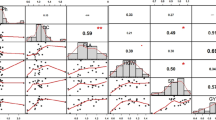
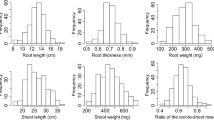
Drought is one of the important constraints affecting rice productivity worldwide. The vigorous shoot and deep root system help to improve drought resistance. In present era, genome-wide association study (GWAS) is the preferred method for mapping of QTLs for complex traits such as root and drought tolerance traits. In the present study, 114 rice genotypes were evaluated for various root and shoot traits under water stress conditions. All genotypes showed a significant amount of variation for various root and shoot traits. Correlation analysis revealed that high dry shoot weight and fresh shoot weight is associated with root length, root volume, fresh root weight and dry root weight. A total of 11 significant marker-trait associations were detected for various root, shoot and drought tolerance traits with the coefficient of determination (R2) ranging from 18.99 to 53.41%. Marker RM252 and RM212 showed association with three root traits which suggests their scope for improvement of root system. In the present study, a novel QTL was detected for root length associated with RM127, explaining 19.30% of variation. The marker alleles with increasing phenotypic effects for root and drought-tolerant traits can be exploited for improvement of root and drought tolerance traits using marker-assisted selection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, S., Dwivedi, S. K., Basu, S., Kumar, G., Mishra, J. S., Koley, T. K., Rao, K. K., Choudhary, A. K., Mondal, S., Kumar, S., Bhakta, N., Bhatt, B. P., Paul, R. K., & Kumar, A. (2020). Anatomical, agromorphological and physiological changes in rice under cumulative and stage specific drought conditions prevailed in eastern region of India. Field Crops Research, 245, 107658.
Yang, X., Wang, B., & Chen, L. (2019). The different influences of drought stress at the flowering stage on rice physiological traits, grain yield, and quality. Science and Reports, 9, 3742.
Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2014; Core Writing Team. In R. K. Pachauri, L. A. Meyer (Eds.) IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, p 151.
Trenberth, K. E., Dai, A., Schrier, G. V. D., Jones, P. D., Barichivich, J., Briffa, K. R., & Sheffield, J. (2014). Global warming and changes in drought. Nature Climate Change, 4, 17–22.
Zhang, J., Zhang, S., Cheng, M., Jiang, H., Zhang, X., Peng, C., Lu, X., Zhang, M., & Jin, J. (2018). Effect of drought on agronomic traits of rice and wheat: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 839.
Daryanto, S., Wang, L., & Jacinthe, P. A. (2017). Global synthesis of drought effects on cereal, legume, tuber and root crops production: A review. Agricultural Water Management, 179, 18–33.
Kim, W., Iizumi, T., Nishimori, M. (2019). Global patterns of crop production losses associated with droughts from 1983 to 2009. J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 1233–1244.
Kim, Y., Chung, Y. S., Lee, E., Tripathi, P., Heo, S., & Kim, K. H. (2020). Root response to drought stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Mol Sci, 21(4), 1513.
Ahmadi, N., Audebert, A., Bennett, M. J., Bishopp, A., de Oliveira, A. C., Courtois, B., Diedhiou, A., Diévart, A., Gantet, P., & Ghesquière, A. (2014). The roots of future rice harvests. Rice, 7, 29.
Dixit, S., Singh, A., & Kumar, A. (2014). Rice breeding for high grain yield under drought: A strategic solution to a complex problem. Int J Agron, 2014, 15.
Palta, J. A., & Yang, J. (2014). Crop root system behaviour and yield. Field Crops Res, 165, 1–4.
Canales, F. J., Nagel, K. A., Müller, C., Rispail, N., & Prats, E. (2019). Deciphering root architectural traits involved to cope with water deficit in Oat. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 1558.
Wasaya, A., Zhang, X., Fang, Q., & Yan, Z. (2018). Root phenotyping for drought tolerance: A review. Agronomy, 8(11), 241.
Comas, L. H., Becker, S. R., Cruz, V. M. V., Byrne, P. F., & Dierig, D. A. (2013). Root traits contributing to plant productivity under drought. Frontiers in Plant Science, 4, 442.
Uga, Y., Sugimoto, K., Ogawa, S., Rane, J., Ishitani, M., Hara, N., Kitomi, Y., Inukai, Y., Ono, K., & Kanno, N. (2013). Control of root system architecture by DEEPER ROOTING 1 increases rice yield under drought conditions. Nature Genetics, 45, 1097–1102.
Verma, H., Borah, J. L., & Sarma, R. N. (2019). Variability assessment for root and drought tolerance traits and genetic diversity analysis of rice germplasm using SSR markers. Science and Reports, 9, 16513.
Uga, Y., Kitomi, Y., Ishikawa, S., & Yano, M. (2015). Genetic improvement for root growth angle to enhance crop production. Breeding Science, 65(2), 111–119.
Vikram, P., Swamy, B., Dixit, S., Ahmed, H. U., Cruz, M. T. S., Singh, A. K., & Kumar, A. (2011). qDTY 1.1, a major QTL for rice grain yield under reproductive-stage drought stress with a consistent effect in multiple elite genetic backgrounds. BMC Genet, 12, 89.
Uga, Y., Okuno, K., & Yano, M. (2011). Dro1, a major QTL involved in deep rooting of rice under upland field conditions. J Expt Bot, 62(8), 2485–2494.
Muthu, V., Abbai, R., Nallathambi, J., Rahman, H., Ramasamy, S., & Kambale, R. (2020). Pyramiding QTLs controlling tolerance against drought, salinity, and submergence in rice through marker assisted breeding. PLoS One, 15(1), e0227421.
Anyaoha, C. O., Fofana, M., Gracen, V., Tongoona, P., & Mande, S. (2019). Introgression of two drought QTLs into FUNAABOR-2 early generation backcross progenies under drought stress at reproductive stage. Rice Science, 26(1), 32141.
Dharmappa, P. M., Doddaraju, P., Malagondanahalli, M. V., Rangappa, R. B., Mallikarjuna, N. M., Rajendrareddy, S. H., Ramanjinappa, R., Mavinahalli, R. P., Prasad, T. G., & Udayakumar, M. (2019). Introgression of root and water use efficiency traits enhances water productivity: An evidence for physiological breeding in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice, 12, 14.
Dixit, S., Singh, A., Sandhu, N., Bhandari, A., Vikram, P., & Kumar, A. (2017). Combining drought and submergence tolerance in rice: Marker assisted breeding and QTL combination effects. Molecular Breeding, 37, 143.
Wijerathna, Y. M. A. M. (2015). Marker Assisted Selection: Biotechnology Tool for Rice Molecular Breeding. Adv Crop Sci Tech, 3, 4.
Bernardo, R. (2008). Molecular markers and selection for complex traits in plants: Learning from the last 20 years. Crop Science, 48, 1649–1664.
Bernier, J., Kumar, A., Venuprasad, R., Spaner, D., Verulkar, S., Mandal, N. P., Sinha, P. K., Peeraju, P., Dongre, P. R., Mahto, R. N., & Atlin, G. (2009). Characterization of the effect of a QTL for drought resistance in rice, qtl12.1, over a range of environments in the Philippines and eastern India. Euphytica, 166, 207–217.
Hoang, G. T., Van Dinh, L., & Nguyen, T. T. (2019). Genome-wide association study of a panel of vietnamese rice landraces reveals new QTLs for tolerance to water deficit during the vegetative phase. Rice, 12, 4.
Korte, A., & Farlow, A. (2013). The advantages and limitations of trait analysis with GWAS: A review. Plant Methods, 9, 29.
Swamy, B. P. M., Shamsudin, N. A. A., Rahman, S. N. A., Mauleon, R., Ratnam, W., Sta Cruz, M. T., & Kumar, A. (2017). Association mapping of yield and yield-related traits under reproductive stage drought stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice, 10, 21.
Hirschhorn, J., & Daly, M. (2005). Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nature Reviews Genetics, 6, 95–108.
Myers, N. (1988). Threatened biotas: “hots spots” in tropical forests. The Environmentalist, 8(3), 187–208.
Travis, A. J., Norton, G. J., Datta, S., Sarma, R., Dasgupta, T., Savio, F. L., Macaulay, M., Hedley, P. E., McNally, K. L., Sumon, M. H., Islam, M. R., & Price, A. H. (2015). Assessing the genetic diversity of rice originating from Bangladesh, Assam and West Bengal. Rice, 8(1), 1–9.
Civán, P., Craig, H., Cox, C. J., & Brown, T. A. (2015). Three geographically separate domestications of Asian rice. Nat Plants, 1, 15164.
Kim, H. J., Jung, J., Singh, N., Greenberg, A., Doyle, J. J., Tyagi, W., Chung, J. W., Kimball, J., Hamilton, R. S., & McCouch, S. R. (2016). Population dynamics among six major groups of the Oryzarufipogon species complex, wild relative of cultivated Asian rice. Rice, 9, 56.
Norton, G. J., Travis, A. J., Douglas, A., Fairley, S., De PaivaAlves, E., Ruang-areerate, P., Naredo, M. E. B., McNally, K. L., Hossain, M., Islam, M. R., & Price, A. H. (2018). Genome wide association mapping of grain and straw biomass traits in the rice bengal and assam aus panel (BAAP) grown under alternate wetting and drying and permanently flooded irrigation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1223.
Verma, H., Devi, K., Baruah, A. R., & Sarma, R. N. (2020). Relationship of root aquaporin genes, OsPIP1;3, OsPIP2;4, OsPIP2;5, OsTIP2;1 and OsNIP2;1 expression with drought tolerance in rice. Indian J Genet, 80(1), 50–57.
Umakanth, B., Vishalakshi, B., Kumar, P. S., Devi, S. J. S. R., Bhadana, V. P., Senguttuvel, P., Kumar, S., Sharma, S. K., Sharma, P. K., Prasad, M. S., & Madhav, M. S. (2017). Diverse rice landraces of North-East India enables the identification of novel genetic resources for Magnaporthe resistance. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1500.
McNally, K., Childs, K. L., Bohnert, R., Davidson, R. M., & Zhao, K. (2009). Genome wide SNP variation reveals relationships among landraces and modern varieties of rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 12273–12278.
Yadav, S., Sandhu, N., Singh, V. K., Catolos, M., & Kumar, A. (2019). Genotyping-by-sequencing based QTL mapping for rice grain yield under reproductive stage drought stress tolerance. Scientific reports, 9, 14326.
IRRI. (2002). Standard evaluation system for rice. International Rice Research Institute.
Reynolds, S. G. (1970). The gravimetric method of soil moisture determination, Part 1 A study of equipments and methodological problems. J Hydrology, 11, 258–273.
Plaschke, J., Ganal, M. W., & Röder, M. S. (1995). Detection of genetic diversity in closely related bread wheat using microsatellite markers. TAG. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. , 91, 1001–1007.
Panaud, O., Chen, X., McCouch, S. R. (1996). Frequency of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L). Genome, 38(l), 1170–1176
Sangeetha, A., Malhotra, P. K., Bhatia, V. K., & Rajendra, P. (2008). Statistical package for agricultural research (SPAR 2.0). J Indian Soc Agric Stat, 62, 65–74.
Wei, T., & Simko, V. (2017). R package “corrplot”: visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.84). https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/corrplot/corrplot.pdf.
Neuwirth, E. (2014). Package ‘RColorBrewer’. https://cran.rproject.org/web/packages/RColorBrewer/RColorBrewer.pdf.
Bradbury, P. J., Zhang, Z., Kroon, D. E., Casstevens, T. M., Ramdoss, Y., & Buckler, E. S. (2007). TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics, 23, 2633–2635.
Zhang, Z., Ersoz, E., Lai, C. Q., Todhunter, R. J., Tiwari, H. K., Gore, M. A., Bradbury, J., Yu, J., Arnett, D. K., Ordovas, J. M., & Buckler, E. (2010). Mixed linear model approach adapted for genome-wide association studies. Nature Genetics, 42, 355–360.
Rincent, R., Moreau, L., Monod, H., Kuhn, E., Melchinger, A., Malvar, R. A., MorenoGonzalez, J., Nicolas, S., Madur, D., Combes, V., Dumas, F., Altmann, T., Brunel, D., Ouzunova, M., Flament, P., Dubreuil, P., Charcosset, A., & MaryHuard, T. (2014). Recovering power in association mapping panels with variable levels of linkage disequilibrium. Genetics, 197, 375–387.
Das, G., Patra, J. K., & Baek, K. H. (2017). Insight into MAS: A molecular tool for development of stress resistant and quality of rice through gene stacking. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 985.
Balasubramanian, S., Schwartz, C., Singh, A., Warthmann, N., Kim, M. C., Maloof, J. N., Loudet, O., Trainer, G. T., Dabi, T., & Borevitz, J. O. (2009). QTL mapping in new Arabidopsis thaliana advanced intercross-recombinant inbred lines. PLoS One, 4(2), e4318.
Ibrahim, A. K., Zhang, L., Niyitanga, S., Afzal, M. Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., & Qi, J. (2020). Principles and approaches of association mapping in plant breeding. Tropical Plant Biol, 13, 212–224.
Zhu, C., Gore, M., Buckler, E. S., & Yu, J. (2008). Status and prospects of association mapping in plants. The plant genome, 1, 5–20.
Pritchard, J., Stephens, M., & Donnelly, P. (2000). Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics, 155, 945–959.
Yu, Y., Lee, H. O., Chin, J. H., Park, H. Y., & Yoo, S. C. (2017). The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Oryza sativa aus-type variety Nagina-22 (Poaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B: Resources, 2(2), 819–820.
Agrama, H. A., Eizenga, G. C., & Yan, W. (2007). Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Molecular Breeding, 19, 341–356.
Dixit, S., Swamy, B. P. M., Vikram, P., Ahmed, H. U., Cruz, M. T. S., Amante, M., Atri, D., Leung, H., & Kumar, A. (2012). Fine mapping of QTLs for rice grain yield under drought reveals sub-QTLs conferring a response to variable drought severities. TAG. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. , 125, 155–169.
Qu, Y., Ping, M., Hongliang, Z., Chen, Y., Gao, Y., Tian, Y., Wen, F., & Li, Z. (2008). Mapping QTLs of root morphological traits at different growth stages in rice. Genetica, 133, 187–200.
Xing, Z., Tan, F., Hua, P., Sun, L., Xu, G., & Zhang, Q. (2002). Characterization of the main effects, epistatic effects and their environmental interactions of QTLs on the genetic basis of yield traits in rice. TAG. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. , 105, 248–257.
Kamoshita, A., Wade, L. J., Ali, M. L., Pathan, M. S., Zjang, J., & Sarkarung, S. (2002). Mapping QTL for root morphology of a rice population adapted to rainfed lowland conditions. TAG. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. , 104, 880–893.
Prince, S. J., Beena, R., Gomez, S. M., Sentivel, S., & Babu, R. C. (2015). Mapping consistent rice (Oryza sativa L.) yield QTLs under drought stress in target rainfed environments. Rice, 8, 25.
Swamy, M. B. P., Vikram, P., Dixit, S., Ahmed, H. U., & Kumar, A. (2011). Meta-analysis of grain yield QTL identified during agricultural drought in grasses showed consensus. BMC Genomics, 12, 319.
Kanagaraj, P., Prince, K. S. J., Annie Sheeba, J., Biji, K. R., Paul, S. B., Senthil, A., & Chandra Babu, R. (2010). Microsatellite markers linked to drought resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Cursos e Congresos da Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, 98, 836–839.
Gomez, S. M., Boopathi, N. M., Kumar, S. S., Ramasubramanian, T., Chengsong, Z., Jeyaprakash, P., Senthil, A., & Babu, R. C. (2010). Molecular mapping and location of QTLs for drought-resistance traits in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) lines adapted to target environments. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 32, 355–364.
Zhao, X. Q., Xu, J. L., Zhao, M., Lafitte, R., Zhu, L. H., Fu, B. Y., Gao, Y. M., & Li, Z. K. (2008). QTLs affecting morpho-physiological traits related to drought tolerance detected in overlapping introgression lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Science, 174(6), 618–625.
Sabar, M., Shabir, G., Shah, S. M., Aslam, K., Naveed, S. A., & Arif, M. (2019). Identification and mapping of QTLs associated with drought tolerance traits in rice by a cross between Super Basmati and IR55419-04. Breeding Science, 69(1), 169–178.
Babu, R. C., Nguyen, B. D., Chamarerk, V., Shanmugasundaram, P., Chezhian, P., Jeyaprakash, P., Ganesh, S. K., Palchamy, A., Sadasivam, S., Sarkarung, S., Wade, L. J., & Nguyen, H. T. (2003). Genetic analysis of drought resistance in rice by molecular markers: Association between secondary traits and field performance. Crop Science, 43, 1457–1469.
Salunkhe, A. S., Poornima, R., Prince, K. S., Kanagaraj, P., Sheeba, J. A., Amudha, K., Suji, K. K., Senthil, A., & Babu, R. C. (2011). Fine mapping QTL for drought resistance traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using bulk segregant analysis. MolBiotechnol, 49(1), 90–95.
Sandhu, N., & Kumar, A. (2017). Bridging the rice yield gaps under drought: QTLs genes and their use in breeding programs. Agronomy, 7(2), 27.
Zheng, H. G., Babu, R. C., Pathan, M. S., Ali, L., Huang, N., Courtois, B., & Nguyen, H. T. (2000). Quantitative trait loci for root-penetration ability and root thickness in rice: Comparison of genetic backgrounds. Genome, 43(1), 53–61.
Singh, S., Pradhan, S. K., Singh, A. K., & Singh, O. N. (2012). Marker validation in recombinant inbred lines and random varieties of rice for drought tolerance. AJCS, 6(4), 606–612.
Zhao, Y., Jiang, C. H., Rehman, R. M. A., Zhang, H. L., Li, J., & Li, Z. C. (2019). Genetic analysis of roots and shoots in rice seedling by association mapping. Genes Genomics, 41, 95–105.
Lanceras, J. C., Pantuwan, G., Jongdee, B., & Toojinda, T. (2004). Quantitative trait loci associated with drought tolerance at reproductive stage in rice. Plant Physiology, 135(1), 384–399.
An, H., Liu, K., Wang, B., Tian, Y., Ge, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Genome-wide association study identifies QTLs conferring salt tolerance in rice. Plant Breeding, 139, 73–82.
Zheng, H., Wang, J., Zhao, H., Liu, H., Sun, J., Guo, J., & Zou, D. (2015). Genetic structure, linkage disequilibrium and association mapping of salt tolerance in japonica rice germplasm at the seedling stage. Molecular Breeding, 35, 152.
Xu, F., Bao, J., He, Q., & Park, Y. J. (2016). Genome-wide association study of eating and cooking qualities in different subpopulations of rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Genomics, 17, 633.
Zhong, M., Wang, L., Yuan, J., Luo, L., Xu, C., & He, Y. Q. (2011). Identification of QTL affecting protein and amino acid contents in rice. Rice Science, 18(3), 187–195.
Guo, L., Guo, W., Zhao, H., & Wang, J. (2015). Association mapping and resistant alleles’ analysis for japonica rice blast resistance. Plant Breeding, 134, 646–652.
Eizenga, G. C., Jia, M. H., Jackson, A. K., Boykin, D. L., Ali, M. L., Shakiba, E., Tran, N. T., McCouch, S. R., & Edwards, J. D. (2019). Validation of yield component traits identified by genome-wide association mapping in a tropical japonica × tropical japonica rice biparental mapping population. Plant Genome, 12, 180021.
Raju, B. R., Narayanaswamy, B. R., Mohankumar, M. V., Sumanth, K. K., Rajanna, M. P., Mohanraju, B., Udayakumar, M., & Sheshshayee, M. S. (2014). Root traits and cellular level tolerance hold the key in maintaining higher spikelet fertility of rice under water limited conditions. Functional Plant Biology, 41(9), 930–939.
Courtois, B., Audebert, A., & Dardou, A. (2013). Genome-wide association mapping of root traits in a japonica rice panel. PLoS One, 8, e78037.
Henry, A., Gowda, V. R. P., Torres, R., Mcnally, K., & Serraj, R. (2011). Variation in root system architecture and drought response in rice (Oryza sativa): Phenotyping of the Oryza SNP panel in rainfed lowland fields. Field Crops Research, 120(2), 205–214.
Gowda, V. R. P., Henry, A., Yamauchi, A., Shashidhar, H. E., & Serraj, R. (2011). Root biology and genetic improvement for drought avoidance in rice. Field Crops Research, 122(1), 1–13.
Wasson, A. P., Richards, R. A., Chatrath, R., Misra, S. C., Prasad, S. V., & Rebetzke, G. J. (2012). Traits and selection strategies to improve root systems and water uptake in water-limited wheat crops. Journal of Experimental Botany, 63, 3485–3498.
Abd Allah, A., Badawy, S. A., & Zayed, & B., El-Gohary, A. . (2010). The role of root system traits in the drought tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.). World Acad Sci Eng Technol, 68, 1378–1382.
Kirkegaard, J. A., Lilley, J. M., Howe, G. N., & Graham, J. M. (2007). Impact of subsoil water use on wheat yield. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 58, 303–315.
DeDorlodot, S., Forster, B., Pagès, L., Price, A., Tuberosa, R., & Draye, X. (2007). Root system architecture: Opportunities and constraints for genetic improvement of crops. Trends in Plant Science, 12, 474–481.
Phung, N. T. P., Mai, C. D., & Hoang, G. T. (2016). Genome-wide association mapping for root traits in a panel of rice accessions from Vietnam. BMC Plant Biology, 16, 64.
Kashiwagi, J., Krishnamurthy, L., Upadhyaya, H., Krishna, H., Chandra, S., & Vadez, V. (2005). Genetic variability of drought-avoidance root traits in the mini-core germplasm collection of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Euphytica, 146, 213–222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, H., Sarma, R.N. Identification of Markers for Root Traits Related to Drought Tolerance Using Traditional Rice Germplasm. Mol Biotechnol 63, 1280–1292 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00380-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00380-1