Abstract
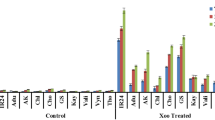
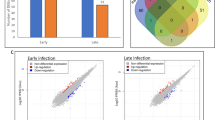
The bacterial leaf blight in rice caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) affects crop losses worldwide. In spite of developing resistant varieties by introgressing different Xa genes, the occurrence of diseases is evident. Here we report identification of several genes that are associated with improved plant immunity against Xoo in a resistant genotype BPT-5204 in comparison with susceptible genotype TN-1. The RNA sequencing information was developed to identify the genes that could provide durable resistance in rice. Xoo-resistant rice genotype BPT-5204 with Xa 5, 13 and 21 genes is compared with sensitive Taichung Native 1 (TN-1) to identify the genetic pathways and gene networks involved in resistance mechanisms. The higher levels of salicylic acid resulted in upregulation of many pathogenesis-related (PR) and redox protein encoding transcripts which resulted in higher hypersensitive response in BPT-5204. Many Serine/threonine protein kinase, leucine-rich repeat (LRR) transmembrane protein kinase, protein kinase family genes, Wall-associated kinase (WAK) were upregulated that resulted in activation of bZIP, WRKY, MYB, DOF and HSFs transcription factors that are associated with improved plant immunity. The study provided roles of many genes and their associated plant immunity pathways that can be used for developing resistant rice cultivars.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, W., Liu, J., Triplett, L., Leach, J. E., & Wang, G.-L. (2014). Novel insights into rice innate immunity against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 52, 213–241.
Bogdanove, A. J., Schornack, S., & Lahaye, T. (2010). TAL effectors: Finding plant genes for disease and defense. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 13(4), 394–401.
ZhiYuan, J., ChunLian, W., & KaiJun, Z. (2018). Rice routes of countering Xanthomonas oryzae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3008.
Suh, J. P., Jeung, J. U., Noh, T. H., Cho, Y. C., Park, S. H., Park, H. S., Shin, M. S., Kim, C. K., & Jena, K. K. (2013). Development of breeding lines with three pyramided resistance genes that confer broad-spectrum bacterial blight resistance and their molecular analysis in rice. Rice, 6(1), 5.
Kottapalli, K. R., Narasu, M. L., & Jena, K. K. (2010). Effective strategy for pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes into fine grain rice cultivar, Samba Mahsuri, using sequence tagged site markers. Biotechnology Letters, 2(7), 989–996.
Singh, A. K., Gopalakrishnan, S., Singh, V. P., Prabhu, K. V., Mohapatra, T., Singh, N. K., Sharma, T. R., Nagarajan, M., Vinod, K. K., Singh, D., et al. (2011). Marker assisted selection: A paradigm shift in Basmati breeding. Indian Journal of Genetics and Plant Breeding, 71(2), 1–9.
Zhang, S., Song, W. Y., Chen, L., Ruan, D., Taylor, N., Ronald, P., Beachy, R., & Fauquet, C. (1998). Transgenic elite Indica rice varieties, resistant to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Molecular Breeding, 4, 551–558.
Tu, J., Ona, I., Zhang, Q., Mew, T. W., Khush, G. S., & Datta, S. K. (1998). Transgenic rice variety ‘IR72’ with Xa21 is resistant to bacterial blight. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 97, 31–36.
Yoshimura, S., Yamanouchi, U., Katayose, Y., Toki, S., Wang, Z. X., Kono, I., Kurata, N., Yano, M., Iwata, N., & Sasaki, T. (1998). Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95(4), 1663–1668.
Hwang, S. H., Sl, K., Jang, J. Y., Fang, I. L., Lee, H., Choi, C., Park, S., Ahn, I., Bae, S., & Hwang, D. J. (2016). OsWRKY51, a rice transcription factor, functions as a positive regulator in defense response against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Cell Reports, 35, 1975–1985.
Wang, C., Tariq, R., Ji, Z., Wei, Z., Zheng, K., Mishra, R., & Zhao, K. (2019). Transcriptome analysis of a rice cultivar reveals the differentially expressed genes in response to wild and mutant mutant strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Scientific Reports, 9, 3757.
Cheng, X. J., He, B., Chen, L., Xiao, S. Q., Fu, J., Chen, Y., Yu, T. Q., Cheng, Z. Q., & Feng, H. (2016). Transcriptome analysis confers a complex disease resistance network in wild rice Oryza meyeriana against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Scientific Reports, 6, 38215.
Djedatin, G., Ndjiondjop, M.-N., Sanni, A., Lorieux, M., Verdier, V., & Ghesquiere, A. (2016). Identification of novel major and minor QTLs associated with Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (African strains) resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice, 9, 18.
Ke, Y., Hui, S., & Yuan, M. (2017). Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae inoculation and growth rate on rice by leaf clipping method. Bio-Protocol, 7, 1–7.
Defraia, C. T., Schmelz, E. A., & Mou, Z. (2008). A rapid biosensor-based method for quantification of free and glucose-conjugated salicylic acid. Plant Methods, 4, 1–11.
Rio, D. C., Ares, M. J., Hannon, G. J., & Nilsen, T. W. (2010). Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, pdb.prot5439.
Pertea, M., Pertea, G. M., Antonescu, C. M., Chang, T. C., Mendell, J. T., & Salzberg, S. L. (2015). StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nature Biotechnology, 33(3), 290–295.
Liu, L., Mei, Q., Yu, Z., Sun, T., Zhang, Z., & Chen, M. (2013). An integrative bioinformatics framework for genome-scale multiple level network reconstruction of rice. Journal of Integrative Bioinformatics, 10(2), 223.
Du, Z., Zhou, X., Ling, Y., Zhang, Z., & Su, Z. (2010). agriGO: A GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community. Nucleic Acids Research, 38(Web Server issue), W64–W70.
Thimm, O., Bläsing, O., Gibon, Y., Nagel, A., Meyer, S., Krüger, P., Selbig, J., Müller, L. A., Rhee, S. Y., & Stitt, M. (2004). MAPMAN: A user-driven tool to display genomics data sets onto diagrams of metabolic pathways and other biological processes. Plant Journal, 37(6), 914–939.
Tsuda, K., & Katagiri, F. (2010). Comparing signaling mechanisms engaged in pattern-triggered and effector-triggered immunity. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 13(4), 459–465.
Vemanna, R. S., Bakade, R., Bharti, P., Kumar, M. K. P., Sreeman, S. M., Senthil-Kumar, M., & Makarla, U. (2019). Cross-talk signaling in rice during combined drought and bacterial blight stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 193.
Kumar, S. V. (2016). Pyramiding of blast resistance genes in to elite rice cultivars.
Yang, D.-L., Yang, Y., & He, Z. (2013). Roles of plant hormones and their interplay in rice immunity. Molecular Plant, 6, 675–685.
Ponciano, G., Yoshikawa, M., Lee, J. L., Ronald, P. C., & Whalen, M. C. (2006). Pathogenesis-related gene expression in rice is correlated with developmentally controlled Xa21-mediated resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 69, 131–139.
Narsai, R., Wang, C., Chen, J., Wu, J., Shou, H., & Whelan, J. (2013). Antagonistic, overlapping and distinct responses to biotic stress in rice (Oryza sativa) and interactions with abiotic stress. BMC Genomics, 14, 93.
Cheval, C., Aldon, D., Galaud, J. P., & Ranty, B. (2013). Calcium/calmodulin-mediated regulation of plant immunity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta—Molecular Cell Research, 1833(7), 1766–1771.
Mur, L. A. J., Kenton, P., Lloyd, A. J., Ougham, H., & Prats, E. (2008). The hypersensitive response; The centenary is upon us but how much do we know? Journal of Experimental Botany, 59(3), 501–520.
Gullner, G., Komives, T., Király, L., & Schröder, P. (2018). Glutathione S-transferase enzymes in plant–pathogen interactions. Frontiers in plant science, 9, 1836.
Jones, J. D. G., & Dangl, J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature, 444, 323–329.
Dodds, P. N., & Rathjen, J. P. (2010). Plant immunity: Towards an integrated view of plant pathogen interactions. Nature Reviews Genetics, 11(8), 539–548.
McHale, L., Tan, X., Koehl, P., & Michelmore, R. W. (2006). Plant NBS-LRR proteins: Adaptable guards. Genome Biology, 7(4), 212.
Tameling, W. I. L., Vossen, J. H., Albrecht, M., Lengauer, T., Berden, J. A., Haring, M. A., Cornelissen, B. J. C., & Takken, F. L. W. (2006). Mutations in the NB-ARC domain of I-2 that impair ATP hydrolysis cause autoactivation. Plant Physiology, 140(4), 1233–1245.
Oliva, R., Ji, C., Atienza-Grande, G., Huguet-Tapia, J. C., Perez-Quintero, A., Li, T., Eom, J. S., Li, C., Nguyen, H., Liu, B., et al. (2019). Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nature Biotechnology, 37(11), 1344–1350.
Ramu, V., Oh, S., Lee, H.-K., Nandety, R. S., Oh, Y., Lee, S., Nakashima, J., Tang, Y., Senthil-Kumar, M., & Mysore, K. S. (2020). A novel role of salt and drought induced RING 1 protein in modulating plant defense against hemibiotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions: MPMI, 34(3), 297–308.
Pooja, S., Sweta, K., Mohanapriya, A., Sudandiradoss, C., Siva, R., Gothandam, K. M., & Babu, S. (2015). Homotypic clustering of OsMYB4 binding site motifs in promoters of the rice genome and cellular-level implications on sheath blight disease resistance. Gene, 561(2), 209–218.
Cao, W. L., Chu, R. Z., Zhang, Y., Luo, J., Su, Y. Y., Xie, L. J., Zhang, H. S., Wang, J. F., & Bao, Y. M. (2015). OsJAMyb, a R2R3-type MYB transcription factor, enhanced blast resistance in transgenic rice. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 92, 154–160.
Yin, Y., Zhu, Q., Dai, S., Lamb, C., & Beachy, R. N. (1997). RF2a, a bZIP transcriptional activator of the phloem-specific vice tungro bacilliform virus promoter, functions in vascular development. EMBO Journal, 16(17), 5247–5259.
Nakashita, H., Yasuda, M., Nitta, T., Asami, T., Fujioka, S., Arai, Y., Sekimata, K., Takatsuto, S., Yamaguchi, I., & Yoshida, S. (2003). Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. The Plant Journal: For Cell and Molecular Biology, 33(5), 887–898.
Liao, H., Xiao, X., Li, X., Chen, Y., Fu, X., Lin, D., Niu, X., Chen, Y., & He, C. (2016). OsBAK1 is involved in rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 10, 75–82.
Li, D., Wang, L., Wang, M., Xu, Y.-Y., Luo, W., Liu, Y.-J., Xu, Z.-H., Li, J., & Chong, K. (2009). Engineering OsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 7, 791–806.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by RCB core grant, Ramanujan fellowship (SB/S2/RJN-046/2016) to VSR. GP acknowledges CSIR-UGC fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
Research involves rice plants and do not involve any human participants and/or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakade, R., Ingole, K.D., Deshpande, S. et al. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Rice Resistant and Susceptible Genotypes to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Identifies Novel Genes to Control Bacterial Leaf Blight. Mol Biotechnol 63, 719–731 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00338-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00338-3