Abstract
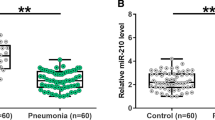
This study designed to investigate the potential role of lncRNA NEAT1/miR-146b in infantile pneumonia. In this study, 58 children with pneumonia and 58 healthy children collected for routine examination from December 2016 to January 2019. The lncRNA NEAT1 and miR-146b expression levels were detected by qPCR in both groups. The pneumonia model was established by inducing human embryonic lung fibroblasts HFL1 with LPS, and then transfected with lncRNA NEAT1 inhibition and miR-146b over-expression vector to observe the effect on cell viability and apoptosis after induction. Starbase predicted the binding site between lncRNA NEAT1 and miR-146b, and the targeted relationship between them was detected by dual luciferase reporter gene. The relative expression of lncRNA NEAT1 in serum of infantile pneumonia was up-regulated. Knocking down lncRNA NEAT1 promotes cell growth and reduces apoptosis in LPS-induced HFL1 cells. Results showed that the fluorescence activity of lncRNA NEAT1 obviously reduced when combined with miR-146b. In conclusion, the relative expression of miR-146b in serum of infantile pneumonia decreased, and over-expressing it could promote LPS-induced cell viability and reduce apoptosis. Taken together, this study demonstrated that the lncRNA NEAT1 regulates infantile pneumonia by sponging miR-146b.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cilloniz, C., Martin-Loeches, I., Garcia-Vidal, C., San Jose, A., & Torres, A. (2016). Microbial etiology of pneumonia: Epidemiology, diagnosis and resistance patterns. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12), 2120
Li, W., Ban, C., Zhang, J., Hu, Y., Han, B., & Han, B. (2017). Correlation study of cough variant asthma and mycoplasma pneumonia infection in children. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 30(3), 1099–1102
Hooven, T. A., & Polin, R. A. (2017). Pneumonia. Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine, 22(4), 206–213
Mandell, L. A. (2015). Community-acquired pneumonia: An overview. Postgraduate Medicine, 127(6), 607–615
Chu, C., Lei, X., & Li, Y. (2019). High expression of miR-222-3p in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Italian Journal of Pediatrics, 45(1), 163
Qian, X., Zhao, J., Yeung, P. Y., Zhang, Q. C., & Kwok, C. K. (2019). Revealing lncRNA structures and interactions by sequencing-based approaches. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 44(1), 33–52
Li, X., Wang, S., & Li, Z. (2017). The lncRNA NEAT1 facilitates cell growth and invasion via the miR-211/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 105(Pt 1), 346–353
Zhang, M., Wu, W. B., Wang, Z. W., & Wang, X. H. (2017). lncRNA NEAT1 is closely related with progression of breast cancer via promoting proliferation and EMT. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 21(5), 1020–1026
Ferrè, F., Colantoni, A., & Helmer-Citterich, M. (2016). Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 17(1), 106–116
Zhou, Y., Do, D. C., & Ishmael, F. T. (2018). Mannose receptor modulates macrophage polarization and allergic inflammation through miR-511-3p. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 141(1), 350-364.e8
Pfeiffer, D., Roßmanith, E., Lang, I., & Falkenhagen, D. (2017). miR-146a, miR-146b, and miR-155 increase expression of IL-6 and IL-8 and support HSP10 in an In vitro sepsis model. PLoS ONE, 12(6), e0179850
Chakravarty, D., Sboner, A., & Nair, S. S. (2014). The oestrogen receptor alpha-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 is a critical modulator of prostate cancer. Nature Communications, 5, 5383
Sun, C., Li, S., & Zhang, F. (2016). Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through regulation of miR-377-3p-E2F3 pathway. Oncotarget, 7(32), 51784–51814
Wang, P., Wu, T., & Zhou, H. (2016). Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes laryngeal squamous cell cancer through regulating miR-107/CDK6 pathway. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 35, 22
Chai, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, Z., & Liu, L. (2016). HuR-regulated lncRNA NEAT1 stability in tumorigenesis and progression of ovarian cancer. Cancer Medicine, 5(7), 1588–1598
Li, Y., Zhang, H., & Dong, Y. (2017). MiR-146b-5p functions as a suppressor miRNA and prognosis predictor in non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of Cancer, 8(9), 1704–1716
Lv, Y. P., Shi, W., Liu, H. X., Kong, X. J., & Dai, D. L. (2017). Identification of miR-146b-5p in tissues as a novel biomarker for prognosis of gallbladder carcinoma. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 21(3), 518–522
Correia, N. C., Fragoso, R., Carvalho, T., Enguita, F. J., & Barata, J. T. (2016). MiR-146b negatively regulates migration and delays progression of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science and Reports, 6, 31894
Liu, J., Xu, J., & Li, H. (2015). miR-146b-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting TRAF6 and predicts the prognosis of human gliomas. Oncotarget, 6(30), 29129–29142
Di, Y. F., Li, D. C., & Shen, Y. Q. (2017). MiR-146b protects cardiomyocytes injury in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion by targeting Smad4. American Journal of Translational Research, 9(2), 656–663
Li, C., Miao, R., & Liu, S. (2017). Down-regulation of miR-146b-5p by long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes cancer growth and metastasis. Oncotarget, 8(17), 28683–28695
Huang, X., Zhong, R., & He, X. (2019). Investigations on the mechanism of progesterone in inhibiting endometrial cancer cell cycle and viability via regulation of long noncoding RNA NEAT1/microRNA-146b-5p mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. IUBMB Life, 71(2), 223–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC, JW, YL, and DX performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and collected, developed the statistical methods, and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Wang, J., Lv, Y. et al. LncRNA NEAT1 Regulates Infantile Pneumonia by Sponging miR-146b. Mol Biotechnol 63, 694–701 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00331-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-021-00331-w