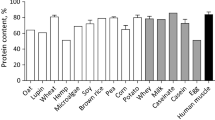
Abstract
Protein–energy malnutrition (PEM) has adversely affected the generations of developing countries. It is a syndrome that in severity causes death. PEM generally affects infants of 1–5 age group. This manifestation is maintained till adulthood in the form of poor brain and body development. The developing nations are continuously making an effort to curb PEM. However, it is still a prime concern as it was in its early years of occurrence. Transgenic crops with high protein and enhanced nutrient content have been successfully developed. Present article reviews the studies documenting genetic engineering-mediated improvement in the pulses, cereals, legumes, fruits and other crop plants in terms of nutritional value, stress tolerance, longevity and productivity. Such genetically engineered crops can be used as a possible remedial tool to eradicate PEM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbadi, A., Domergue, F., Bauer, J., Napier, J. A., Welti, R., Zähringer, U., et al. (2004). Biosynthesis of very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in transgenic oilseeds: constraints on their accumulation. The Plant Cell, 16, 2734–2748.
Abdula, S. E., Lee, H. J., Ryu, H., Kang, K. K., Nou, I., Sorrells, M. E., et al. (2016). Enhances abiotic stress tolerance by increasing proline biosynthesis in rice. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 34, 501–511.
Acciarri, N., Restaino, F., Vitelli, G., Perrone, D., Zottini, M., Pandolfini, T., et al. (2002). Genetically modified parthenocarpic eggplants: improved fruit productivity under both greenhouse and open field cultivation. BMC Biotechnology, 2, 4.
Agius, F., González-Lamothe, R., Caballero, J. L., Muñoz-Blanco, J., Botella, M. A., & Valpuesta, V. (2003). Engineering increased vitamin C levels in plants by overexpression of a D-galacturonic acid reductase. Nature Biotechnology, 21, 177–181.
Ahmed, T., Rahman, S., & Cravioto, A. (2009). Oedematous malnutrition. Indian Journal of Medical Research, 130, 651–654.
Ahn, M. J., Noh, S. A., Ha, S. H., Back, K., Lee, S. W., & Myung Bae, J. M. (2012). Production of ketocarotenoids in transgenic carrot plants with an enhanced level of â-carotene. Plant Biotechnology Reports, 6, 133–140.
Aluru, M., Xu, Y., Guo, R., Wang, Z., Li, S., White, W., et al. (2008). Generation of transgenic maize with enhanced provitamin A content. Journal of Experimental Botany, 59, 3551–3562.
Amara, I., Capellades, M., Ludevid, M. D., Pages, M., & Goday, A. (2013). Enhanced water stress tolerance of transgenic maize plants over-expressing LEA Rab28 gene. Journal of Plant Physiology, 170, 864–873.
Amede, T., Stroud, A., & Aune, J. (2004). Advancing human nutrition without degrading land resources through modeling cropping systems in the Ethiopian highlands. Food and Nutrition Bulletin, 25, 344–353.
Anai, T., Koga, M., Tanaka, H., Kinoshita, T., Rahman, S. M., & Takagi, Y. (2003). Improvement of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seed oil quality through introduction of a soybean microsomal omega-3 fatty acid desaturase gene. Plant Cell Reports, 21, 988–992.
Augustine, S. M., Narayan, A. J., Syamaladevi, D. P., Appunu, C., Chakravarthi, M., Ravichandran, V., et al. (2015). Overexpression of EaDREB2 and pyramiding of EaDREB2 with the pea DNA helicase gene (PDH45) enhance drought and salinity tolerance in sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid). Plant Cell Reports, 34, 247–263.
Badaloo, A. V., Forrester, T., Reid, M., & Jahoor, F. (2006). Lipid kinetic differences between children with kwashiorkor and those with marasmus. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 83, 1283–1288.
Badejo, A. A., Eltelib, H. A., Fukunaga, K., Fujikawa, Y., & Esaka, M. (2009). Increase in ascorbate content of transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing the acerola (Malpighia glabra) phosphomannomutase gene. Plant and Cell Physiology, 50, 423–428.
Badejo, A. A., Tanaka, N., & Esaka, M. (2008). Analysis of GDP-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase gene promoter from acerola (Malpighia glabra) and increase in ascorbate content of transgenic tobacco expressing the acerola gene. Plant Cell Physiology, 49, 126–132.
Bañuelos, G., LeDuc, D. L., Pilon-Smits, E. A. H., Tagmount, A., & Terry, N. (2007). Transgenic Indian mustard overexpressing selenocysteine lyase or selenocysteine methyltransferase exhibit enhanced potential for selenium phytoremediation under field conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 599–605.
Bañuelos, G., Terry, N., LeDuc, D. L., Pilon-Smits, E. A. H., & Mackey, B. (2005). Field trial of transgenic Indian mustard plants shows enhanced phytoremediation of selenium-contaminated sediment. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 1771–1777.
Betancor, M. B., Sprague, M., Usher, S., Sayanova, O., Campbell, P. J., Napier, J. A., et al. (2015). A nutritionally-enhanced oil from transgenic Camelina sativa effectively replaces fish oil as a source of eicosapentaenoic acid for fish. Scientific Reports, 5, 8104–8114.
Bhutia, D. T. (2014). Protein Energy Malnutrition in India: The plight of our under five children. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 3, 63–67.
Bortesia, L., & Fischer, R. (2015). The CRISPR/Cas9 system for plant genome editing and beyond. Biotechnology Advances, 33, 41–52.
Bouaziz, D., Pirrello, J., Charfeddine, M., Hammami, A., Jbir, R., Dhieb, A., et al. (2013). Overexpression of StDREB1 transcription factor increases tolerance to salt in transgenic potato plants. Molecular Biotechnology, 54, 803–817.
Bouis, H. E. (1996). Enrichment of food staples through plant breeding: A new strategy for fighting micronutrient malnutrition. Nutrition Reviews, 54, 131–137.
Bouis, H. E. (2002). Plant breeding: A new tool for fighting micronutrient malnutrition. Journal of Nutrition, 132, 491S–494S.
Brar, D. S., Ohtani, T., & Uchimiya, H. (1996). Genetically engineered plants for quality improvement. Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews, 13, 167–180.
Bulley, S., Wright, M., Rommens, C., Yan, H., Rassam, M., Lin-Wang, K., et al. (2012). Enhancing ascorbate in fruits and tubers through over-expression of the l-galactose pathway gene GDP-l-galactose phosphorylase. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 10, 390–397.
Cahoon, E. B., Hall, S. E., Ripp, K. G., Ganzke, T. S., Hitz, W. D., & Coughlan, S. J. (2003). Metabolic redesign of vitamin E biosynthesis in plants for tocotrienol production and increased antioxidant content. Nature Biotechnology, 21, 1082–1087.
Caimi, P. G., McCole, L. M., Klein, T. M., & Kerr, P. S. (1996). Fructan accumulation and sucrose metabolism in transgenic maize endosperm expressing a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SacB gene. Plant Physiology, 110, 355–363.
Campos-Bowers, M. H., & Wittenmyer, B. F. (2007). Biofortification in China: Policy and practice. Health Research Policy and Systems, 5, 10–17.
Chakraborty, S., Chakraborty, N., & Datta, A. (2000). Increased nutritive value of transgenic potato by expressing a nonallergenic seed albumin gene from Amaranthus hypochondriacus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 3724–3729.
Chakraborty, S., Chakraborty, N., Agrawal, L., Ghosh, S., Narula, K., Shekhar, S., et al. (2010). Next-generation protein-rich potato expressing the seed protein gene Am A1 is a result of proteome rebalancing in transgenic tuber. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 17533–17538.
Chakraborty, S., Gupta, S. B., Chaturvedi, B., & Chakraborty, S. K. (2006). A study of protein energy malnutrition (PEM) in Children (0 to 6 Year) in a rural population of Jhansi District (U.P.). Indian Journal of Community Medicine, 31, 291–292.
Chapman, K. D., Austin-Brown, S., Sparace, S. A., Kinney, A. J., Ripp, K. G., Pirtle, I. L., et al. (2001). Transgenic cotton plants with increased seed oleic acid content. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society, 78, 941–947.
Chen, Z., Young, T. E., Ling, J., Chang, S. C., & Gallie, D. R. (2003). Increasing vitamin C content of plants through enhanced ascorbate recycling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 3525–3530.
Chen, H., Liu, L., Wang, L., Wang, S., & Cheng, X. (2016). VrDREB2A, a DREB-binding transcription factor from Vigna radiata, increased drought and high-salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Plant Research, 129, 263–273.
Cho, E. A., Lee, C. A., Kim, Y. S., Baek, S. H., De Los Reyes, B. G., & Yun, S. J. (2005). Expression of gamma-tocopherol methyltransferase transgene improves tocopherol composition in lettuce (Latuca sativa L.). Molecules and Cells, 19, 16–22.
Comai, L., Schilling-Cordaro, C., Mergia, A., & Houck, C. M. (1983). A new technique for genetic engineering of Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid, 10, 21–30.
Costantini, E., Landi, L., Silvestroni, O., Pandolfini, T., Spena, A., & Mezzetti, B. (2007). Auxin synthesis-encoding transgene enhances grape fecundity. Plant Physiology, 143, 1689–1694.
Damor, R. D., Pithadia, P. R., Lodhiya, K. K., Yadav, S. B., & Mehta, J. P. (2013). A study on assessment of nutritional and immunization status of under-five children in urban slums of Jamnagar city, Gujarat. Healthline, 4, 2320.
Dehesh, K., Jones, A., Knutzon, D. S., & Voelker, T. A. (1996). Production of high levels of 8:0 and 10:0 fatty acids in transgenic canola by overexpression of Ch FatB2, a thioesterase cDNA from Cuphea hookeriana. The Plant Journal, 9, 167–172.
De Onis, M., Monteiro, C., Akre, J., & Glugston, G. (1993). The worldwide magnitude of protein-energy malnutrition: an overview from the WHO global database on child growth. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 71, 703–712.
de la Díaz, G. R., Quinlivan, E. P., Klaus, S. M., Basset, G. J., Gregory, J. F., & Hanson, A. D. (2004). Folate biofortification in tomatoes by engineering the pteridine branch of folate synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101, 13720–13725.
Diaz-Vivancos, P., Faize, M., Barba-Espin, G., Faize, L., Petri, C., Hernández, J. A., et al. (2013). Ectopic expression of cytosolic superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase leads to salt stress tolerance in transgenic plums. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 11, 976–985.
Dinkins, R. D., Reddy, M. S. S., Meurer, C. A., Yan, B., Trick, H., Thibaud-Nissen, F., et al. (2001). Increased sulfur amino acids in soybean plants overexpressing the maize 15 kD azein protein. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology, 37, 742–747.
Diretto, G., Al-Babili, S., Tavazza, R., Papacchioli, V., Beyer, P., & Giuliano, G. (2007). Metabolic engineering of potato carotenoid content through tuber-specific overexpression of a bacterial mini-pathway. PLoS ONE, 2, e350.
Down, R. E., Gatehouse, A. M. R., Hamilton, W. D. O., & Gatehouse, J. A. (1996). Snowdrop lectin inhibits development and decreases fecundity of the glasshouse potato aphid (Aulacorthum solani) when administered in vitro and via transgenic plants both in laboratory and glasshouse trials. Journal of Insect Physiology, 42, 1035–1045.
Drakakaki, G., Marcel, S., Glahn, R. P., Lund, E. K., Pariagh, S., Fischer, R., et al. (2005). Endosperm-specific co-expression of recombinant soybean ferritin and Aspergillus phytase in maize results in significant increases in the levels of bioavailable iron. Plant Molecular Biology, 59, 869–880.
Ducreux, L. J. M., Morris, W. L., Hedley, P. E., Shepherd, T., Davies, H. V., Millam, S., et al. (2005). Metabolic engineering of high carotenoid potato tubers containing enhanced levels of â-carotene and lutein. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56, 81–89.
Duggan, C., Watkins, J. B., & Walker, W. A. (2004). Nutrition in pediatrics: Basic science, clinical application. USA: PMPH.
Eltayeb, A. E., Yamamoto, S., Habora, M. E. E., Yin, L., Tsujimoto, H., & Tanaka, K. (2011). Transgenic potato overexpressing Arabidopsis cytosolic AtDHAR1 showed higher tolerance to herbicide, drought and salt stresses. Breeding Science, 61, 3–10.
Enfissi, E. M., Fraser, P. D., Lois, L. M., Boronat, A., Schuch, W., & Bramley, P. M. (2005). Metabolic engineering of the mevalonate and non-mevalonate isopentenyl diphosphate-forming pathways for the production of health-promoting isoprenoids in tomato. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 3, 17–27.
Esvelt, K. M., & Wang, H. H. (2013). Genome-scale engineering for systems and synthetic biology. Molecular Systems Biology, 9, 641.
Ezzati, M., Lopez, A. D., Rodgers, A., Vander Hoorn, S., Murray, C. J., & Comparative risk assessment collaborating group. (2002). Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet, 360, 1347–1360.
Faber, M., & Wenhold, F. (2007). Nutrition in contemporary South Africa. Water SA, 33, 393–400.
Falco, S. C., Guida, T., Locke, M., Mauvais, J., Sandres, C., Ward, R. T., et al. (1995). Transgenic canola and soybean seeds with increased lysine. Biotechnology, 13, 577–582.
Fitches, E., Angharad, M. R., & Gatehouse, J. A. (1997). Effects of snowdrop lectin (GNA) delivered via artificial diet and transgenic plants on the development of tomato moth (Lacano biaoleracea) larvae in laboratory and glasshouse trials. Journal of Insect Physiology, 43, 727–739.
Fraser, P. D., Römer, S., Kiano, J. W., Shipton, C. A., Mills, P. B., Drake, R., et al. (2001). Elevation of carotenoids in tomato by genetic manipulation. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 81, 822–827.
Gil, A., Serra-Majem, L., Calder, P. C., & Uauy, R. (2012). Systematic reviews of the role of omega-3 fatty acids in the prevention and treatment of disease. British Journal of Nutrition, 107, S1–S2.
Gilgen, D., Mascie-Taylor, C. G., & Rosetta, L. (2001). Intestinal helminth infections, anaemia and labour productivity of female tea pluckers in Bangladesh. Tropical Medicine & International Health, 6, 449–457.
Girgi, M., Breese, W. A., Lorz, H., & Oldach, K. H. (2006). Rust and downy mildew resistance in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) mediated by heterologous expression of the afp gene from Aspergillus giganteus. Transgenic Research, 15, 313–324.
Girijashankar, V., Sharma, H. C., Sharma, K. K., Swathisree, V., Prasad, L. S., Bhat, B. V., et al. (2005). Development of transgenic sorghum for insect resistance against the spotted stem borer (Chilo partellus). Plant Cell Reports, 24, 513–522.
Goldberg, I. (1994). Functional foods, designer foods, pharmafoods, nutraceuticals. New York: Chapman and Hall.
Goto, F., Yoshihara, T., Shigemoto, N., Toki, S., & Takaiwa, F. (1999). Iron fortification of rice seed by the soybean ferritin gene. Nature Biotechnology, 17, 282–286.
Guan, Q. J., Ma, H. Y., Wang, Z. J., Wang, Z. Y., Bu, Q. Y., & Liu, S. K. (2016). A rice LSD1-like-type ZFP gene OsLOL5 enhances saline-alkaline tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana, yeast and rice. BMC Genomics, 17, 142.
Halder, M., & Halder, S. Q. (1984). Assessment of protein calorie malnutrition. Clinical Chemistry, 30, 1266–1299.
Upadhyaya, C. P., Akula, N., Young, K. E., Chun, S. C., Kim, D. H., & Park, S. W. (2010). Enhanced ascorbic acid accumulation in transgenic potato confers tolerance to various abiotic stresses. Biotechnology Letters, 32, 321–330.
Herman, E. M. (2003). Genetically modified soybeans and food allergies. Journal of Experimental Botany, 54, 1317–1319.
Herrera-Estrella, L. R. (2000). Genetically modified crops and developing countries. Plant Physiology, 124, 3923–3926.
Herrera-Estrella, L., & Alvarez-Morales, A. (2001). Genetically modified crops: Hope for developing countries? EMBO Reports, 2, 256–258.
Hsieh, T. H., Lee, J. T., Charng, Y. Y., & Chan, M. T. (2002). Tomato plants ectopically expressing Arabidopsis CBF1 show enhanced resistance to water deficit stress. Plant Physiology, 130, 618–626.
Hu, T., Zhu, S., Tan, L., Qi, W., He, S., & Wang, G. (2016). Overexpression of OsLEA4 enhances drought, high salt and heavy metal stress tolerance in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 123, 68–77.
Iqbal, M. M., Nazir, F., Ali, S., Asif, M. A., Zafar, Y., Iqbal, J., et al. (2012). Overexpression of rice chitinase gene in transgenic peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) improves resistance against leaf spot. Molecular Biotechnology, 50, 129–136.
Jabeen, N., Chaudhary, Z., Gulfraz, M., Rashid, H., & Mirza, B. (2015). Expression of rice chitinase gene in genetically engineered tomato confers enhanced resistance to Fusarium wilt and early blight. The Plant Pathology Journal, 31, 252–258.
Jain, A. K., & Nessler, C. L. (2000). Metabolic engineering of an alternative pathway for ascorbic acid biosynthesis in plants. Molecular Breeding, 6, 73–78.
James, C. (1998). Update in the development and commercialisation of genetically modified crops. International Service for the Acquisition of Agrobiotechnology Applications Briefs, 5, 1–20.
James, C. (2014). Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2014. Ithaca, NY, USA: ISAAA.
Joo, J., Choi, H. J., Lee, Y. H., Kim, Y. K., & Song, S. I. (2013). A transcriptional repressor of the ERF family confers drought tolerance to rice and regulates genes preferentially located on chromosome 11. Planta, 238, 155–170.
Kasuga, M., Liu, Q., Miura, S., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., & Shinozaki, K. (1999). Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nature Biotechnology, 17, 287–291.
Kasukabe, Y., He, L., Nada, K., Misawa, S., Ihara, I., & Tachibana, S. (2004). Overexpression of spermidine synthase enhances tolerance to multiple environmental stresses and up-regulates the expression of various stress-regulated genes in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant and Cell Physiology, 45, 712–722.
Kawakatsu, T., Wang, S., Wakasa, Y., & Takaiwa, F. (2010). Increased lysine content in rice grains by over-accumulation of BiP in the endosperm. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 74, 2529–2531.
Khan, M. S., Ahmad, D., & Khan, M. A. (2015). Utilization of genes encoding osmoprotectants in transgenic plants for enhanced abiotic stress tolerance. EJB, 18, 257–266.
Kim, M. J., Kim, J. K., Kim, H. J., PakJH, Lee J. H., KimDH, Choi K. H., Jung, H. W., et al. (2012). Genetic modification of the soybean to enhance the â-carotene content through seed-specific expression. PLoS ONE, 7, e48287.
Kishimoto, K., Nishizawa, Y., Tabei, Y., Hibi, T., Nakajima, M., & Akutsu, K. (2002). Detailed analysis of rice chitinase gene expression in transgenic cucumber plants showing different levels of disease resistance to gray mold (Botrytis cinerea). Plant Science, 162, 655–662.
Klümper, W., & Qaim, M. (2014). A meta-analysis of the impacts of genetically modified crops. PLoS ONE, 9, e111629.
Knight, J. G., Mather, D. W., Holdsworth, D. K., & Ermen, D. F. (2007). Acceptance of GM food-an experiment in six countries. Nature Biotechnology, 25, 507–508.
Kotut, J., Wafula, S., Ettyang, G., & Mbagaya, G. (2014). Protein-energy malnutrition among women of child bearing age in semi arid areas of Keiyo District, Kenya. Advances in Life Science and Technology, 24, 80–91.
Kovács, G., Sági, L., Jacon, G., Arinaitwe, G., Busogoro, J. P., Thiry, E., et al. (2013). Expression of a rice chitinase gene in transgenic banana (‘Gros Michel’, AAA genome group) confers resistance to black leaf streak disease. Transgenic Research, 22, 117–130.
Kumar, V., Chattopadhyay, A., Ghosh, S., Irfan, M., Chakraborty, N., Chakraborty, S., Datta, A. (2015). Improving nutritional quality and fungal tolerance in soya bean and grass pea by expressing an oxalate decarboxylase. Plant Biotechnology Journal (Epub ahead of print).
Kwon, S. Y., Choi, S. M., Ahn, Y. O., Lee, H. S., Lee, H. B., Park, Y. M., et al. (2003). Enhanced stress-tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants expressing a human dehydroascorbate reductase gene. Journal of Plant Physiology, 160, 347–353.
Latha, A. M., Rao, K. V., Reddy, T. P., & Reddy, V. D. (2006). Development of transgenic pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br.) plants resistant to downy mildew. Plant Cell Reports, 29, 927–935.
LeDuc, D. L., Tarun, A. S., Montes-Bayon, M., Meija, J., Malit, M. F., Wu, C. P., et al. (2004). Overexpression of selenocysteine methyltransferase in Arabidopsis and Indian mustard increases selenium tolerance and accumulation. Plant Physiology, 135, 377–383.
Li, L., Liu, S., Hu, Y., Zhao, W., & Lin, Z. (2001). Increase of sulphur-containing amino acids in transgenic potato with 10 ku zein gene from maize. Chinese Science Bulletin, 46, 482–484.
Li, F., Wu, Q. Y., Sun, Y. L., Wang, L. Y., Yang, X. H., & Meng, Q. W. (2010). Overexpression of chloroplastic monodehydroascorbate reductase enhanced tolerance to temperature and methyl viologen-mediated oxidative stresses. Physiologia Plantarum, 139, 421–434.
Lonnerdal, B. (2003). Genetically modified plants for improved trace element nutrition. Journal of Nutrition, 133, 1490S–1493S.
Lonnerdal, B., & Iyer, S. (1995). Lactoferrin: Molecular structure and biological function. Annual Review of Nutrition, 15, 93–110.
Losey, J. E., Rayor, L. S., & Carter, M. E. (1999). Transgenic pollen harms monarch larvae. Nature, 399, 214.
Lu, S., Van, E. J., Zhou, X., Lopez, A. B., O’Halloran, D. M., Cosman, K. M., et al. (2006). The cauliflower Or gene encodes a DnaJ cysteine-rich domain-containing protein that mediates high levels of beta-carotene accumulation. Plant Cell, 18, 3594–3605.
Lucca, P., Hurrell, R., & Potrykus, I. (2001). Genetic engineering approaches to improve the bioavailability and the level of iron in rice grains. TAG Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 102, 392–397.
Lucht, J. M. (2015). Public acceptance of plant biotechnology and GM crops. Viruses, 7, 4254–4281.
Lukaszewicz, M., Matysiak-Kata, I., Skala, J., Fecka, I., Cisowski, W., & Szopa, J. (2004). Antioxidant capacity manipulation in transgenic potato tuber by changes in phenolic compounds content. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52, 1526–1533.
Mallikarjuna, G., Mallikarjuna, K., Reddy, M. K., & Kaul, T. (2011). Expression of OsDREB2A transcription factor confers enhanced dehydration and salt stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biotechnology Letters, 33, 1689–1697.
Manary, M. J., & Brewster, D. R. (1997). Potassium supplementation in kwashiorkor. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 24, 194–201.
Masrizal, M. A. (2003). Effects of protein-energy malnutrition on the immune system. Makara, Sains, 7, 69–73.
Masuda, H., Ishimaru, Y., Aung, M. S., Kobayashi, T., Kakei, Y., Takahashi, M., et al. (2012). Iron biofortification in rice by the introduction of multiple genes involved in iron nutrition. Scientific Reports, 2, 543–549.
Mayer, J. E., Pfeiffer, W. H., & Beyer, P. (2008). Biofortified crops to alleviate micronutrient malnutrition. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 11, 166–170.
Mazur, B., Krebbers, E., & Tingey, S. (1999). Gene discovery and product development for grain quality traits. Science, 285, 372–375.
Mehta, R. A., Cassol, T., Li, N., Ali, N., Handa, A. K., & Mattoo, A. K. (2002). Engineered polyamine accumulation in tomato enhances phytonutrient content, juice quality, and vine life. Nature Biotechnology, 20, 613–618.
Mezzetti, B., Landi, L., Pandolfini, T., & Spena, A. (2004). The defH9-iaaM auxin-synthesizing gene increases plant fecundity and fruit production in strawberry and raspberry. BMC Biotechnology, 4, 4.
Mittler, R. (2002). Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends in Plant Science, 7, 405–410.
Molvig, L., Tabe, L. M., Eggum, B. O., Moore, A. E., Craig, S., Spencer, D., et al. (1997). Enhanced methionine levels and increased nutritive value of seeds of transgenic lupins (Lupinus angustifolius L.) expressing a sunflower seed albumin gene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94, 8393–8398.
Moon, W., & Balasubramanian, S. K. (2002). Public perceptions and willingness-to-pay a premium for non-GM foods in the US and UK. AgBioForum, 4, 221–231.
Muller, O., & Krawinkel, M. (2003). Malnutrition and health in developing countries. CMAJ, 173, 279–286.
Murray, L. E., Takaiwa, F., Goto, F., Yoshihara, T., Theil, E. C., & Beard, J. L. (2002). Transgenic rice is a source of iron for iron-depleted rats. Journal of Nutrition, 132, 957–960.
Muthukrishnan, S., Jeoung, J. M., Liang, G. H., & Krishnaveni, S. (2001). Transgenic sorghum plants constitutively expressing a rice chitinase gene show improved resistance to stalk rot [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Journal of Genetics & Breeding, 55, 151–158.
Nandakumar, R., Babu, S., Kalpana, K., Raguchander, T., Balasubramanian, P., & Samiyappan, R. (2007). Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of indica rice with chitinase gene for enhanced sheath blight resistance. Biologia Plantarum, 51, 142–148.
Naylor, R. L., Hardy, R. W., Bureau, D. P., Chiu, A., Elliott, M., Farrell, A. P., et al. (2009). Feeding aquaculture in an era of finite resources. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 15103–15110.
Nguyen, H. C., Hoefgen, R., & Hesse, H. (2012). Improving the nutritive value of rice seeds: Elevation of cysteine and methionine contents in rice plants by ectopic expression of a bacterial serine acetyltransferase. Journal of Experimental Botany, 63, 5991–6001.
Niggeweg, R., Michael, A. J., & Martin, C. (2004). Engineering plants with increased levels of the antioxidant chlorogenic acid. Nature Biotechnology, 22, 746–754.
Nirala, N. K., Das, D. K., Srivastava, P. S., Sopory, S. K., & Upadhyaya, K. C. (2010). Expression of a rice chitinase gene enhances antifungal potential in transgenic grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Vitis, 49, 181–187.
Niu, C. F., Wei, W., Zhou, Q. Y., Tian, A. G., Hao, Y. J., Zhang, W. K., et al. (2012). Wheat WRKY genes TaWRKY2 and TaWRKY19 regulate abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant, Cell and Environment, 35, 1156–1170.
Nnakwe, N. (1995). The effect and causes of protein energy malnutrition in Nigerian children. Nutrition Research, 15, 785–794.
Oakes, J., Brackenridge, D., Colletti, R., Daley, M., Hawkins, D. J., Xiong, H., et al. (2011). Expression of fungal diacylglycerol acyltransferase2 genes to increase kernel oil in maize. Plant Physiology, 155, 1146–1157.
Paine, J. A., Shipton, C. A., Chaggar, S., Howells, R. M., Kennedy, M. J., Vernon, G., et al. (2005). Improving the nutritional value of Golden Rice through increased pro-vitamin A content. Nature Biotechnology, 23, 482–487.
Pereira, A. (2000). A transgenic perspective on plant functional genomics. Transgenic Research, 9, 245–260.
Pilon-Smits, E. A. H., Hwang, S. B., Lytle, C. M., Zhu, Y. L., Tai, J. C., Bravo, R. C., et al. (1999). Overexpression of ATP sulfurylase in Brassica juncea leads to increased selenate uptake, reduction and tolerance. Plant Physiology, 119, 123–132.
Rascón-Cruz, Q., Sinagawa-García, S., Osuna-Castro, J. A., Bohorova, N., & Paredes-López, O. (2004). Accumulation, assembly, and digestibility of amarantin expressed in transgenic tropical maize. TAG Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 108, 335–342.
Ravikumar, G., Manimaran, P., Voleti, S. R., Subrahmanyam, D., Sundaram, R. M., Bansal, K. C., et al. (2014). Stress-inducible expression of AtDREB1A transcription factor greatly improves drought stress tolerance in transgenic indica rice. Transgenic Research, 23, 421–439.
Rayman, M. P. (2012). Selenium and human health. Lancet, 379, 1256–1268.
Römer, S., Fraser, P. D., Kiano, J. W., Shipton, C. A., Misawa, N., Schuch, W., et al. (2000). Elevation of the pro-vitamin A content of transgenic tomato plants. Nature Biotechnology, 18, 666–669.
Rong, W., Qi, L., Wang, A., Ye, X., Du, L., Liang, H., et al. (2014). The ERF transcription factor TaERF3 promotes tolerance to salt and drought stresses in wheat. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 12, 468–479.
Rosati, C., Aquilani, R., Dharmapuri, S., Pallara, P., Marusic, C., Tavazza, R., et al. (2000). Metabolic engineering of beta-carotene and lycopene content in tomato fruit. The Plant Journal, 24, 413–419.
Sato, H., Todaka, D., Kudo, M., Mizoi, J., Kidokoro, S., Zhao, Y., Shinozaki, K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2016). The Arabidopsis transcriptional regulator DPB3-1 enhances heat stress tolerance without growth retardation in rice. Plant Biotechnology Journal (Epub ahead of print).
Sauvion, N., Rahbé, Y., Peumans, W. J., Damme, E. J. M. V., Gatehouse, J. A., & Gatehouse, A. M. R. (1996). Effects of GNA and other mannose binding lectins on development and fecundity of the peach-potato aphid Myzus persicae. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 79, 285–293.
Scheinfeld, N.S., Lin, A., Mokashi, A. (2015) Protein-energy malnutrition: Background, pathophysiology, epidemiology. Medscape Reference.
Schmidt, M. A., Parrott, W. A., Hildebrand, D. F., Berg, R. H., Cooksey, A., Pendarvis, K., et al. (2014). Transgenic soya bean seeds accumulating â-carotene exhibit the collateral enhancements of oleate and protein content traits. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 1–11.
Sévenier, R., Hall, R. D., van der Meer, I. M., Hakkert, H. J. C., van Tunen, A. J., & Koops, A. J. (1998). High level fructan accumulation in a transgenic sugar beet. Nature Biotechnology, 16, 843–846.
Shekhar, S., Agrawal, L., Mishra, D., Buragohain, A. K., Unnikrishnan, M., Mohan, C., et al. (2016). Ectopic expression of amaranth seed storage albumin modulates photoassimilate transport and nutrient acquisition in sweet potato. Sci. Rep., 6, 25384.
Shen, B., Allen, W. B., Zheng, P., Li, C., Glassman, K., Ranch, J., et al. (2010). Expression of ZmLEC1 and ZmWRI1 increases seed oil production in maize. Plant Physiology, 153, 980–987.
Shewmaker, C. K., Sheehy, J. A., Daley, M., Colburn, S., & Ke, D. Y. (1999). Seed-specific overexpression of phytoene synthase: Increase in carotenoids and other metabolic effects. The Plant Journal, 20, 401–412X.
Shin, Y. M., Park, H. J., Yim, S. D., Baek, N. I., Lee, C. H., An, G., et al. (2006). Transgenic rice lines expressing maize C1 and R-S regulatory genes produce various flavonoids in the endosperm. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 4, 303–315.
Shintani, D., & DellaPenna, D. (1998). Elevating the Vitamin E content of plants through metabolic engineering. Science, 282, 2098–2100.
Sidhu, H., Schmidt, M. E., Cornelius, J. G., Thamilselvan, S., Khan, S. R., Hesse, A., et al. (1999). Direct correlation between hyperoxaluria/oxalate stone disease and the absence of the gastrointestinal tract-dwelling bacterium Oxalobacter formigenes: Possible prevention by gut recolonization or enzyme replacement therapy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 10, S334–S340.
Singh, N., Mishra, A., & Jha, B. (2014). Over-expression of the peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase (SBPAPX) gene cloned from halophyte Salicornia brachiata confers salt and drought stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Marine Biotechnology, 16, 321–332.
Slattery, C. J., Kavakli, I. H., & Okita, T. W. (2000). Engineering starch for increased quantity and quality. Trends in Plant Science, 5, 291–298.
Stark, D. M., Timmerman, K. P., Barry, G. F., Preiss, J., & Kishore, G. M. (1992). Regulation of the amount of starch in plant tissues by ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase. Science, 258, 287–292.
Stark-Lorenzen, P., Nelke, B., Hänßler, G., Mühlbach, H. P., & Thomzik, J. E. (1997). Transfer of a grapevine stilbene synthase gene to rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Reports, 16, 668–673.
Storozhenko, S., De Brouwer, V., Volckaert, M., Navarrete, O., Blancquaert, D., Zhang, G. F., et al. (2007). Folate fortification of rice by metabolic engineering. Nature Biotechnology, 25, 1277–1279.
Subramanian, M., & Subrahmanyam, G. (2013). Determinants of protein energy malnutrition among rural preschool children. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences, 2, 9157–9162.
Sunkar, R., Bartels, D., & Kirch, H. H. (2003). Overexpression of a stress-inducible aldehyde dehydrogenase gene from Arabidopsis thaliana in transgenic plants improves stress tolerance. The Plant Journal, 35, 452–464.
Suzuki, Y. A., Kelleher, S. L., Yalda, D., Wu, L., Huang, J., Huang, N., et al. (2003). Expression, characterization and biological activity of recombinant human lactoferrin in rice. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 36, 190–199.
Swaminathan, M. (2000). Advanced textbook on food and nutrition (pp. 317–320). Bangalore: Bangalore Printing and Publishing Co. Ltd.
Szankowski, I., Briviba, K., Fleschhut, J., Schönherr, J., Jacobsen, H. J., & Kiesecker, H. (2003). Transformation of apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) with the stilbene synthase gene from grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) and a PGIP gene from kiwi (Actinidia deliciosa). Plant Cell Reports, 22, 141–149.
Takahashi, M., Nakanishi, H., Kawasaki, S., Nishizawa, N. K., & Mori, S. (2001). Enhanced tolerance of rice to low iron availability in alkaline soils using barley nicotianamine aminotransferase genes. Nature Biotechnology, 19, 466–469.
Tavya, V. S., Kim, Y. H., Kagan, I. A., Dinkins, R. D., Kim, K. H., & Collins, G. B. (2007). Increased alpha-tocopherol content in soybean seed overexpressing the Perilla frutescens gamma-tocopherol methyltransferase gene. Plant Cell Reports, 26, 61–70.
Tontisirin, K., Nantel, G., & Bhattacharjee, L. (2002). Food-based strategies to meet the challenges of micronutrient malnutrition in the developing world. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 61, 243–250.
Ubesie, A. C., & Ibeziakor, N. S. (2012). High burden of protein–energy malnutrition in Nigeria: Beyond the health care setting. Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research, 2, 66–69.
UNDP. (2003). Human development report: Millennium development goals. In A compact among nations to end Human Poverty. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Varzakas, T. H., Arvanitoyannis, I. S., & Baltas, H. (2007). The Politics and Science behind GMO Acceptance. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 47, 335–361.
Vasconcelos, M., Datta, K., Oliva, N., Khalekuzzaman, M., Torrizo, L., Krishnan, S., et al. (2003). Enhanced iron and zinc accumulation in transgenic rice with the ferritin gene. Plant Science, 164, 371–378.
Wang, F., Chen, H. W., Li, Q. T., Wei, W., Li, W., Zhang, W. K., et al. (2015). GmWRKY27 interacts with GmMYB174 to reduce expression of GmNAC29 for stress tolerance in soybean plants. The Plant Journal, 83, 224–236.
Wang, H., Wang, H., Shao, H., & Tang, X. (2016). Recent advances in utilizing transcription factors to improve plant abiotic stress tolerance by transgenic technology. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 67.
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Tian, J., Lim, B. L., Yan, X., & Liao, H. (2009). Overexpressing AtPAP15 enhances phosphorus efficiency in Soybean. Plant Physiology, 151, 233–240.
Weber, R. L. M., Wiebke-Strohm, B., Bredemeier, C., Margis-Pinheiro, M., de Brito, G. G., Rechenmacher, C., et al. (2014). Expression of an osmotin-like protein from Solanum nigrum confers drought tolerance in transgenic soybean. BMC Plant Biology, 14, 343.
WHO. (2000). Management of the child with a serious infection or severe malnutrition. Geneva: Guidelines for care at the first-referral level in developing countries.
Xu, J., Xing, X. J., Tian, Y. S., Peng, R. H., Xue, Y., Zhao, W., et al. (2015). Transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing tomato Glutathione S-Transferase showed enhanced resistance to salt and drought stress. PLoS ONE, 10, e0136960.
Ye, X., Al-Babili, S., Klöti, A., Zhang, J., Lucca, P., Beyer, P., et al. (2000). Engineering the provitamin A (beta-carotene) biosynthetic pathway into (carotenoid-free) rice endosperm. Science, 287, 303–305.
Zeh, M., Casazza, A. P., Kreft, O., Roessner, U., Bieberich, K., Willmitzer, L., et al. (2001). Antisense inhibition of threonine synthase leads to high methionine content in transgenic potato plants. Plant Physiology, 127, 792–802.
Zhai, Y., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Lei, T., Yan, F., Su, L., et al. (2013). Isolation and molecular characterization of GmERF7, a soybean ethylene-response factor that increases salt stress tolerance in tobacco. Gene, 513, 174–183.
Zhang, H., Liu, W., Wan, L., Li, F., Dai, L., Li, D., et al. (2010). Functional analyses of ethylene response factor JERF3 with the aim of improving tolerance to drought and osmotic stress in transgenic rice. Transgenic Research, 19, 809–818.
Zhang, C., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Cai, X., Gong, P., Zhang, J., et al. (2011). Overexpression of SlGMEs leads to ascorbate accumulation with enhanced oxidative stress, cold, and salt tolerance in tomato. Plant Cell Reports, 30, 389–398.
Zhang, J., Martin, J. M., Beecher, B., Lu, C., Hannah, L. C., Wall, M. L., et al. (2010). The ectopic expression of the wheat Puroindoline genes increase germ size and seed oil content in transgenic corn. Plant Molecular Biology, 74, 353–365.
Zhu, W., Yang, L., Yang, S., Gai, J., & Zhu, Y. (2016). Overexpression of rice phosphate transporter gene OsPT2 enhances nitrogen fixation and ammonium assimilation in transgenic soybean under phosphorus deficiency. Journal of Plant Biology, 59, 172–181.
Zou, J., Katavic, V., Giblin, E. M., Barton, D. L., MacKenzie, S. L., Keller, W. A., et al. (1997). Modification of seed oil content and acyl composition in the Brassicaceae by expression of a yeast SN-2 acyltransferase gene. Plant Cell, 9, 909–923.
Acknowledgements
PG is very thankful to The Vice Chancellor, DAV University, Jalandhar, for his support and encouragement. She is also grateful to DST SERB, GOI for financial support in the form of Project YSS/2015/000719.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guleria, P., Kumar, V. & Guleria, S. Genetic Engineering: A Possible Strategy for Protein–Energy Malnutrition Regulation. Mol Biotechnol 59, 499–517 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-0033-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-017-0033-8