Abstract
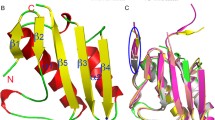
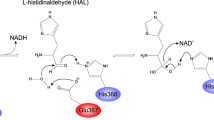
Recently, two l-carnitine dehydrogenases from soil isolates Rhizobium sp. (Rs-CDH) and Xanthomonas translucens (Xt-CDH) have demonstrated to exhibit mutually differing affinities toward l-carnitine. To identify residues important for affinity to the substrate, we compared the primary structure of Xt-CDH and Rs-CDH with the recognized 3D structure of 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (PDB code: 1F0Y). Then, six residues of Xt-CDH (Phe143, Gly188, Ile190, Ala191, Gly223, and Ala224) and the corresponding residues of Rs-CDH (Tyr140, Ala185, Val187, Gly188, Ser220, and Phe221) were selected for further mutagenesis. The residues of Xt-CDH were replaced with that of Rs-CDH at the corresponding position and vice versa. All Rs-CDH mutants exhibited slight effects on substrate affinity, except for the double mutants Rs-V187I/G188A, which was devoid of enzyme activity. All Xt-CDH mutants showed different K m values. Xt-F143Y caused a higher increase in the K m value. Furthermore, the kinetic parameters of 10 mutants at Xt-F143 and Rs-Y140 were investigated. All Rs-Y140 mutants, except aromatic residues (Phe, Trp), produced proteins that were almost entirely devoid of enzyme activity and with disrupted affinity to l-carnitine. All Xt-F143 variants showed a marked reduction (P ≤ 0.05) in enzyme activity. Overall, our results suggest that the aromatic rings of Tyr140 in Rs-CDH and Phe143 of Xt-CDH are essential for substrate recognition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma, S., & Black, S. M. (2009). Carnitine homeostasis, mitochondrial function and cardiovascular disease. Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms, 6, 31–39.
Bremer, J. (1983). Carnitine metabolism and functions. Physiological Reviews, 63, 1420–1480.
Nikula, P., Ruohola, H., Alhonen-Hongisto, L., & Janne, J. (1985). Carnitine prevents the early mitochondrial damage induced by methylglyoxal bis (guanylhydrazone) in L1210 leukaemia cells. Biochemical Journal, 228, 513–516.
Hagen, T. M., Ingersoll, R. T., Wehr, C. M., Lykkesfeldt, J., Vinarsky, V., Bartholomew, J. C., et al. (1998). l-Carnitine fed to old rats partially restores mitochondrial function and ambulatory activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United State of America, 95, 9562–9566.
Youn, S. C. (2008). Effects of l-carnitine on obesity, diabetes, and as an ergogenic aid. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 17, 306–308.
Veselá, E., Racek, J., Trefil, L., Jankovy’ch, V., & Pojer, M. (2001). Effect of l-carnitine supplementation in hemodialysis patients. Nephron, 88, 218–223.
Xin, Z. M., Fang, L. M., & Suodi, Z. M. (2007). Effect of l-carnitine and/or l-acetyl-carnitine in nutrition treatment for male infertility: A systematic review. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 16, 383–390.
Peter, L., Douglas, L. J., Eric, M. Y., & Sandra, S. (2012). Carnitine deficiency presenting with encephalopathy and hyperammonemia in a patient receiving chronic enteral tube feeding: A case report. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 6, 227–230.
De-Sousa, C., English, N. R., Stacey, T. E., & Chalmers, R. A. (1990). Measurement of l-carnitine and acylcarnitines in body fluids and tissues in children and in adult. Clinica Chimica Acta, 187, 317–328.
McEntyre, C. J., Lever, M., & Storer, M. K. (2004). High performance liquid chromatographic method for the measurement of total carnitine in human plasma and urine. Clinica Chimica Acta, 344, 123–130.
Vernez, L., Hopfgartner, G., Wenk, M., & Krahenbuhl, S. (2003). Determination of carnitine and acylcarnitines in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization ion trap tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 984, 203–213.
Marquis, N. R., & Fritz, I. B. (1964). Enzymological determination of free carnitine concentrations in rat tissues. Journal of Lipid Research, 5, 184–187.
Schopp, W., & Schafer, A. (1985). Quantitative bestimmung von l-carnitine mit hilfe von carnitindehydrogenase aus Pseudomonas putida. Fresenius Z Analytical Chemistry, 320, 285–289.
Takahashi, M., Ueda, S., Misaki, H., Sugiyama, N., Matsumoto, K., Matsuo, N., et al. (1994). Carnitine determination by an enzymatic cycling method with carnitine dehydrogenase. Clinical Chemistry, 40, 817–821.
Aurich, H., Kleber, H. P., Sorger, H., & Tauchert, H. (1968). Purification and properties of carnitine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. European Journal of Biochemistry, 6, 196–201.
Goulas, P. (1988). Purification and properties of carnitine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida. BBA—Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology, 957, 335–339.
Mori, N., Kasugai, T., Kitamoto, Y., & Ichikawa, Y. (1988). Purification and some properties of carnitine dehydrogenase from Xanthomonas translucens. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 52, 249–250.
Houriyou, K., Takahashi, M., Mizoguchi, J., & Imamura, S. (1993). Essentially pure microorganism capable of producing carnitine dehydrogenase. Japan patent no, 161492–A/1.
Mori, N., Mitsuzumi, H., & Kitamoto, Y. (1994). Purification and properties of carnitine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas sp. YS-240. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 78, 337–340.
Hanschmann, H., Ehricht, R., & Kleber, H. (1996). Purification and properties of l-carnitine dehydrogenase from Agrobacterium sp. BBA—General Subjects, 1290, 177–183.
Wargo, M. J., & Hogan, D. A. (2009). Identification of genes required for Pseudomonas aeruginosa carnitine catabolism. Microbiology, 155, 2411–2419.
Armia, J., Uesumi, A., Mitsuzumi, H., & Mori, N. (2010). Biochemical characterization of l-carnitine dehydrogenases from Rhizobium sp. and Xanthomonas translucens. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 74, 1237–1242.
Barycki, J. J., O’Brien, K. L., Strauss, A. W., & Banaszak, L. J. (2000). Sequestration of the active site by interdomain shifting (Crystallographic and spectroscopic evidence for distinct conformations of L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 27186–27196.
Birktoft, J. J., Holden, H. M., Hamlin, R., Xuong, N. H., & Banaszak, L. J. (1987). Structure of l-3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase: preliminary chain tracing at 2.8 Å resolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United State of America, 84, 8262–8266.
Barycki, J. J., O’Brien, L. K., Strauss, A. W., & Banaszak, L. J. (2001). Glutamate 170 of human l-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase is required for proper orientation of the catalytic histidine and structural integrity of the enzyme. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 36718–36726.
Goldberg, J. M., Swanson, R. V., Goodman, H. S., & Kirsch, J. F. (1991). The Tyrosine-225 to Phenylalanine mutation of Escherichia coli aspartate aminotransferase results in an alkaline transition in the spectrophotometric and kinetic pKa values and reduced values of both k cat and K m. Biochemistry, 30, 305–312.
Kanai, R., Haga, K., Akiba, T., Yamane, K., & Harata, K. (2004). Role of Phe283 in enzymatic reaction of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp.1011: Substrate binding and arrangement of the catalytic site. Protein Science, 13, 457–465.
Mori, N., Shirota, K., Kitamoto, Y., & Ichikawa, Y. (1988). Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the carnitine dehydrogenase gene from Xanthomonas translucens. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 52, 851–852.
Pace, C. N., Horn, G., Hebert, E. J., Bechert, J., Shaw, K., Urbanikova, L., et al. (2001). Tyrosine hydrogen bonds make a large contribution to protein stability. Journal of Molecular Biology, 312, 393–404.
Escobar, W. A., Miller, J., & Fink, A. L. (1994). Effects of site-specific mutagenesis of tyrosine 105 in a class A beta-lactamase. Biochemical Journal, 303, 555–558.
Guan, Y., Hickey, M. J., Borgstahl, G. E. O., Hallewell, R. A., Lepock, J. R., O’Connor, D., et al. (1998). Crystal structure of Y34F mutant human mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase and the functional role of tyrosine 34. Biochemistry, 37, 4722–4730.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eltayeb, M.M., Mohamed Ahmed, I.A., Arima, J. et al. Identification of Residues Essential for the Activity and Substrate Affinity of l-Carnitine Dehydrogenase. Mol Biotechnol 55, 268–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9678-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9678-0