Abstract
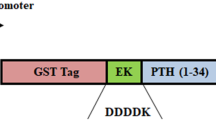
Somatostatin/growth hormone-inhibiting hormone is the peptide that inhibits secretion of somatotropin/growth hormone. Solid-phase synthesis methods are being currently used to produce somatostatin. Recombinant peptide synthesis is widely described for the production of small proteins and peptides; however, the production at industrial scale of peptides for biopharmaceutical applications is limited for economic reasons. Here, we propose the use of a new pGB-SMT plasmid to produce Somatostatin, as a C-terminal fusion protein with a Kluyveromyces lactis β-galactosidase fragment. To facilitate removal of that fragment by CNBr cleavage, a methionine residue was introduced at the N-terminal of the hormone peptide. The use of this construction enables an IPTG-free expression system. The suitability of this procedure has been assessed in a 15 l scale-up experiment yielding almost 300 mg, with purity >99 % and it is being implemented for commercial scale. The plasmid pGB-SMT here described is an alternative option for a cheap and high expression of other short peptide hormones.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel, Y. C. (1999). Somatostatin and its receptor family. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 20, 157–198.
Zeng, Y. X., Du, N. X., & Tan, J. Y. (1991). Expression of somatostatin gene in Escherichia coli D29A1. Yi Chuan Xue Bao, 18, 282–288.
Patel, Y. C., & Reichlin, S. (1978). Somatostatin in hypothalamus, extrahypothalamic brain, and peripheral tissues of the rat. Endocrinology, 102, 523–530.
Mentlein, R., Eichler, O., Forstreuter, F., & Held-Feindt, J. (2001). Somatostatin inhibits the production of vascular endothelial growth factor in human glioma cells. International Journal of Cancer, 92, 545–550.
Reynaert, H., & Geerts, A. (2003). Pharmacological rationale for the use of somatostatin and analogues in portal hypertension. Aliment Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 18, 375–386.
Albericio, F. (2004). Developments in peptide and amide synthesis. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 8, 211–221.
Bruckdorfer, T., Marder, O., & Albericio, F. (2004). From production of peptides in milligram amounts for research to multi-tons quantities for drugs of the future. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 5, 29–43.
Loffet, A. (2002). Peptides as drugs, is there a market? Journal of Peptide Science, 8, 1–7.
Itakura, K., Hirose, T., Crea, R., Riggs, A. D., Heyneker, H. L., Bolivar, F., et al. (1977). Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science, 198, 1056–1063.
Karpova, S. K., Sazina, E. T., Karasev, V. S., Bader, L. B., Sergienko, O. V., Shishkina, A. A., et al. (1993). Synthesis of somatostatin in Escherichia coli cells, isolation and characteristics. Bioorganicheskaia Khimiia, 19, 612–622.
Hanahan, D., Jessee, J., & Bloom, F. R. (1991). Plasmid transformation of Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Methods in Enzymology, 204, 63–113.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
Schägger, H., & von Jagow, G. (1987). Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDalton. Analytical Biochemistry, 166, 368–379.
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. (2001). Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual (3rd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Grosjean, H., & Fiers, W. (1982). Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes, the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene, 18, 99–209.
Rubio-Texeira, M., Castrillo, J. I., Adam, A. C., Ugalde, U. O., & Polaina, J. (1998). Highly efficient assimilation of lactose by a metabolically engineered strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast, 14, 827–837.
Gros, E. (1967). The cyanogen bromide reaction. Methods in Enzymology, 11, 238–255.
Juárez, P., Sanz, L., & Calvete, J. J. (2004). Snake venomics, characterization of protein families in Sistrurus barbouri venom by cysteine mapping, N-terminal sequencing, and tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Proteomics, 4, 327–338.
Seed, B. (1987). An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. Nature, 329, 840–842.
Cserjan-Puschmann, M., Grabherr, R., Striedner, G., Clementschitsch, F., & Bayer, K. (2002). Optimizing recombinant microbial fermentation processes. Biopharma International, 15, 26–34.
Cserjan-Puschmann, M., Kramer, W., Duerrschmid, E., Striedner, G., & Bayer, K. (1999). Metabolic approaches for the optimisation of recombinant fermentation processes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 53, 43–50.
Tolia, N. H., & Joshua-Tor, L. (2006). Strategies for protein coexpression in Escherichia coli. Nature Methods, 3, 55–64.
Sadeghi, H. M., Rabbani, M., Rismani, E., Moazen, F., Khodabakhsh, F., Dormiani, K., et al. (2011). Optimization of the expression of reteplase in Escherichia coli. Res Pharm Sci, 6, 87–92.
Grindley, J., & Odgen, J. (2000). Understanding biopharmaceuticals, manufacturing and regulatory issues. Florida: CRC Press.
Hansen, L. H., Knudsen, S., & Sørensen, S. J. (1998). The effect of the lacY gene on the induction of IPTG inducible promoters, studied in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Current Microbiology, 36, 341–347.
Studier, F. W. (2005). Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expression and Purification, 41, 207–234.
Jensen, P. R., Westerhoff, H. V., & Michelsen, O. (1993). The use of lac-type promoters in control analysis. European Journal of Biochemistry, 211, 181–191.
Choi, J. H., & Lee, S. Y. (2004). Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 64, 625–635.
Yoon, S. H., Kim, S. K., & Kim, J. F. (2010). Secretory production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Recent Patents on Biotechnology, 4, 23–29.
Sauter, S. R., Diekmann, S., & Braun, V. (2003). Two-step purification of the outer membrane transporter and activator protein ShlB from Escherichia coli using internally His6-tagged constructs. Journal of Chromatography B Analytical Technologies Biomedical and Life Science, 25, 33–37.
Dong, X. Y., Feng, X. D., & Sun, Y. (2010). His-tagged protein purification by metal-chelate affinity extraction with nickel-chelate reverse micelles. Biotechnology Progress, 26, 1088–1094.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Dr. J. Polaina for kindly providing plasmid pMR11 and Dr J. J. Calvete for mass spectrometry analysis. We thank P. Vicente, Dr. F. Bosch and Emeritus Professor R. Sentandreu for stimulating support to this project. This project was supported by Génesis Especialidades Farmacéuticas y Biotecnología S.A. Fund, Spanish Government Fund (CDTI-05-0469) and Generalitat Valenciana Fund (IMPIVA-INCOMA-05-19). S. M. and A. N. were supported by Torres Quevedo Grants from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación-Spanish Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maicas, S., Moukadiri, I., Nieto, A. et al. Construction of an Expression Vector for Production and Purification of Human Somatostatin in Escherichia coli . Mol Biotechnol 55, 150–158 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9667-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9667-3