Abstract
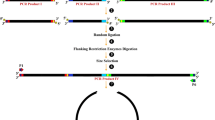
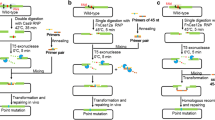
Site-directed mutagenesis is a very important technique in molecular biological researches. We have developed a new method for long distance multiple-site plasmid mutation by one-step PCR using non-overlap primers. These primers were carefully designed and contained desired mutations in the middle of the primers flanked with 18–25 bp of correct sequence. One pair of the primers was able to generate a short megaprimer. Decreases in the concentrations of these primers increased efficiency of the multiple-site plasmid mutation. All of the mutant PCRs were performed at a common annealing temperature at 55 °C. This method could be widely used in all multiple-site plasmid mutations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunkel, T. A. (1985). Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 82, 488–492.
Shen, B. (2002). PCR approaches to DNA mutagenesis and recombination. An overview. Methods in Molecular Biology, 192, 167–174.
Sarkar, G., & Sommer, S. S. (1990). The “megaprimer” method of site-directed mutagenesis. BioTechniques, 8, 404–407.
Xu, Z., Colosimo, A., & Gruenert, D. C. (2003). Site-directed mutagenesis using the megaprimer method. Methods in Molecular Biology, 235, 203–207.
Angelaccio, S., Marsango, S., & Bonaccorsi di Patti, M. C. (2002). Site-directed mutagenesis by the megaprimer PCR method: Variations on a theme for simultaneous introduction of multiple mutations. Analytical Biochemistry, 306, 346–349.
Wei, D., Li, M., Zhang, X., & Xing, L. (2004). An improvement of the site-directed mutagenesis method by combination of megaprimer, one-side PCR and DpnI treatment. Analytical Biochemistry, 331, 401–403.
Nagy, Z. B., Felfoldi, F., Tamas, L., & Puskas, L. G. (2004). A one-tube, two-step polymerase chain reaction-based site-directed mutagenesis method with simple identification of the mutated product. Analytical Biochemistry, 324, 301–303.
Chapnik, N., Sherman, H., & Froy, O. (2008). A one-tube site-directed mutagenesis method using PCR and primer extension. Analytical Biochemistry, 372, 255–257.
Kumar, R., & Rajagopal, K. (2008). Single-step overlap-primer-walk polymerase chain reaction for multiple mutagenesis without overlap extension. Analytical Biochemistry, 377, 105–107.
Vincentz, J. W., Barnes, R. M., Rodgers, R., Firulli, B. A., Conway, S. J., & Firulli, A. B. (2008). An absence of Twist1 results in aberrant cardiac neural crest morphogenesis. Developmental Biology, 320, 131–139.
Tseng, W. C., Lin, J. W., Wei, T. Y., & Fang, T. Y. (2008). A novel megaprimed and ligase-free, PCR-based, site-directed mutagenesis method. Analytical Biochemistry, 375, 376–378.
Li, J., Li, C., Xiao, W., Yuan, D., Wan, G., & Ma, L. (2008). Site-directed mutagenesis by combination of homologous recombination and DpnI digestion of the plasmid template in Escherichia coli. Analytical Biochemistry, 373, 389–391.
Liu, H., & Naismith, J. H. (2008). An efficient one-step site-directed deletion, insertion, single and multiple-site plasmid mutagenesis protocol. BMC Biotechnology, 8, 91.
Klock, H. E., Koesema, E. J., Knuth, M. W., & Lesley, S. A. (2008). Combining the polymerase incomplete primer extension method for cloning and mutagenesis with microscreening to accelerate structural genomics efforts. Proteins, 71, 982–994.
Fonfara, I., Curth, U., Pingoud, A., & Wende, W. (2012). Creating highly specific nucleases by fusion of active restriction endonucleases and catalytically inactive homing endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 847–860.
Munteanu, B., Braun, M., & Boonrod, K. (2012). Improvement of PCR reaction conditions for site-directed mutagenesis of big plasmids. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B, 13, 244–247.
Scott, S. P., Teh, A., Peng, C., & Lavin, M. F. (2002). One-step site-directed mutagenesis of ATM cDNA in large (20 kb) plasmid constructs. Human Mutation, 20, 323.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grants from Shanghai Commission for Science and Technology (08540702800), and the Specialized Research Fund for the Key Laboratory of Brain Functional Genomics, Ministry of Education, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Brain Functional Genomics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, Y., Wang, H., Li, J. et al. Long Distance Multiple-Site Directed Plasmid Mutagenesis by One-Step PCR Using Non-overlapped Primers. Mol Biotechnol 55, 49–53 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9665-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-013-9665-5