Abstract
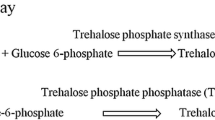
Trehalose (1-α-d-glucopyranosyl-1-α-d-glucopyranoside), a non-reducing disaccharide is a major compatible solute, which maintains fluidity of membranes and protects the biological structure of organisms under stress. In this study, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (otsA) and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase (otsB) genes encoding for trehalose biosynthesis from Escherichia coli was cloned as an operon and expressed in E. coli M15(pREP4). The recombinant E. coli strain showed a threefold increase in the activity of otsBA pathway enzymes, compared to the control strain. The transgenic E. coli accumulated up to 0.86 mg/l of trehalose. The sequence of otsA and otsB genes reported in this study contains several base substitutions with that of reported sequences in GenBank, resulting in the altered amino acid sequences of the translated proteins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madigan, M. T., & Oren, A. (1999). Thermophilic and halophilic extremophiles. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2, 265–269.
Yancey, P. H., Clark, M. E., Hand, S. C., Bowlus, R. D., & Somero, G. N. (1982). Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems. Science, 217, 1214–1222.
Richards, A. B., Krakowka, S., Dexter, L. B., Schmid, H., Wolterbeek, A. P. M., Waalkens Berendsen, D. H., et al. (2002). Trehalose: A review of properties, history of use and human tolerance, and results of multiple safety studies. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 40, 871–898.
Elbein, A. D., Pan, Y. T., Pastuszak, I., & Carroll, D. (2003). New insights on trehalose: A multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology, 13, 17R–27R.
Arguelles, J. C. (2000). Physiological roles of trehalose in bacteria and yeast: A comparative analysis. Archives of Microbiology, 174, 217–224.
Strom, A. R., & Kaasen, I. (1993). Trehalose metabolism in Escherichia coli: Stress protection and stress regulation of gene expression. Molecular Microbiology, 8, 205–210.
Horlacher, R., & Boss, W. (1997). Characterization of TreR, the major regulator of the Escherichia coli trehalose system. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 13026–13032.
Giaever, H. M., Styrvold, O. B., Kaasen, I., & Strom, A. R. (1988). Biochemical and genetic characterization of osmoregulatory trehalose synthesis in Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology, 170, 2841–2849.
Kaasen, I., McDougall, J., & Strom, A. R. (1994). Analysis of the otsBA operon for osmoregulatory trehalose synthesis in Escherichia coli and homology of the OtsA and OtsB proteins to the yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase complex. Gene, 145, 9–15.
Reinders, A., Burckert, N., Hohmann, S., Thevelein, J. M., Boller, T., Wiemken, A., et al. (1997). Structural analysis of the subunits of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their function during heat shock. Molecular Microbiology, 24, 687–695.
Maruta, K., Hattori, K., Nakada, T., Kubota, M., Sugimoto, T., & Kurimoto, M. (1996). Cloning and sequencing of trehalose biosynthesis genes from Arthrobacter sp. Q36. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1289, 10–13.
Schiraldi, C., Di Lernia, I., & De Rosa, M. (2002). Trehalose production: Exploiting novel approaches. Trends in Biotechnology, 20, 420–425.
Kienle, I., Burgert, M., & Holtzer, H. (1993). Assay of trehalose with acid trehalase purified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast, 9, 607–611.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Goddijn, O. J. M., Verwoerd, T. C., Voogd, E., Krutwagen, R. W. H. H., De Graaf, P. T. H. M., Poelos, J., et al. (1997). Inhibition of trehalase activity enhances trehalose accumulation in transgenic plants. Plant Physiology, 113, 181–190.
Bencini, D. A., Wild, J. R., & O’Donovan, G. A. (1983). Linear one-step assay for the determination of orthophosphate. Analytical Biochemistry, 132, 254–258.
Padilla, L., Kramer, R., Stephanopoulos, G., & Agosin, E. (2004). Overproduction of trehalose: Heterologous expression of Escherichia coli trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 370–376.
Uy, D., Delaunay, S., Engasser, J., & Goergen, J. (1999). A method for the determination of pyruvate carboxylase activity during the glutamic acid fermentation with Corynebacterium glutamicum. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 39, 91–96.
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., & Higgins, D. G. (1997). The CLUSTAL X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 4876–4882.
Kaasen, I., Falkenberg, P., Styrvold, O. B., & Strom, A. R. (1992). Molecular cloning and physical mapping of the otsBA genes, which encode the osmoregulatory trehalose pathway of Escherichia coli: Evidence that transcription is activated by katF (AppR). Journal of Bacteriology, 174, 889–898.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Director, Central Institute of Fisheries Technology (CIFT), Cochin for providing the necessary facilities to carry out this research work and Indian Council for Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, T.C., Rajan, L.A., Thampuran, N. et al. Functional Characterization of Trehalose Biosynthesis Genes from E. coli: An Osmolyte Involved in Stress Tolerance. Mol Biotechnol 46, 20–25 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9259-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-010-9259-4