Abstract
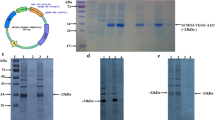
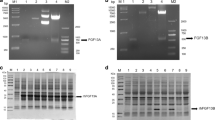
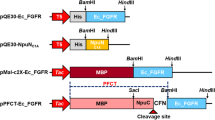
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) can stimulate the division of various cell types and has potential clinical applications that stimulate growth and differentiation. HB-EGF has an EGF-like domain typical of all members of the EGF family. The high expression of active HB-EGF in Escherichia coli has not been successful as the protein contains three intra-molecular disulfide bonds, the same as other members of the EGF super family that are difficult to form correctly in the bacterial intracellular environment. This work fused the non-glycosylated HB-EGF gene with a small ubiquitin-related modifier gene (SUMO) by over-lap PCR. The resulting fusion gene SUMO-HBEGF was highly expressed in BL21(DE3) that the soluble SUMO-HBEGF was up to 30% of the total cellular protein. The fusion protein was purified by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography and cleaved by a SUMO-specific protease Ulp1 to obtain the native HB-EGF, which was further purified by Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. MTT assays indicated the purified HB-EGF, as well as SUMO-HBEGF, had mitogenic activity in a dose-dependent manner.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerhard, R., & Michael, K. (1997). Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1333, F179–F199.
Lee, K. S., Park, J. H., Lee, S., Lim, H. J., Choi, H. E., & Park, H. Y. (2007). HB-EGF induces delayed STAT3 activation via NF-κB mediated IL-6 secretion in vascular smooth muscle cell. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1773, 1637–1644.
Tan, Y., Li, M., Cox, S., Davis, M. K., Tawfik, O., Paria, B. C., et al. (2004). HB-EGF directs stromal cell polyploidy and decidualization via cyclin D3 during implantation. Developmental Biology, 265, 181–195.
Chobotova, K., Spyropoulou, I., Carver, J., Manek, S., Heath, J. K., Gullick, W. J., et al. (2002). Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor and its receptor ErbB4 mediate implantation of the human blastocyst. Mechanisms of Development, 119, 137–144.
Iwamoto, R., & Mekada, E. (2000). Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor: A juxtacrine growth factor. Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews, 11, 335–344.
Su, Z., Huang, Y., Zhou, Q., Wu, Z., Wu, X., Zheng, Q., et al. (2006). High-level expression and purification of human epidermal growth factor with SUMO fusion in Escherichia coli. Protein and Peptide Letters, 8, 785–792.
Le, P. U., Lenferink, A. E., Pinard, M., Baardsnes, J., Massie, B., & O’Connor-McCourt, M. D. (2009). Escherichia coli expression and refolding of E/K-coil-tagged EGF generates fully bioactive EGF for diverse applications. Protein Expression and Purification, 64, 108–117.
Abdull Razis, A. F., Ismail, E. N., Hambali, Z., Abdullah, M. N., Ali, A. M., & Mohd-Lila, M. A. (2008). Expression of recombinant human epidermal growth factor in Escherichia coli and characterization of its biological activity. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 144, 249–261.
Sharma, K., Babu, P. V., Sasidhar, P., Srinivas, V. K., Mohan, V. K., & Krishna, E. (2008). Recombinant human epidermal growth factor inclusion body solubilization and refolding at large scale using expanded-bed adsorption chromatography from Escherichia coli. Protein Expression and Purification, 60, 7–14.
Sun, Z., Xia, Z., Bi, F., & Liu, J. N. (2008). Expression and purification of human urodilatin by small ubiquitin-related modifier fusion in Escherichia coli. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 78, 495–502.
Malakhov, M. P., Mattern, M. R., Malakhova, O. A., Drinker, M., Weeks, S. D., & Butt, T. R. (2004). SUMO fusions and SUMO-specific protease for efficient expression and purification of proteins. Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics, 5, 75–86.
Marblestone, J. G., Edavett, S. C., Lim, Y., Lim, P., Zuo, X., & Butt, T. R. (2006). Comparison of SUMO fusion technology with traditional gene fusion systems: Enhanced expression and solubility with SUMO. Protein Science, 15, 1182–1189.
Zuo, X., Li, S., Hall, J., Mattern, M. R., Tran, H., Shoo, J., et al. (2005). Enhanced expression and purification of membrane proteins by SUMO fusion in Escherichia coli. Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics, 6, 103–111.
Lee, C. D., Sun, H. C., Hu, S. M., Chiu, C. F., Homhuan, A., Liang, S. M., et al. (2008). An improved SUMO fusion protein system for effective production of native proteins. Protein Science, 17, 1241–1248.
Lu, W. G., Cao, P., Cai, X. T., Yu, J. M., Hu, C. P., Cao, M., et al. (2009). Molecular cloning, expression, and bioactivity of dove B lymphocyte stimulator (doBAFF). Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 128, 5374–5380.
Cao, P., Zhang, S. Q., Zhang, J., & Wang, M. (2006). Construction and characterization of a bi-functional EGFP/sBAFF fusion protein. Biochimie, 88, 29–635.
Ferrer Soler, L., Cedano, J., Querol, E., & de Llorens, R. (2003). Cloning, expression and purification of human epidermal growth factor using different expression systems. Journal of Chromatography. B. Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 788, 113.
Butt, T. R., Edavettal, S. C., Hall, J. P., & Mattern, M. R. (2005). SUMO fusion technology for difficult-to-express proteins. Protein Expression and Purification, 43, 1–9.
Ahn, J. W., Lee, Y. A., Ahn, J. H., & Choi, C. Y. (2009). Covalent conjugation of Groucho with SUMO-1 modulates its corepressor activity. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 379, 160–165.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from Nature Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. SBK20082754) and the Scientific and Technological Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2008C33062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, W., Cao, P., Lei, H. et al. High-Level Expression and Purification of Heparin-Binding Epidermal Growth Factor (HB-EGF) with SUMO Fusion. Mol Biotechnol 44, 198–203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9226-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9226-0