Abstract
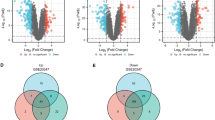
The mechanism by which DNMT3B facilitates esophageal cancer (ESCA) progression is currently unknown, despite its association with adverse prognoses in several cancer types. To investigate the potential therapeutic effects of the Chinese herbal medicine rhubarb on esophageal cancer (ESCA), we adopted an integrated bioinformatics approach. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was first utilized to screen active anti-ESCA components in rhubarb. We then employed Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) to identify key molecular modules and targets related to the active components and ESCA pathogenesis. This system-level strategy integrating multi-omics data provides a powerful means to unravel the molecular mechanisms underlying the anticancer activities of natural products, like rhubarb. To investigate module gene functional enrichment, Gene Ontology (GO), and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were conducted. In addition, we evaluated the predictive impact of DNMT3B expression on ESCA patients utilizing the Kaplan–Meier method. Finally, we conducted experiments on cell proliferation and the cell cycle to explore the biological roles of DNMT3B. In this study, we identified Rhein as the main active ingredient of rhubarb that exhibited significant anti-ESCA activity. Rhein markedly suppressed ESCA cell proliferation. Utilizing Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis, we determined that the blue module was associated with Rhein target genes and the cell cycle. Additionally, DNMT3B was identified as a Rhein target gene. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database revealed that higher DNMT3B levels were associated with poor prognosis in ESCA patients. Furthermore, Rhein partially reversed the overexpression of DNMT3B to inhibit ESCA cell proliferation. In vitro studies demonstrated that Rhein and DNMT3B inhibition disrupted the S phase of the cell cycle and affected the production of cell cycle-related proteins. In this study, we found that Rhein exerts its anti-proliferative effects in ESCA cells by targeting DNMT3B and regulating the cell cycle.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7–33.
Huang FL, Yu SJ. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J Surg. 2018;41(3):210–5.
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381(9864):400–12.
Zhang HZ, Jin GF, Shen HB. Epidemiologic differences in esophageal cancer between Asian and Western populations. Chin J Cancer. 2012;31(6):281–6.
Tian SL, Yang Y, Liu XL, Xu QB. Emodin attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities in rats. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:1–10.
Gao Y, Chen X, Fang L, Liu F, Cai R, Peng C, Qi Y. Rhein exerts pro- and anti-inflammatory actions by targeting IKKβ inhibition in LPS-activated macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;72:104–12.
Shia CS, Suresh G, Hou YC, Lin YC, Chao PD, Juang SH. Suppression on metastasis by rhubarb through modulation on MMP-2 and uPA in human A549 lung adenocarcinoma: an ex vivo approach. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;133(2):426–33.
Hopkins AL. Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(11):682–90.
Wu L, Liu X, Cao KX, Ni ZH, Li WD, Chen ZP. Synergistic antitumor effects of rhein and doxorubicin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(10):4009–21.
Zhao Q, Wang X, Chen A, Cheng X, Zhang G, Sun J, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Zhu Y. Rhein protects against cerebral ischemic-/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(5):2802–12.
Wen Q, Miao J, Lau N, Zhang C, Ye P, Du S, Mei L, Weng H, Xu Q, Liu X, Chen D, Zhang F, Li C, Li H. Rhein attenuates lipopolysaccharide-primed inflammation through NF-κB inhibition in RAW264.7 cells: targeting the PPAR-γ signal pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;98(6):357–65.
Guo MZ, Li XS, Xu HR, Mei ZC, Shen W, Ye XF. Rhein inhibits liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002;23(8):739–44.
Zhang Q, Yin S, Liu L, Liu Z, Cao W. Rhein reversal of DNA hypermethylation-associated Klotho suppression ameliorates renal fibrosis in mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34597.
Tu Y, Gu L, Chen D, Wu W, Liu H, Hu H, Wan Y, Sun W. Rhein inhibits autophagy in rat renal tubular cells by regulation of AMPK/mTOR Signaling. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43790.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(43):15545–50.
Tominaga H, et al. A water-soluble tetrazolium salt useful for colorimetric cell viability assay. Anal Commun. 1999;36:47–50.
Tierney, L. (2012). The R Statistical Computing Environment. In: Feigelson, E., Babu, G. (eds) Statistical Challenges in Modern Astronomy V. Lecture Notes in Statistics, volume 902. Springer, New York, NY.
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009;30(16):2785–91.
N. Alexander, N. Woetzel and J. Meiler, "Bcl::Cluster: A method for clustering biological molecules coupled with visualization in the Pymol Molecular Graphics System," 2011 IEEE 1st International Conference on Computational Advances in Bio and Medical Sciences (ICCABS), Orlando, FL, USA, 2011, pp. 13–18.
Chen YY, Chiang SY, Lin JG, Ma YS, Liao CL, Weng SW, Lai TY, Chung JG. Emodin, aloe-emodin and rhein inhibit migration and invasion in human tongue cancer SCC-4 cells through the inhibition of gene expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Int J Oncol. 2010;36(5):1113–20.
Lin ML, Chen SS, Lu YC, Liang RY, Ho YT, Yang CY, Chung JG. Rhein induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial death pathway in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(5A):3313–22.
Zhou G, Peng F, Zhong Y, Chen Y, Tang M, Li D. Rhein suppresses matrix metalloproteinase production by regulating the Rac1/ROS/MAPK/AP-1 pathway in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2017;50(3):933–41.
Zhen YZ, Lin YJ, Gao JL, Zhao YF, Xu AJ. Rhein lysinate inhibits cell growth by modulating various mitogen-activated protein kinases in cervical cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2011;2(1):129–33.
Lin YJ, Zhen YS. Rhein lysinate suppresses the growth of breast cancer cells and potentiates the inhibitory effect of Taxol in athymic mice. Anticancer Drugs. 2009;20(1):65–72.
Shi P, Huang Z, Chen G. Rhein induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402 cells. Am J Chin Med. 2008;36(4):805–13.
Yang L, Lin S, Kang Y, Xiang Y, Xu L, Li J, Dai X, Liang G, Huang X, Zhao C. Rhein sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells to EGFR inhibitors by inhibiting STAT3 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):31.
Wang A, Jiang H, Liu Y, Chen J, Zhou X, Zhao C, Chen X, Lin M. Rhein induces liver cancer cells apoptosis via activating ROS-dependent JNK/Jun/caspase-3 signaling pathway. J Cancer. 2020;11(2):500–7.
Gabano E, Gariboldi MB, Caron G, Ermondi G, Marras E, Vallaro M, Ravera M. Application of the anthraquinone drug rhein as an axial ligand in bifunctional Pt(IV) complexes to obtain antiproliferative agents against human glioblastoma cells. Dalton Trans. 2022;51(15):6014–26.
He ZH, Zhou R, He MF, Lau CB, Yue GG, Ge W, But pp. Anti-angiogenic effect and mechanism of rhein from Rhizoma Rhei. Phytomedicine. 2011;18(6):470–8.
Gagliardi M, Strazzullo M, Matarazzo MR. DNMT3B functions: novel insights from human disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:140.
Leppert S, Matarazzo MR. De novo DNMTs and DNA methylation: novel insights into disease pathogenesis and therapy from epigenomics. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(11):1812–8.
Cao Y, Xu K, Chen B, Wang Y, Li B, Li C, Xu P. Expression of DNMT3b in human bladder cancer tissue and its correlation with clinical prognosis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020;40(9):1295–300 (Chinese).
Chen WC, Chen MF, Lin PY. Significance of DNMT3b in oral cancer. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(3): e89956.
Lai SC, Su YT, Chi CC, Kuo YC, Lee KF, Wu YC, Lan PC, Yang MH, Chang TS, Huang YH. DNMT3b/OCT4 expression confers sorafenib resistance and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through IL-6/STAT3 regulation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):474.
Xu K, Chen B, Li B, Li C, Zhang Y, Jiang N, Lang B. DNMT3B silencing suppresses migration and invasion by epigenetically promoting miR-34a in bladder cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(23):23668–83.
Zhu A, Hopkins KM, Friedman RA, Bernstock JD, Broustas CG, Lieberman HB. DNMT1 and DNMT3B regulate tumorigenicity of human prostate cancer cells by controlling RAD9 expression through targeted methylation. Carcinogenesis. 2021;42(2):220–31.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Research project of Health Commission of Heilongjiang Province (Grant number 20221313050598). In addition, the authors would like to thank The Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical University for their support in conducting the experiments and data analysis. We also appreciate the help of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical University in editing the manuscript.
Funding
Research project of Health Commission of Heilongjiang Province (Grant Number 20221313050598).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.L. provided study materials and patients. B.X.W. conceived and designed the manuscript. W.H.N. provided administrative support. J.J.Y. collected and curated the data. Y.F. analyzed and interpreted the data. X.X.S., M.M.S., and J.S. wrote the main manuscript text. All authors approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have stated that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
As a result, no ethical approval was required.
Research involving human/animal participants
This study did not involve any animal or human experimentation.
Consent for publication
This manuscript does not contain any data from human or animal subjects. Therefore, no patient consent for publication is required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Yu, J., Feng, Y. et al. Rhein suppresses esophageal cancer development by regulating cell cycle through DNMT3B gene. Med Oncol 41, 153 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-024-02359-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-024-02359-9