Abstract
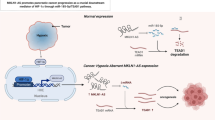
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) play important roles in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and tumor development. Previous studies have demonstrated that IL-6 promotes EMT, invasion, and metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) cells by activating the STAT3/HIF-1α pathway. MicroRNA (miRNA) is non-coding small RNAs that also play an important role in tumor development. Notably, Let-7 and miR-200 families are prominently altered in EOC. However, whether IL-6 regulates the expression of Let-7 and miR-200 families through the STAT3/HIF-1α signaling to induce EMT in EOC remains poorly understood. In this study, we conducted in vitro and in vivo investigations using two EOC cell lines, SKOV3, and OVCAR3 cells. Our findings demonstrate that IL-6 down-regulates the mRNA levels of Let-7c and miR-200c while up-regulating their target genes HMGA2 and ZEB1 through the STAT3/HIF-1α signaling in EOC cells and in vivo. Additionally, to explore the regulatory role of HIF-1α on miRNAs, both exogenous HIF blockers YC-1 and endogenous high expression or inhibition of HIF-1α can be utilized. Both approaches can confirm that the downstream molecule HIF-1α inhibits the expression and function of Let-7c and miR-200c. Further mechanistic research revealed that the overexpression of Let-7c or miR-200c can reverse the malignant evolution of EOC cells induced by IL-6, including EMT, invasion, and metastasis. Consequently, our results suggest that IL-6 regulates the expression of Let-7c and miR-200c through the STAT3/HIF-1α pathway, thereby promoting EMT, invasion, and metastasis in EOC cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. 2020;71(2021):209–49.
Cooke SL, Brenton JD. Evolution of platinum resistance in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:1169–74.
Yuan Y. Il-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes the generation of breast cancer stem-like cells analogous to mammosphere cultures. Int J Oncol. 2011;40:1171–9.
Gyamfi J, Lee Y, Eom M, Choi J. Interleukin-6/stat3 signalling regulates adipocyte induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8:8859.
Zhang T, Yang J, Sun Y, Song J. Interleukin-6 and hypoxia synergistically promote EMT-mediated invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer via the IL-6/STAT3/HIF-1α feedback loop. Anal Cell Pathol. 2023;2023:1–14.
Xu S, Yu C, Ma X, et al. IL-6 promotes nuclear translocation of HIF-1α to aggravate chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;894: 173817.
Pan G, Liu Y, Shang L, Zhou F, Yang S. EMT-associated microRNAs and their roles in cancer stemness and drug resistance. Cancer Commun. 2021;41(3):199–217.
Macciò A, Madeddu C. The role of interleukin-6 in the evolution of ovarian cancer: clinical and prognostic implications-a review. J Mol Med. 2013;91:1355–68.
Bose S, Saha P, Chatterjee B, Srivastava AK. Chemokines driven ovarian cancer progression, metastasis and chemoresistance: potential pharmacological targets for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86(Pt 2):568–79.
Mir MA, Bashir M, Jan N. The role of interleukin (IL)-6/IL-6 receptor axis in cancer, cytokine and chemokine networks in cancer. Singapore: Springer; 2023. p. 137–64.
Colomiere M, Ward AC, Riley C, Trenerry MK, Cameron-Smith D, Findlay J, et al. Cross talk of signals between EGFR and IL-6 through jak2/stat3 mediate epithelial–mesenchymal transition in ovarian carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:134–44.
Cheng Z, Sun B, Wang S, Gao Y, Zhang Y, Zhou H, et al. Nuclear factor-κb–dependent epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by HIF-1α activation in pancreatic cancer cells under hypoxic conditions. PLoS ONE. 2011;6: e23752.
Cheng Z, Wang D, Liu T, Liu W, Xia W, Xu J, et al. Effects of the hif-1α and NF-κb loop on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance induced by hypoxia in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2014;31:1891–8.
Joseph JV, Conroy S, Pavlov K, Sontakke P, Tomar T, Eggens-Meijer E, et al. Hypoxia enhances migration and invasion in glioblastoma by promoting a mesenchymal shift mediated by the HIF1α-ZEB1 axis. Cancer Lett. 2015;359:107–16.
Yang M, Wu K. Twist activation by hypoxia inducible factor-1 (hif-1): implications in metastasis and development. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2090–6.
Zare M, Bastami M, Solali S, Alivand MR. Aberrant mirna promoter methylation and emt-involving mirnas in breast cancer metastasis: diagnosis and therapeutic implications. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:3729–44.
Mahmood N, Mushtaq S, Jamal Q, Hanif M, Akhlaq H, Awan R. Potential utility of cell free high mobility group at-hook 2 (hmga2) as a prognostic biomarker in liquid biopsies of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev: APJCP. 2021;22:407.
Guo L, Chen C, Shi M, Wang F, Chen X, Diao D, et al. Stat3-coordinated lin-28–let-7–hmga2 and mir-200–zeb1 circuits initiate and maintain oncostatin m-driven epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 2013;32:5272–82.
Mahajan A, Liu Z, Gellert L, Zou X, Yang G, Lee P, et al. Hmga2: a biomarker significantly overexpressed in high-grade ovarian serous carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2010;23:673–81.
Shi Z, Li X, Wu D, Tang R, Chen R, Xue S, et al. Silencing of hmga2 suppresses cellular proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer. Tumor Biology. 2016;37:7515–23.
Xi Y, Xin X, Ye H. Effects of hmga2 on malignant degree, invasion, metastasis, proliferation and cellular morphology of ovarian cancer cells. Asian Pacific J Trop Med. 2014;7:289–92.
Sulaiman SA, Ab Mutalib N, Jamal R. Mir-200c regulation of metastases in ovarian cancer: potential role in epithelial and mesenchymal transition. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:271.
Abaurrea A, Araujo AM, Caffarel MM. The role of the IL-6 cytokine family in epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8334.
Huang CX, Chen N, Wu XJ, He Y, Huang CH, Liu H, Wang WM, Wang HL. Zebrafish let-7b acts downstream of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α to assist in hypoxia-mediated cell proliferation and cell cycle regulation. Life Sci. 2017;171:21–9.
Shang Y, Chen H, Ye J, Wei X, Liu S, Wang R. Hif-1α/ascl2/mir-200b regulatory feedback circuit modulated the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2017;360:243–56.
Yang W, Ma J, Zhou W, Cao B, Zhou X, Zhang H, Zhao Q, Liu H, Fan D. Reciprocal regulations between miRNAs and HIF-1α in human cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(3):453–71.
Shan F, Li J, Huang QY. HIF-1 alpha-induced up-regulation of miR-9 contributes to phenotypic modulation in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells during hypoxia. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(10):1511–20.
Kang L, Cui X, Zhang Y, Yang C, Jiang Y. Identification of microRNAs associated with sexual maturity in chicken ovary by illumina small RNA deep sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:352.
Gao Y, Wu J. Microrna-200c and microrna-141 as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Tumor Biology. 2015;36:4843–50.
Tsai C, Lin L, Wang C, Chiu Y, Chou Y, Chiu S, et al. Over-expression of cofilin-1 suppressed growth and invasion of cancer cells is associated with up-regulation of let-7 microRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1852;2015:851–61.
Yan Y, Zhang F, Fan Q, Li X, Zhou K. Breast cancer-specific trail expression mediated by miRNA response elements of let-7 and mir-122. Neoplasma. 2014;61:672–9.
Canale M, Foschi FG, Andreone P, Ercolani G, Marisi G, Conti F, et al. Role of circulating microRNAs to predict hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence in patients treated with radiofrequency ablation or surgery. HPB. 2022;24:244–54.
Mayr C, Hemann MT, Bartel DP. Disrupting the pairing betweenlet-7 and hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science. 2007;315:1576–9.
Rokavec M, Wu W, Luo J. IL6-mediated suppression of mir-200c directs constitutive activation of inflammatory signaling circuit driving transformation and tumorigenesis. Mol Cell. 2012;45:777–89.
Garg M, Potter JA, Abrahams VM. Identification of microRNAs that regulate tlr2-mediated trophoblast apoptosis and inhibition of IL-6 miRNA. PLoS ONE. 2013;8: e77249.
Kim HL, Cassone M, Otvos L, Vogiatzi P. HIF-1α and STAT3 client proteins interacting with the cancer chaperone Hsp90: therapeutic considerations. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7(1):10–4.
Nilsson CL, Dillon R, Devakumar A, Shi SDH, Greig M, Rogers JC, et al. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of the stat3/il-6/hif1α signaling network: an initial study in gsc11 glioblastoma stem cells. J Proteome Res. 2010;9:430–43.
Kozak J, Jonak K, Maciejewski R. The function of mir-200 family in oxidative stress response evoked in cancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;125: 110037.
Wong T, Man O, Tsang C, Tsao S, Tsang RK, Chan JY, et al. MicroRNA let-7 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells proliferation through down regulating c-myc expression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137:415–22.
Li Q, Shi J, Liu W. The role of wnt/β-catenin-lin28a/let-7 axis in embryo implantation competency and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18:108.
Korpal M, Kang Y. The emerging role of miR-200 family of microRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. RNA Biol. 2008;5(3):115–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Andrew L Kung (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, USA) for providing pCMVh-HA-ssHIF-1α and the control pCMVh-HA plasmids.
Funding
This research was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81572852, 81273520), the Great Program of Science Foundation of Tianjin (No. 18JCZDJC33200) and Center Innovation Team Project (KYCXTD0502, KYCXTD0203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QYG, JNS and YMC conceived the work that led to the acquisition of literatures and drafted the manuscript. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by HNY and WSX. YS and XN provided supervision throughout the study. YW and XC designed the outline of the review, revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Q.Y., Song, J.N., Chen, Y.M. et al. IL-6 regulates epithelial ovarian cancer EMT, invasion, and metastasis by modulating Let-7c and miR-200c through the STAT3/HIF-1α pathway. Med Oncol 41, 155 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-024-02328-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-024-02328-2