Abstract
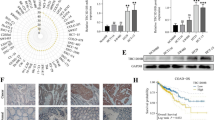
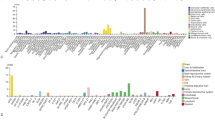
Sine oculis homeobox 4 (SIX4), a critical transcription factor modulating organ development, potentially participates in tumorigenesis through numerous pathways. Here, we investigated siRNA-mediated knockdown effects of SIX4 on pancreatic cancer cells and underlying molecular mechanisms. The expression of SIX4 in pancreatic cancer and adjacent tissues were investigated in clinical tissue samples and bioinformatically approved by gene expression omnibus (GEO) database. Appropriate siRNA transfected into PANC1 pancreatic cancer cells in order to SIX4 knockdown. The survival, migration, invasion, colony formation, mitochondrial membrane potential, apoptosis, autophagy, and cell cycle in the cancer cells were investigated after knockdown of SIX4. In addition, expression of genes involved in apoptosis and metastasis were assessed in the transfected cancer cells in mRNA and protein levels. High-throughput analysis using GEO database confirmed the overexpression of SIX4 in pancreatic cancer tissues by six independent pancreatic cancer microarrays. Knockdown of SIX4 by specific siRNA significantly decreased survival, colony formation, and mitochondrial membrane potential of the cancer cells. Further assessments demonstrated that knockdown of SIX4 increases the apoptosis and autophagy rates in the cancer cells through modifying the expression of related genes. Moreover, a significant decrease in migration and invasion rates were observed in SIX4 suppressed group. Furthermore, frequency of the cells transfected with SIX4 siRNA increased slightly in G1 and Sub-G1 phases of cell cycle. Our study suggested that siRNA-mediated knockdown of SIX4 increases the pancreatic cancer cells death and reduces the invasion and migration of the cancer cells through different molecular pathways.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Maisonneuve P. Epidemiology and burden of pancreatic cancer. La Presse Médicale. 2019;48(3):e113–23.
Jadid MF, Shademan B, Chavoshi R, Seyyedsani N, Aghaei E, Taheri E, Goleij P, Hajazimian S, Karamad V, Behroozi J, Sabet MN. Enhanced anticancer potency of hydroxytyrosol and curcumin by PLGA-PAA nano-encapsulation on PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cell line. Environ Toxicol. 2021;36(6):1043–51.
Mehralizadeh H, Nazari A, Oruji F, Roostaie M, Hosseininozari G, Yazdani O, Esbati R, Roudini K. Cytokine sustained delivery for cancer therapy; special focus on stem cell-and biomaterial-based delivery methods. Pathol-Res Pract. 2023;247: 154528.
Cicenas J, Kvederaviciute K, Meskinyte I, Meskinyte-Kausiliene E, Skeberdyte A, Cicenas J Jr. KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, SMAD4, BRCA1, and BRCA2 mutations in pancreatic cancer. Cancers. 2017;9(5):42.
Shabani S, Moghadam MF, Gargari SL. Isolation and characterization of a novel GRP78-specific single-chain variable fragment (scFv) using ribosome display method. Med Oncol. 2021;38(9):115.
Hu S, Mamedova A, Hegde RS. DNA-binding and regulation mechanisms of the SIX family of retinal determination proteins. Biochemistry. 2008;47(11):3586–94.
Kawakami K, Ohto H, Ikeda K, Roeder RG. Structure, function and expression of a murine homeobox protein AREC3, a homologue of Drosophila sine oculis gene product, and implication in development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996;24(2):303–10.
Hashemi A, Bigdeli R, Shahnazari M, Oruji F, Fattahi S, Panahnejad E, Ghadri A, Movahedi-Asl E, Mahdavi-Ourtakand M, Asgary V, Baghbani-Arani F. Evaluation of inflammasome activation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of hemodialysis treated patients with glomerulonephritis. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021;20(3):609.
Wurmser M, Chaverot N, Madani R, Sakai H, Negroni E, Demignon J, Saint-Pierre B, Mouly V, Amthor H, Tapscott S, Birchmeier C. SIX1 and SIX4 homeoproteins regulate PAX7+ progenitor cell properties during fetal epaxial myogenesis. Development. 2020;147(19):dev185975.
Tang X, Yang Y, Song X, Liu X, Wang X, Huang F, Li Y, Chen F, Wan H. SIX4 acts as a master regulator of oncogenes that promotes tumorigenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;516(3):851–7.
Wang CA, Drasin D, Pham C, Jedlicka P, Zaberezhnyy V, Guney M, Li H, Nemenoff R, Costello JC, Tan AC, Ford HL. Homeoprotein Six2 promotes breast cancer metastasis via transcriptional and epigenetic control of E-cadherin expression. Cancer Res. 2014;74(24):7357–70.
Kaboli PJ, Shabani S, Sharma S, Nasr MP, Yamaguchi H, Hung MC. Shedding light on triple-negative breast cancer with Trop2-targeted antibody-drug conjugates. Am J Cancer Res. 2022;12(4):1671.
Na XY, Shang XS, Zhao Y, Ren PP, Hu XQ. MiR-203a functions as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer by targeting SIX4. Neoplasma. 2019;66(2):211–21.
Li G, Hu F, Luo X, Hu J, Feng Y. SIX4 promotes metastasis via activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. PeerJ. 2017;5: e3394.
Wei Q, Yu WW, Zhao KL, Fu XL, Zhu ZF, Qin GQ, Chen H, Zhang ZX, Gu YZ, Xiang JQ, Chen HQ. Expression of Six1 and Six4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their correlation with clinical prognosis. China J Pathol. 2013;42(7):446–50.
Camolotto SA, Belova VK, Torre-Healy L, Vahrenkamp JM, Berrett KC, Conway H, Shea J, Stubben C, Moffitt R, Gertz J, Snyder EL. Reciprocal regulation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth and molecular subtype by HNF4α and SIX1/4. Gut. 2021;70(5):900–14.
Kozani PS, Shabani S. Adverse events and side effects of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy in patients with hematologic malignancies. Trends Med Sci. 2021;1(1): e116301.
Mohamed RJ, Aldulaimi A, Aowda SA. Synthesized of new alkaloid compounds and study their anticancer activity. AIP Conf Proc. 2022;2660(1):020082.
Rabiee F, Eghbalifard N, Fathi M, Rajabi H, Riazi SS. Evaluation of the potential of the MicroRNAs to predict chemotherapy resistance in breast cancer patients: a systemic review with meta-analysis. Int J Sci Res Dent Med Sci. 2023.
Fathi M, Riazi SS, Pourdamghan N. Triple-negative breast cancer therapy using RNA nanoparticles targeting stem cell markers with anti-miRNA: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Sci Res Dent Med Sci. 2023;5:96–101.
Esmailzadeh S, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Shanehbandi D, Baradaran B. siRNA-mediated silencing of HMGA2 induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human colorectal carcinoma. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2017;48(2):156–63.
Hoelder S, Clarke PA, Workman P. Discovery of small molecule cancer drugs: successes, challenges and opportunities. Mol Oncol. 2012;6(2):155–76.
Sun X, Ma J, Chen Q, Hou Z, Luo X, Wang G, Wang J, Hu J, Cao Z. SIX4 promotes metastasis through STAT3 activation in breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(1):224.
Oruji F, Baghbani Arani F, Mahdavi OM. Evaluation of the gene expression of IL-1β and Casp-1 related to inflammation process in glomerulonephritis patients. J Anim Environ. 2018;10(3):477–82.
Soheilyfar S, Velashjerdi Z, Hajizadeh YS, Maroufi NF, Amini Z, Khorrami A, Azimian SH, Isazadeh A, Taefehshokr S, Taefehshokr N. In vivo and in vitro impact of miR-31 and miR-143 on the suppression of metastasis and invasion in breast cancer. J Buon. 2018;23(5):1290–6.
Salehi Kahrizsangi F, Mehrafar N, Pezhman Ghadami F, Rabiee F, Shariati Y. Evaluation of the clinical outcome of nab-paclitaxel on multiple primary malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Sci Res Dent Med Sci. 2022;4(4):183–90.
Taheri E, Ghorbani S, Safi M, Sani NS, Amoodizaj FF, Hajazimian S, Heidari M, Isazadeh A, Heidari M. Inhibition of colorectal cancer cell line CaCo-2 by essential oil of Eucalyptus camaldulensis through induction of apoptosis. Acta Med Iran. 2020;58(6):260–5.
Isazadeh A, Hajazimian S, Shadman B, Safaei S, Bedoustani AB, Chavoshi R, Shanehbandi D, Mashayekhi M, Nahaei M, Baradaran B. Anti-cancer effects of probiotic lactobacillus acidophilus for colorectal cancer cell line caco-2 through apoptosis induction. Pharm Sci. 2020;27(2):262–7.
Fath MK, Naderi M, Hamzavi H, Ganji M, Shabani S, Khalesi B, Pourzardosht N, Hashemi ZS, Khalili S. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic effects of different vitamins and minerals in COVID-19 patients. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022;73: 127044.
Emre Kızıl H, Gür C, Ayna A, Darendelioğlu E, Küçükler S, Sağ S. Contribution of oxidative stress, apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy pathways to the ameliorative effects of hesperidin in NaF-induced testicular toxicity. Chem Biodivers. 2023;20(3): e202200982.
Varışlı B, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Gür C, Ayna A, Genç A, Taysı S. Chrysin mitigates diclofenac-induced hepatotoxicity by modulating oxidative stress, apoptosis, autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(1):433–42.
Azziz SS, Aldulaimi AK, Aowda SA, Bakri YM, Majhool AA, Ibraheem RM, Aldulaimi TK, Idris H, Wong CF, Awang K, Litaudon M. Secondary metabolites from leaves of Polyalthia lateriflora and their antimicrobial activity. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2020;11(3):4353–8.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the whole staff of the Immunology Research Center of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences and Gastroenterology and Liver Disease Research Center of Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences for their assistance in this research. We also thank the whole staff of the Imam Khomeini Hospital for providing cancer tissue samples.
Funding
This project was financially supported by the funds from the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences and Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BB, and MH conceived and designed research. ER and JG conducted the experiments. MA contributed new reagents or analytical tools. MA and JB analyzed the data. AI wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript and all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no financial or non-financial interests that are directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
Ethical approval
This research was reviewed and approved by the Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences institutional review board. All participants were informed about the study and signed a consent form according to the Declaration of Helsinki ethical standards (the ethical code: IR.BMSU.REC.1399.426).
Consent for publication
All the authors read and agreed to publish this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Heiat, M., Rezaei, E., Gharechahi, J. et al. Knockdown of SIX4 inhibits pancreatic cancer cells via apoptosis induction. Med Oncol 40, 287 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02163-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02163-x