Abstract
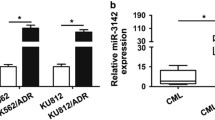
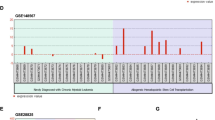
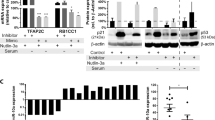
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is characterized by presence of Philadelphia chromosome, which harbors BCR-ABL oncogene responsible for encoding BCR-ABL oncoprotein. This oncoprotein interferes with cellular signaling pathways, resulting in tumor progression. Among these pathways, PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway is significantly upregulated in CML. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are current standard therapy for CML, and they have shown remarkable efficacy. However, emergence of TKIs drug resistance has necessitated investigation of novel therapeutic approaches. Components of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway have emerged as attractive targets in this context, as this pathway is known to be activated in TKIs-resistant CML cells/patients. Inhibiting this pathway may provide a complementary approach to improving TKIs’ efficacy and treatment outcomes. Given previous research indicating that miRNAs play an inhibitory role in cancer, current study used computational tools to identify miRNAs that specifically target pathway’s core components. A comprehensive analysis was performed, resulting in identification of 111 miRNAs that potentially target PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. From this extensive list, 7 miRNAs was selected for further investigation based on their consistent downregulation across leukemia subtypes. Except for hsa-miR-199a-3p, remaining six miRNAs have been extensively studied in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Given high similarity between AML and CML, it is believed that six miRNAs which are not studied in context of CML may also be advantageous for curing chemoresistance in CML. Building upon this knowledge, it is reasonable to speculate that a combination therapy approach involving use of miRNAs alongside TKIs may offer improved therapy for TKIs-resistant CML compared to TKIs monotherapy alone.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated for the preparation of this manuscript.
References
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV. The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000;96:3343–56.
Singh P, Gupta SK, Ali V, Verma M. Downregulation of bcr-abl oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia by micro RNAs. Asian Pac J Health Sci. 2018;5:65–84.
Saußele S, Silver RT. Management of chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis. Ann Hematol. 2015;94:159–65.
Singh P, Kumar V, Gupta SK, Kumari G, Verma M. Combating TKI resistance in CML by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in combination with TKIs: a review. Med Oncol. 2021;38:1–16.
Aalto AP, Pasquinelli AE. Small non-coding RNAs mount a silent revolution in gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24:333–40.
Mendell JT, MicroRNAs. Critical regulators of Development, Cellular Physiology and Malignancy. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:1179–84.
Wang Z, Zhou H, Cheng F, Zhang Z, Long S. MiR-21 regulates epithelial–mesenchymal transition in intestinal fibrosis of Crohn’s disease by targeting PTEN/mTOR. Dig Liv Dis. 2022;54:1358–66.
Huang C, Huang J, Ma P, Yu G. microRNA-143 acts as a suppressor of hemangioma growth by targeting Bcl-2. Gene. 2017;628:211–17.
Kharas MG, Fruman DA. ABL oncogenes and phosphoinositide 3-Kinase: mechanism of activation and downstream Effectors. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2047–53.
Foukas LC, Berenjeno IM, Gray A, Khwaja A, Vanhaesebroeck B. Activity of any class IA PI3K isoform can sustain cell proliferation and survival. PNAS. 2010;107:11381–86.
Ren S, Xue F, Feng J, Skorski T. Intrinsic regulation of the interactions between the SH3 domain of p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and the protein network of BCR/ABL oncogenic tyrosine kinase. Exp Hematol. 2005;33:1222–28.
Jean S, Kiger AA. Classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:923–8.
Hay N. The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:179–83.
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P, Helman LJ. Rapamycin induces feedback activation of akt signaling through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 2007;26:1932–40.
Malanga D, Scrima M, De Marco C, Fabiani F, De Rosa N, de Gisi S, et al. Activating E17K mutation in the gene encoding the protein kinase AKT in a subset of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:665–9.
Yang J, Nie J, Ma X, Wei Y, Peng Y, Wei X. Targeting PI3K in cancer: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:26.
Janku F. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway inhibitors in solid tumors: from laboratory to patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;59:93–101.
Gericke A, Leslie NR, Lösche M, Ross AH. PtdIns(4,5)P2-Mediated cell signaling: emerging principles and PTEN as a paradigm for Regulatory mechanism. 2013. p.85–104.
Szymonowicz K, Oeck S, Malewicz N, Jendrossek V. New Insights into protein kinase B/Akt signaling: role of localized akt activation and compartment-specific target proteins for the Cellular Radiation Response. Cancers. 2018;10:78.
Danisz K, Blasiak J. Role of anti-apoptotic pathways activated by BCR/ABL in the resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia cells to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Biochim Pol. 2013;60–72.
Mojtahedi H, Yazdanpanah N, Rezaei N. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells: targeting therapeutic implications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:603–30.
Rossari F, Minutolo F, Orciuolo E. Past, present, and future of bcr-abl inhibitors: from chemical development to clinical efficacy. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:84–96.
Zhong L, Li Y, Xiong L, Wang W, Wu M, Yuan T, et al. Small molecules in targeted cancer therapy: advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:201.
Moloney JN, Cotter TG. ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;80:50–64.
Andersen GB, Tost J. Circulating miRNAs as Biomarker in Cancer. 2020. p. 277–98.
Vishnoi A, Rani S. MiRNA Biogenesis and Regulation of Diseases: An Overview. 2017. p. 1–10.
Papadaki C, Monastirioti A, Rounis K, Makrakis D, Kalbakis K, Nikolaou C, et al. Circulating MicroRNAs regulating DNA damage response and responsiveness to Cisplatin in the prognosis of patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer treated with first-line platinum chemotherapy. Cancers. 2020;12:1282.
Ge X, Jiang Y, Hu X, Yu X. MicroRNA-106a-5p alleviated the resistance of cisplatin in lung cancer cells by targeting Jumonji domain containing 6. Transpl Immunol. 2021;69:101478.
Wang S, Wang Z, Wang Q, Cui Y, Luo S. Clinical significance of the expression of miRNA-21, miRNA-31 and miRNA-let7 in patients with lung cancer. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019;26:777–81.
Dai H, Meng XW, Ye K, Jia J, Kaufmann SH. Therapeutics targeting BCL2 family proteins. Mechanisms of Cell Death and Opportunities for Therapeutic Development. Elsevier; 2022. pp. 197–260.
Chauhan N, Dhasmana A, Jaggi M, Chauhan SC, Yallapu MM. miR-205: a potential biomedicine for Cancer Therapy. Cells. 2020;9:1957.
Corrà F, Agnoletto C, Minotti L, Baldassari F, Volinia S. The network of non-coding RNAs in Cancer Drug Resistance. Front Oncol. 2018;8.
Zhang J, Cao Z, Yang G, You L, Zhang T, Zhao Y. MicroRNA-27a (miR-27a) in solid tumors: a review based on mechanisms and clinical observations. Front Oncol. 2019;9.
Niklander S, Guerra D, Contreras F, González-Arriagada W, Marín C. MicroRNAs and their role in the malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: a scoping review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2022;e77–84.
Lu J, Zhan Y, Feng J, Luo J, Fan S. MicroRNAs associated with therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14:390–7.
Qin Z, Liu X, Li Z, Wang G, Feng Z, Liu Y, et al. LncRNA LINC00667 aggravates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating androgen receptor expression as a miRNA-130a-3p sponge. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7:387.
Wang Q, Ye B, Wang P, Yao F, Zhang C, Yu G. Overview of microRNA-199a regulation in Cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:10327–35.
Huang Z, Xu Y, Wan M, Zeng X, Wu J. miR-340: a multifunctional role in human malignant diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:236–46.
He X, Zou K. MiRNA-96-5p contributed to the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by targeting FOXO3. J Biochem. 2020;167:101–8.
Pratama MY, Pascut D, Massi MN, Tiribelli C. The role of microRNA in the resistance to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7:577–7.
Hua Y-T, Xu W-X, Li H, Xia M. Emerging roles of MiR-133a in human cancers. J Cancer. 2021;12:198–206.
Ye D, Zhang T, Lou G, Liu Y. Role of miR-223 in the pathophysiology of liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1–12.
Li T, Chen Q, Dai J, Huang Z, Luo Y, Mou T, et al. MicroRNA-141-3p attenuates oxidative stress-induced hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49:7575–85.
Li K, Wang Z. Splicing factor SRSF2-centric gene regulation. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:1708–15.
Amorim R, Pinheiro C, Miranda-Gonçalves V, Pereira H, Moyer MP, Preto A, et al. Monocarboxylate transport inhibition potentiates the cytotoxic effect of 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2015;365:68–78.
Yu W, Liang X, Li X, Zhang Y, Sun Z, Liu Y, et al. MicroRNA-195: a review of its role in cancers. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:7109–23.
Farasati Far B, Vakili K, Fathi M, Yaghoobpoor S, Bhia M, Naimi- Jamal MR. The role of microRNA-21 (miR-21) in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prognosis of gastrointestinal cancers: a review. Life Sci. 2023;316:121340.
Asghariazar V, Sakhinia E, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Baradaran B. Tumor suppressor microRNAs in lung cancer: an insight to signaling pathways and drug resistance. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:19274–89.
Braicu C, Gulei D, Raduly L, Harangus A, Rusu A, Berindan-Neagoe I. Altered expression of miR-181 affects cell fate and targets drug resistance-related mechanisms. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;70:90–105.
Song C, Xiao Y, Ouyang Z, Shen M, Shi X. Efficient co-delivery of microRNA 21 inhibitor and doxorubicin to cancer cells using core–shell tecto dendrimers formed via supramolecular host–guest assembly. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8:2768–74.
Badr M, Said H, Louka ML, Elghazaly HA, Gaballah A, Atef Abd El Mageed M. MicroRNA-21 as a predictor and prognostic factor for trastuzumab therapy in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2‐positive metastatic breast cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:3459–66.
Du F, Yu L, Wu Y, Wang S, Yao J, Zheng X, et al. miR-137 alleviates doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer through inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting DUSP4. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:922.
Ozyurt R, Ozpolat B. Molecular Mechanisms of Anti-Estrogen Therapy Resistance and Novel targeted Therapies. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14:5206.
Sun Q, Liu S, Feng J, Kang Y, Zhou Y, Guo S. Current status of MicroRNAs that target the wnt signaling pathway in regulation of Osteogenesis and Bone Metabolism: a review. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e929510.
Zangouei AS, Alimardani M, Moghbeli M. MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of doxorubicin resistance in breast tumor cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:213.
Bahrami A, Aledavood A, Anvari K, Hassanian SM, Maftouh M, Yaghobzade A, et al. The prognostic and therapeutic application of microRNAs in breast cancer: tissue and circulating microRNAs. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:774–86.
Martens-de Kemp SR, Komor MA, Hegi R, Bolijn AS, Tijssen M, de Groen FLM, et al. Overexpression of the mir-17-92 cluster in colorectal adenoma organoids causes a carcinoma-like gene expression signature. Neoplasia. 2022;32:100820.
Guo X, Li Y, Che X, Hou K, Qu X, Li C. microRNA-569 inhibits tumor metastasis in pancreatic cancer by directly targeting NUSAP1. Aging. 2022;14:3652–65.
Yılmaz M, Dilhan Kuru R, Erdoğan I, Soysal T, Hacıhanefioglu S, Baykara O. Investigation of 13q14.3 deletion by cytogenetic analysis and FISH technique and miRNA-15a and miRNA-16-1 by real time PCR in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Afr Health Sci. 2022;22:173–82.
Zhang L, Liao Y, Tang L. MicroRNA-34 family: a potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:53.
Si W, Shen J, Zheng H, Fan W. The role and mechanisms of action of microRNAs in cancer drug resistance. Clin Epigenetics. 2019;11:1–24.
Zhao H, Zhang J, Shao H, Liu J, Jin M, Chen J, et al. Transforming growth factor β1/Smad4 signaling affects osteoclast differentiation via regulation of miR-155 expression. Mol Cells. 2017;40:211–21.
Shang Y, Chen H, Ye J, Wei X, Liu S, Wang R. HIF-1α/Ascl2/miR-200b regulatory feedback circuit modulated the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2017;360:243–56.
Huang S, Wang C, Yi Y, Sun X, Luo M, Zhou Z, et al. Krüppel-like factor 9 inhibits glioma cell proliferation and tumorigenicity via downregulation of miR-21. Cancer Lett. 2015;356:547–55.
He D-X, Gu X-T, Jiang L, Jin J, Ma X. A methylation-based Regulatory Network for MicroRNA 320a in chemoresistant breast Cancer. Mol Pharmacol. 2014;86:536–47.
Li P, Shan J-X, Chen X-H, Zhang D, Su L-P, Huang X-Y, et al. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-149 in cancer-associated fibroblasts mediates prostaglandin E2/interleukin-6 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Res. 2015;25:588–603.
Ali SR, Humphreys KJ, McKinnon RA, Michael MZ. Impact of histone deacetylase inhibitors on microRNA expression and Cancer therapy: a review. Drug Dev Res. 2015;76:296–317.
Karimi E, Dehghani A, Azari H, Zarei M, Shekari M, Mousavi P. Molecular mechanisms of miR-214 involved in Cancer and Drug Resistance. Curr Mol Med. 2023;23:589–605.
Geismann C, Arlt A. Coming in the air: Hypoxia meets Epigenetics in Pancreatic Cancer. Cells. 2020;9:2353.
Hernández-Preciado MR, Morán-Moguel MC, Dávalos-Rodríguez IP, Enríquez-Barajas CM, Valdovinos-Maravilla JP, Díaz-Pérez AL, et al. miRNA-24 Gene sequence, DHFR – 829 C-T genotypes, and Methotrexate Response in Mexican patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2019;23:223–7.
Sharma AR, Vohra M, Shukla V, Guddattu V, Razak UKA, Shetty R, et al. Coding SNPs in hsa-mir-1343-3p and hsa-mir-6783-3p target sites of CYP2C19 modulates clopidogrel response in individuals with cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 2020;245:117364.
Arif KMT, Bradshaw G, Nguyen TTN, Smith RA, Okolicsanyi RK, Youl PH, et al. Genetic Association Analysis implicates six MicroRNA-Related SNPs with increased risk of breast Cancer in australian caucasian women. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021;21:e694–703.
Hoxhaj G, Manning BD. The PI3K–AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:74–88.
Tian T, Li X, Zhang J. mTOR Signaling in Cancer and mTOR inhibitors in solid Tumor Targeting Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:755.
Fujimoto Y, Morita TY, Ohashi A, Haeno H, Hakozaki Y, Fujii M, et al. Combination treatment with a PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitor overcomes resistance to anti-HER2 therapy in PIK3CA-mutant HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10:21762.
Cretella D. Giovannetti, Cavazzoni. PTEN alterations as a potential mechanism for Tumor cell escape from PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11:1318.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. PNAS. 2002;99:15524–9.
Ke K, Lou T. MicroRNA-10a suppresses breast cancer progression via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:5994–6000.
Guo P, Xiong X, Zhang S, Peng D. miR-100 resensitizes resistant epithelial ovarian cancer to cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 2016;36:3552–8.
Xu S, Fu G-B, Tao Z, OuYang J, Kong F, Jiang B-H, et al. MiR-497 decreases cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells by targeting mTOR/P70S6K1. Oncotarget. 2015;6:26457–71.
Akbarzadeh M, Mihanfar A, Akbarzadeh S, Yousefi B, Majidinia M. Crosstalk between miRNA and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer. Life Sci. 2021;285:119984.
Jia CY, Li HH, Zhu XC, Dong YW, Fu D, Zhao QL, et al. MiR-223 suppresses cell proliferation by targeting IGF-1R. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e27008.
Schotte D, De Menezes RX, Moqadam FA, Khankahdani LM, Lange-Turenhout E, Chen C, et al. MicroRNA characterize genetic diversity and drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2011;96:703–11.
Li X-J, Luo X-Q, Han B-W, Duan F-T, Wei P-P, Chen Y-Q. MicroRNA-100/99a, deregulated in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis by regulating the FKBP51 and IGF1R/mTOR signalling pathways. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2189–98.
Pekarsky Y, Croce CM. Is miR-29 an oncogene or tumor suppressor in CLL? Oncotarget. 2010;1:224–7.
Tu Y-X, Wang S-B, Fu L-Q, Li S-S, Guo Q-P, Wu Y, et al. Ovatodiolide targets chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by epigenetically upregulating hsa-miR-155, suppressing the BCR-ABL fusion gene and dysregulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget. 2018;9:3267–77.
Chen X, Yang S, Zeng J, Chen M. Mir-1271-5p inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting ZIC2. Mol Med Rep. 2018.
Wang X-X, Zhang R, Li Y. Expression of the miR-148/152 family in Acute myeloid leukemia and its clinical significance. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:4768–78.
Li Y, Deng X, Zeng X, Peng X. The role of Mir-148a in Cancer. J Cancer. 2016;7:1233–41.
Wang X, Zhang H, Li Y. Preliminary study on the role of miR-148a and DNMT1 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19:2943–52.
Gao D-W, Wen Z-D. Phthalate esters in the environment: a critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes. Sci Total Environ. 2016;541:986–1001.
Bølling AK, Sripada K, Becher R, Bekö G. Phthalate exposure and allergic diseases: review of epidemiological and experimental evidence. Environ Int. 2020;139:105706.
Duan X-L, Ma C-C, Hua J, Xiao T-W, Luan J. Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) triggers the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia cells via upregulation of PDK4. Toxicol in Vitro. 2020;62:104693.
Li S, Guo W, Geng H, Wang C, Yang S, Xu X. LINC00511 exacerbated T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia via miR-195-5p/LRRK1 axis. Biosci Rep. 2020;40:BSR20193631.
Li Q, Wang J. Long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 enhances adriamycin resistance in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia through the miR-195/Myb axis. RSC Adv. 2019;9:28126–34.
Cicirò Y, Sala A. MYB oncoproteins: emerging players and potential therapeutic targets in human cancer. Oncogenesis. 2021;10:19.
Liu X, Cui M-M, Zhu H-Z, Fu P-Y, Wang G-C, Huang L. MiR-199a-3p overexpression suppressed cell proliferation and sensitized chronic myeloid leukaemia cells to Imatinib by inhibiting mTOR signalling. Acta Haematol. 2022;145:484–98.
Zhuang M, Chaolumen Q, Li L, Chen B, Su Q, Yang Y, et al. MiR-29b-3p cooperates with miR-29c-3p to affect the malignant biological behaviors in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia via TFAP2C/GPX1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;527:511–7.
Zhou L, Shan Z, Fan J. Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow stem cells inhibit acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell growth by inhibiting MAPK pathway via the miR-29b-3p/GDF15 axis. Acta Haematol. 2022;1.
Tang Y-J, Wu W, Chen Q-Q, Liu S-H, Zheng Z-Y, Cui Z-L, et al. miR-29b-3p suppresses the malignant biological behaviors of AML cells via inhibiting NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways by targeting HuR. BMC Cancer. 2022;22:1–16.
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledge the support received from the Central University of Punjab, Bathinda, in writing this manuscript. The author is also gratified to the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi (DST-FIST-SR/FST/LS-I/2018/125©) for financial support under the DST-FIST programs to the Department of Biochemistry, Central University of Punjab. PS is grateful to CSIR-UGC, New Delhi for providing her fellowship.
Funding
The author declares that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Author response
PS authored the manuscript and was responsible for creating the illustrations within it, all of which are original and free from copyrighted material.
Conflict of interest
The author declares there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants.
Consent to publish
This article does not contain any studies with human research participants, so informed conse1.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P. MicroRNA based combinatorial therapy against TKIs resistant CML by inactivating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: a review. Med Oncol 40, 300 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02161-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02161-z