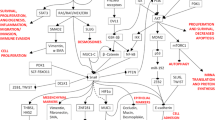
Abstract
Renal cancer is the most lethal urological cancer and characterized by high metastasis rate at initial diagnosis and drug resistance to current chemotherapeutics. Betulinic acid is a pentacyclic triterpene with broad biological activity that occurs naturally in variety of plants. Even though the anti-cancer efficacy of betulinic acid have been reported by many studies, the information about the pathways and the molecules which are affected by betulinic acid in renal cancer are limited. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is considered as the initial step of metastasis and contributes to drug resistance of cancer cells. Depending on the role of EMT in cancer progression and drug resistance, targeting EMT may represent an effective strategy in this context. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the anti-metastatic effects of betulinic acid on renal cell carcinoma cells by evaluating two EMT markers, SNAIL-1, and SDC-2. Following the treatment of betulinic acid at determined doses by WST-1 cytotoxicity assay in our previous study, SDC-2 expression level was decreased in both cell lines. Additionally, in correlation with this result, we also found a reduction in SDC-2 and SNAIL-1 protein levels which are measured by ELISA. Furthermore, the migration and invasion capacities were suppressed by betulinic acid treatment in metastatic renal adenocarcinoma ACHN cells. Taken together, our findings indicate that betulinic acid may constitute a potential treatment approach for renal cancer with further investigations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, Boorjian SA, Bray F, Coleman J, Gore JL, Sun M, Wood C, Russo P. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2019;75(1):74–84.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.
Inamura K. Renal cell tumors: understanding their molecular pathological epidemiology and the 2016 WHO classification. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2195.
Linehan WM, Ricketts CJ. The cancer genome atlas of renal cell carcinoma: findings and clinical implications. Nat Rev Urol. 2019;16(9):539–52.
Bhatt JR, Finelli A. Landmarks in the diagnosis and treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol. 2014;11(9):517–25.
Jonasch E, Gao J, Rathmell WK. Renal cell carcinoma. BMJ. 2014;349: g4797.
Zeng Q, Zhang W, Li X, Lai J, Li Z. Bioinformatic identification of renal cell carcinoma microenvironment-associated biomarkers with therapeutic and prognostic value. Life Sci. 2020;243: 117273.
Pontes O, Oliveira-Pinto S, Baltazar F, Costa M. Renal cell carcinoma therapy: current and new drug candidates. Drug Discov Today. 2022;27(1):304–14.
Dutta S, Mahalanobish S, Saha S, Ghosh S, Sil PC. Natural products: An upcoming therapeutic approach to cancer. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019;128:240–55.
Lou H, Li H, Zhang S, Lu H, Chen Q. A review on preparation of betulinic acid and its biological activities. Molecules. 2021;26(18):5583.
Zhang X, Hu J, Chen Y. Betulinic acid and the pharmacological effects of tumor suppression (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(5):4489–95.
Kun-Liu, Wang JY, Zhang L, Pan YY, Chen XY, Yuan Y.(2020) Effects of betulinic acid on synovial inflammation in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.;34:2058738420945078.
Kim KD, Jung HY, Ryu HG, Kim B, Jeon J, Yoo HY, Park CH, Choi BH, Hyun CK, Kim KT, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits high-fat diet-induced obesity and improves energy balance by activating AMPK. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2019;29(4):409–20.
Musayeva A, Unkrig JC, Zhutdieva MB, Manicam C, Ruan Y, Laspas P, Chronopoulos P, Göbel ML, Pfeiffer N, Brochhausen C, et al. Betulinic Acid Protects from ischemia-reperfusion injury in the mouse retina. Cells. 2021;10(9):2440.
Pisha E, Chai H, Lee IS, Chagwedera TE, Farnsworth NR, Cordell GA, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Kinghorn AD, Brown DM, et al. Discovery of betulinic acid as a selective inhibitor of human melanoma that functions by induction of apoptosis. Nat Med. 1995;1(10):1046–51.
Zhang Y, He N, Zhou X, Wang F, Cai H, Huang SH, Chen X, Hu Z, Jin X. Betulinic acid induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis via Bmi-1/ROS/AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 axis in human bladder cancer cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(17):21251–67.
Zeng A, Hua H, Liu L, Zhao J. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of human colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019;27(12):2546–52.
Fares J, Fares MY, Khachfe HH, Salhab HA, Fares Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: a hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):28.
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(3):178–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3758.
Dongre A, Weinberg RA. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(2):69–84.
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(6):415–28.
Hua R, Yu J, Yan X, Ni Q, Zhi X, Li X, Jiang B, Zhu J. Syndecan-2 in colorectal cancer plays oncogenic role via epithelial-mesenchymal transition and MAPK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121: 109630.
Mytilinaiou M, Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A, Kostouras A, Papoutsidakis A, Tsatsakis AM, Tzanakakis GN. Emerging roles of syndecan 2 in epithelial and mesenchymal cancer progression. IUBMB Life. 2017;69(11):824–33.
Ergen A, Iplik ES, Ertugrul B, Atas MN, Kasarci G, Cakmakoglu B. Examination of the apoptotic effects of betulinic acid on renal cancer cell lines. Marmara Medical Journal. 2021;33(3):113–8.
Fulda S, Scaffidi C, Susin SA, Krammer PH, Kroemer G, Peter ME, Debatin KM. Activation of mitochondria and release of mitochondrial apoptogenic factors by betulinic acid. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(51):33942–8.
Xu T, Pang Q, Wang Y, Yan X. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis by regulating PI3K/Akt signaling and mitochondrial pathways in human cervical cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1669–78.
Shankar E, Zhang A, Franco D, Gupta S. Betulinic acid-mediated apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells involves p53 and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathways. Molecules. 2017;22(2):264.
Shin J, Lee HJ, Jung DB, Jung JH, Lee HJ, Lee EO, Lee SG, Shim BS, Choi SH, Ko SG, et al. Suppression of STAT3 and HIF-1 alpha mediates anti-angiogenic activity of betulinic acid in hypoxic PC-3 prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(6): e21492.
Krebs AM, Mitschke J, Lasierra Losada M, Schmalhofer O, Boerries M, Busch H, Boettcher M, Mougiakakos D, Reichardt W, Bronsert P, et al. The EMT-activator Zeb1 is a key factor for cell plasticity and promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(5):518–29.
Rasti A, Madjd Z, Abolhasani M, Mehrazma M, Janani L, Saeednejad Zanjani L, Asgari M. Cytoplasmic expression of Twist1, an EMT-related transcription factor, is associated with higher grades renal cell carcinomas and worse progression-free survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Med. 2018;18(2):177–90.
Xu H, Xu WH, Ren F, Wang J, Wang HK, Cao DL, Shi GH, Qu YY, Zhang HL, Ye DW. Prognostic value of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(1):866–83.
Işeri OD, Kars MD, Arpaci F, Atalay C, Pak I, Gündüz U. Drug resistant MCF-7 cells exhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene expression pattern. Biomed Pharmacother. 2011;65(1):40–5.
Ma JL, Zeng S, Zhang Y, Deng GL, Shen H. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition plays a critical role in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to oxaliplatin. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(5):6177–84.
Popović A, Demirović A, Spajić B, Stimac G, Kruslin B, Tomas D. Expression and prognostic role of syndecan-2 in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010;13(1):78–82.
Wang J, Lu C, Chen J, Chen X, Wang S, Lu X, Tang X. Expression of Syndecan-2 in gastric adenocarcinoma and its effect on tumorigenesis in vitro. Transl Cancer Res. 2017. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2017.08.04.
Jang B, Jung H, Chung H, Moon BI, Oh ES. Syndecan-2 enhances E-cadherin shedding and fibroblast-like morphological changes by inducing MMP-7 expression in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;477(1):47–53.
Sun L, Cao J, Chen K, Cheng L, Zhou C, Yan B, Qian W, Li J, Duan W, Ma J, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits stemness and EMT of pancreatic cancer cells via activation of AMPK signaling. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(1):98–110.
Kim SY, Hwangbo H, Kim MY, Ji SY, Kim DH, Lee H, Kim GY, Moon SK, Leem SH, Yun SJ, et al. Betulinic acid restricts human bladder cancer cell proliferation in vitro by inducing caspase-dependent cell death and cell cycle arrest, and decreasing metastatic potential. Molecules. 2021;26(5):1381.
Funding
This work was funded by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University. Project No. TSA-2019–35150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MNA; Laboratory Analysis and Writing, BE; Laboratory Analysis, ESİ; Statistical Analysis, BÇ; Data Extraction, AE; Study Design and Writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ataş, M.N., Ertuğrul, B., İplik, E.S. et al. The inhibitory effect of betulinic acid on epithelial–mesenchymal transition pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol 39, 170 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01775-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01775-z