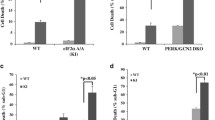
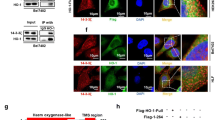
Abstract
Heme-regulated inhibitor (HRI) kinase is a serine–threonine kinase, controlling the initiation of protein synthesis via phosphorylating α subunit of eIF2 on serine 51 residue, mainly in response to heme deprivation in erythroid cells. However, recent studies showed that HRI is also activated by several diverse signals, causing dysregulations in intracellular homeostatic mechanisms in non-erythroid cells. For instance, it was reported that the decrease in protein synthesis upon the 26S proteasomal inhibition by MG132 or bortezomib is mediated by increased eIF2α phosphorylation in an HRI-dependent manner in mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. The increase in eIF2α phosphorylation level through the activation of HRI upon 26S proteasomal inhibition is believed to protect cells against the buildup of misfolded and ubiquitinated proteins, having the potential to trigger the apoptotic response. In contrast, prolonged and sustained HRI-mediated eIF2α phosphorylation can induce cell death, which may involve ATF4 and CHOP expression. Altogether, these studies suggest that HRI-mediated eIF2α phosphorylation may be cytoprotective or cytotoxic depending on the cells, type, and duration of pharmacological agents used. It is thus hypothesized that both HRI activators, inducing eIF2α phosphorylation or HRI inhibitors causing disturbances in eIF2α phosphorylation, may be effective as novel strategies in cancer treatment if the balance in eIF2α phosphorylation is shifted in favor of autophagic or apoptotic response in cancer cells. It is here aimed to review the role of HRI in various biological mechanisms as well as the therapeutic potentials of recently developed HRI activators and inhibitors, targeting eIF2α phosphorylation in cancer cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Burwick N, Aktas BH. The eIF2-alpha kinase HRI: a potential target beyond the red blood cell. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017;21(12):1171–7.
Donnelly N, Gorman AM, Gupta S, Samali A. The eIF2alpha kinases: their structures and functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(19):3493–511.
Sudhakar A, Ramachandran A, Ghosh S, Hasnain SE, Kaufman RJ, Ramaiah KV. Phosphorylation of serine 51 in initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2 alpha) promotes complex formation between eIF2 alpha(P) and eIF2B and causes inhibition in the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of eIF2B. Biochemistry. 2000;39(42):12929–38.
Liu CY, Schroder M, Kaufman RJ. Ligand-independent dimerization activates the stress response kinases IRE1 and PERK in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. The J Biol Chem. 2000;275(32):24881–5.
Lu J, O’Hara EB, Trieselmann BA, Romano PR, Dever TE. The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase PKR will phosphorylate serine, threonine, or tyrosine at residue 51 in eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(45):32198–203.
Lu YN, Kavianpour S, Zhang T, Zhang X, Nguyen D, Thombre R, He L, Wang J. MARK2 phosphorylates eIF2alpha in response to proteotoxic stress. PLoS Biol. 2021;19(3):e3001096.
Suragani RNVS, Zachariah RS, Velazquez JG, Liu SJ, Sun CW, Townes TM, Chen JJ. Heme-regulated eIF2 alpha kinase activated Atf4 signaling pathway in oxidative stress and erythropoiesis. Blood. 2012;119(22):5276–84.
Wang YC, Li X, Shen Y, Lyu J, Sheng H, Paschen W, Yang W. PERK (protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase) branch of the unfolded protein response confers neuroprotection in ischemic stroke by suppressing protein synthesis. Stroke. 2020;51(5):1570–7.
Demirsoy S, Martin S, Maes H, Agostinis P. Adapt, recycle, and move on: proteostasis and trafficking mechanisms in melanoma. Front Oncol. 2016;6:240.
Nam SM, Jeon YJ. Proteostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum: road to cure. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(11):1793.
Clemens MJ. PKR–A protein kinase regulated by double-stranded RNA. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29(7):945–9.
Misra J, Holmes MJ, T. Mirek E, Langevin M, Kim HG, Carlson KR, Watford M, Dong XC, Anthony TG, Wek RC. Discordant regulation of eIF2 kinase GCN2 and mTORC1 during nutrient stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(10):5726–42.
Wu CC, Peterson A, Zinshteyn B, Regot S, Green R. Ribosome collisions trigger general stress responses to regulate cell fate. Cell. 2020;182(2):404–16.
Nyati S, Chator A, Schinske K, Gregg BS, Ross BD, Rehemtulla A. A Requirement for ZAK kinase activity in canonical TGF-beta signaling. Transl Oncol. 2016;9(6):473–81.
Suzuki A, Hirata M, Kamimura K, Maniwa R, Yamanaka T, Mizuno K, Kishikawa M, Hirose H, Amano Y, Izumi N, et al. aPKC acts upstream of PAR-1b in both the establishment and maintenance of mammalian epithelial polarity. Curr Biol. 2004;14(16):1425–35.
Alone PV, Dever TE. Direct binding of translation initiation factor eIF2gamma-G domain to its GTPase-activating and GDP-GTP exchange factors eIF5 and eIF2B epsilon. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(18):12636–44.
Kim E, Kim JH, Seo K, Hong KY, An SWA, Kwon J, Lee SV, Jang SK. eIF2A, an initiator tRNA carrier refractory to eIF2alpha kinases, functions synergistically with eIF5B. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(23):4287–300.
Somers J, Poyry T, Willis AE. A perspective on mammalian upstream open reading frame function. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(8):1690–700.
Vasudevan D, Neuman SD, Yang A, Lough L, Brown B, Bashirullah A, Cardozo T, Ryoo HD. Translational induction of ATF4 during integrated stress response requires noncanonical initiation factors eIF2D and DENR. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4677.
Wei L, Lin Q, Lu Y, Li G, Huang L, Fu Z, Chen R, Zhou Q. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-mediated ATF4 expression promotes malignancy and gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via the TGF-beta1/SMAD2/3 pathway and ABCC1 transactivation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(4):334.
Wortel IMN, van der Meer LT, Kilberg MS, van Leeuwen FN. Surviving stress: modulation of ATF4-mediated stress responses in normal and malignant cells. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017;28(11):794–806.
Schubert U, Anton LC, Gibbs J, Norbury CC, Yewdell JW, Bennink JR. Rapid degradation of a large fraction of newly synthesized proteins by proteasomes. Nature. 2000;404(6779):770–4.
Igarashi J, Murase M, Iizuka A, Pichierri F, Martinkova M, Shimizu T. Elucidation of the heme binding site of heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase and the role of the regulatory motif in heme sensing by spectroscopic and catalytic studies of mutant proteins. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(27):18782–91.
Chen JJ. Regulation of protein synthesis by the heme-regulated eIF2alpha kinase: relevance to anemias. Blood. 2007;109(7):2693–9.
Mense SM, Zhang L. Heme: a versatile signaling molecule controlling the activities of diverse regulators ranging from transcription factors to MAP kinases. Cell Res. 2006;16(8):681–92.
Rafie-Kolpin M, Chefalo PJ, Hussain Z, Hahn J, Uma S, Matts RL, Chen JJ. Two heme-binding domains of heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor-2alpha kinase. N terminus and kinase insertion. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(7):5171–8.
Chen JJ, London IM. Regulation of protein synthesis by heme-regulated eIF-2 alpha kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20(3):105–8.
Lu L, Han AP, Chen JJ. Translation initiation control by heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase in erythroid cells under cytoplasmic stresses. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(23):7971–80.
Mukherjee T, Ramaglia V, Abdel-Nour M, Bianchi AA, Tsalikis J, Chau HN, Kalia SK, Kalia LV, Chen JJ, Arnoult D, et al. The eIF2alpha kinase HRI triggers the autophagic clearance of cytosolic protein aggregates. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100050.
Yerlikaya A, Dokudur H. Investigation of the eIF2alpha phosphorylation mechanism in response to proteasome inhibition in melanoma and breast cancer cells. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2010;44(5):859–66.
Yerlikaya A, Kimball SR, Stanley BA. Phosphorylation of eIF2alpha in response to 26S proteasome inhibition is mediated by the haem-regulated inhibitor (HRI) kinase. Biochem J. 2008;412(3):579–88.
Mellor H, Flowers KM, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding rat PKR, the double-stranded RNA-dependent eukaryotic initiation factor-2 kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1219(3):693–6.
Girardin SE, Cuziol C, Philpott DJ, Arnoult D. The eIF2alpha kinase HRI in innate immunity, proteostasis, and mitochondrial stress. FEBS J. 2021;288(10):3094–107.
Abdel-Nour M, Carneiro LAM, Downey J, Tsalikis J, Outlioua A, Prescott D, Da Costa LS, Hovingh ES, Farahvash A, Gaudet RG, et al. The heme-regulated inhibitor is a cytosolic sensor of protein misfolding that controls innate immune signaling. Science. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw4144.
Caruso R, Warner N, Inohara N, Nunez G. NOD1 and NOD2: signaling, host defense, and inflammatory disease. Immunity. 2014;41(6):898–908.
Fessler E, Eckl EM, Schmitt S, Mancilla IA, Meyer-Bender MF, Hanf M, Philippou-Massier J, Krebs S, Zischka H, Jae LT. A pathway coordinated by DELE1 relays mitochondrial stress to the cytosol. Nature. 2020;579(7799):433–7.
Guo X, Aviles G, Liu Y, Tian R, Unger BA, Lin YT, Wiita AP, Xu K, Correia MA, Kampmann M. Mitochondrial stress is relayed to the cytosol by an OMA1-DELE1-HRI pathway. Nature. 2020;579(7799):427–32.
Liu S, Suragani RN, Wang F, Han A, Zhao W, Andrews NC, Chen JJ. The function of heme-regulated eIF2alpha kinase in murine iron homeostasis and macrophage maturation. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(11):3296–305.
Ramos-Fernandez E, Arrazola MS, Oliva CA, Arredondo SB, Varela-Nallar L, Inestrosa NC. Wnt5a promotes hippocampal postsynaptic development and GluN2B-induced expression via the eIF2alpha HRI kinase. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):7395.
Han AP, Yu C, Lu L, Fujiwara Y, Browne C, Chin G, Fleming M, Leboulch P, Orkin SH, Chen JJ. Heme-regulated eIF2alpha kinase (HRI) is required for translational regulation and survival of erythroid precursors in iron deficiency. EMBO J. 2001;20(23):6909–18.
Pazos M, Andersen ML, Skibsted LH. Heme-mediated production of free radicals via preformed lipid hydroperoxide fragmentation. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56(23):11478–84.
Chen JJ, Pal JK, Petryshyn R, Kuo I, Yang JM, Throop MS, Gehrke L, London IM. Amino acid microsequencing of internal tryptic peptides of heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit kinase: homology to protein kinases. PNAS. 1991;88(2):315–9.
Bauer BN, Rafie-Kolpin M, Lu L, Han A, Chen JJ. Multiple autophosphorylation is essential for the formation of the active and stable homodimer of heme-regulated eIF2alpha kinase. Biochemistry. 2001;40(38):11543–51.
Lee JM, Lee WH, Kay HY, Kim ES, Moon A, Kim SG. Hemin, an iron-binding porphyrin, inhibits HIF-1alpha induction through its binding with heat shock protein 90. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(3):716–27.
Fiorito V, Chiabrando D, Petrillo S, Bertino F, Tolosano E. The multifaceted role of heme in cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1540.
Robichaud N, Sonenberg N, Ruggero D, Schneider RJ. Translational control in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019;11(7):a032896.
Lobo MV, Martin ME, Perez MI, Alonso FJ, Redondo C, Alvarez MI, Salinas M. Levels, phosphorylation status and cellular localization of translational factor eIF2 in gastrointestinal carcinomas. Histochem J. 2000;32(3):139–50.
Uchenunu O, Pollak M, Topisirovic I, Hulea L. Oncogenic kinases and perturbations in protein synthesis machinery and energetics in neoplasia. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019;62(2):R83–103.
Rosenwald IB, Koifman L, Savas L, Chen JJ, Woda BA, Kadin ME. Expression of the translation initiation factors eIF-4E and eIF-2* is frequently increased in neoplastic cells of Hodgkin lymphoma. Hum Pathol. 2008;39(6):910–6.
Chen T, Ozel D, Qiao Y, Harbinski F, Chen L, Denoyelle S, He X, Zvereva N, Supko JG, Chorev M, et al. Chemical genetics identify eIF2alpha kinase heme-regulated inhibitor as an anticancer target. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7(9):610–6.
Donze O, Jagus R, Koromilas AE, Hershey JW, Sonenberg N. Abrogation of translation initiation factor eIF-2 phosphorylation causes malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1995;14(15):3828–34.
Marshall L, Kenneth NS, White RJ. Elevated tRNA(iMet) synthesis can drive cell proliferation and oncogenic transformation. Cell. 2008;133(1):78–89.
Rosen MD, Woods CR, Goldberg SD, Hack MD, Bounds AD, Yang Y, Wagaman PC, Phuong VK, Ameriks AP, Barrett TD, et al. Discovery of the first known small-molecule inhibitors of heme-regulated eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha (HRI) kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009;19(23):6548–51.
Palrecha S, Lakade D, Kulkarni A, Pal JK, Joshi M. Computational insights into the interaction of small molecule inhibitors with HRI kinase domain. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019;37(7):1715–23.
Burwick N, Zhang MY, de la Puente P, Azab AK, Hyun TS, Ruiz-Gutierrez M, Sanchez-Bonilla M, Nakamura T, Delrow JJ, MacKay VL, et al. The eIF2-alpha kinase HRI is a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 2017;55:23–32.
Hu H, Tian M, Ding C, Yu S. The C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) transcription factor functions in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and microbial infection. Front Immunol. 2018;9:3083.
Teng Y, Gao M, Wang J, Kong Q, Hua H, Luo T, Jiang Y. Inhibition of eIF2alpha dephosphorylation enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in hepatoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1060.
Zhang Q, Du R, Reis Monteiro Dos Santos GR, Yefidoff-Freedman R, Bohm A, Halperin J, Chorev M, Aktas BH. New activators of eIF2alpha Kinase Heme-Regulated Inhibitor (HRI) with improved biophysical properties. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;187:111973.
Alvarez-Castelao B, Tom Dieck S, Fusco CM, Donlin-Asp P, Perez JD, Schuman EM. The switch-like expression of heme-regulated kinase 1 mediates neuronal proteostasis following proteasome inhibition. eLife. 2020;9:e52714.
White MC, Schroeder RD, Zhu K, Xiong K, McConkey DJ. HRI-mediated translational repression reduces proteotoxicity and sensitivity to bortezomib in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene. 2018;37(32):4413–27.
Nowis D, Bugajski M, Winiarska M, Bil J, Szokalska A, Salwa P, Issat T, Was H, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J, et al. Zinc protoporphyrin IX, a heme oxygenase-1 inhibitor, demonstrates potent antitumor effects but is unable to potentiate antitumor effects of chemotherapeutics in mice. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:197.
Yang JM, London IM, Chen JJ. Effects of hemin and porphyrin compounds on intersubunit disulfide formation of heme-regulated eIF-2 alpha kinase and the regulation of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(28):20519–24.
Yerlikaya A, Okur E. An investigation of the mechanisms underlying the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib resistance in PC3 prostate cancer cell line. Cytotechnology. 2020;72(1):121–30.
Vallelian F, Deuel JW, Opitz L, Schaer CA, Puglia M, Lonn M, Engelsberger W, Schauer S, Karnaukhova E, Spahn DR, et al. Proteasome inhibition and oxidative reactions disrupt cellular homeostasis during heme stress. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(4):597–611.
Lin PH, Chiang MT, Chau LY. Ubiquitin-proteasome system mediates heme oxygenase-1 degradation through endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1783(10):1826–34.
Yerlikaya A. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in response to proteasomal inhibition. Protein Pept Lett. 2012;19(12):1330–3.
Yerlikaya A, Kanbur E. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and resistance mechanisms developed against the proteasomal inhibitors in cancer cells. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(13):1313–25.
Yerlikaya A, Kanbur E, Stanley BA, Tumer E. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and epigenetic modifications in cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(1):20–32.
Wang T, Ashrafi A, Modareszadeh P, Deese AR, Chacon Castro MDC, Alemi PS, Zhang L. An analysis of the multifaceted roles of heme in the pathogenesis of cancer and related diseases. Cancers. 2021;13(16):4142.
Chen L, Madura K. Increased proteasome activity, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and eEF1A translation factor detected in breast cancer tissue. Cancer Res. 2005;65(13):5599–606.
Yefidoff-Freedman R, Fan J, Yan L, Zhang Q, Dos Santos GRR, Rana S, Contreras JI, Sahoo R, Wan D, Young J, et al. Development of 1-((1,4-trans)-4-aryloxycyclohexyl)-3-arylurea activators of heme-regulated inhibitor as selective activators of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2alpha) phosphorylation arm of the Integrated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response. J Med Chem. 2017;60(13):5392–406.
McEwen E, Kedersha N, Song B, Scheuner D, Gilks N, Han A, Chen JJ, Anderson P, Kaufman RJ. Heme-regulated inhibitor kinase-mediated phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 inhibits translation, induces stress granule formation, and mediates survival upon arsenite exposure. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(17):16925–33.
Tian X, Zhang S, Zhou L, Seyhan AA, Hernandez Borrero L, Zhang Y, El-Deiry WS. Targeting the integrated stress response in cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:747837.
Staudt LM. Oncogenic activation of NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2(6):a000109.
Tornatore L, Sandomenico A, Raimondo D, Low C, Rocci A, Tralau-Stewart C, Capece D, D’Andrea D, Bua M, Boyle E, et al. Cancer-selective targeting of the NF-kappaB survival pathway with GADD45beta/MKK7 inhibitors. Cancer Cell. 2014;26(4):495–508.
Smith KH, Budhraja A, Lynch J, Roberts K, Panetta JC, Connelly JP, Turnis ME, Pruett-Miller SM, Schuetz JD, Mullighan CG, et al. The heme-regulated inhibitor pathway modulates susceptibility of poor prognosis B-lineage acute leukemia to BH3-mimetics. Mol Cancer Res. 2021;19(4):636–50.
Beroukhim R, Mermel CH, Porter D, Wei G, Raychaudhuri S, Donovan J, Barretina J, Boehm JS, Dobson J, Urashima M, et al. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature. 2010;463(7283):899–905.
Campbell KJ, Dhayade S, Ferrari N, Sims AH, Johnson E, Mason SM, Dickson A, Ryan KM, Kalna G, Edwards J, et al. MCL-1 is a prognostic indicator and drug target in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):19.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AY designed, wrote, and drafted the manuscript. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.