Abstract
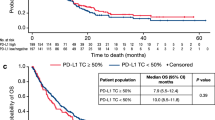
There is no established biomarker for cetuximab efficacy in recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). The aim of the present study was to evaluate the prognostic and predictive impact of PTEN, cMET, and p16 expression in recurrent HNSCC. In this retrospective study, 112 patients with recurrent HNSCC received chemotherapy (CT) alone (n = 37) or chemotherapy with cetuximab (n = 75). PTEN, cMET, and p16 protein expression were evaluated by immunohistochemistry. The median overall survival (mOS) for the patients treated with cetuximab + CT versus CT alone was 11.4 months and 7.0 months, (p = 0.949). The median progression-free survival (mPFS) was 6.2 months versus 3.0 months (p = 0.154). Patients with PTEN loss exhibited a mOS of 5.8 months versus 10.5 months (p = 0.002) and a mPFS of 3.2 months versus 4.7 months (p = 0.019). A multivariate analysis identified an independent association between PTEN loss and OS (HR 2.27; 95% confidence 95% CI 1.27–4.08; p = 0.006) and with PFS (HR 1.85; 95% CI 1.09–2.99; p = 0.022). A negative prognostic impact of PTEN loss was observed in the patients treated with cetuximab + CT, and not in the CT only group. Expression of cMET and p16 showed no impact on OS or PFS. The present findings confirm that PTEN is a prognostic factor for metastatic HNSCC and they support further studies of PTEN expression to evaluate its predictive value to cetuximab response.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442.
Instituo Nacional do Câncer (Brasil). Estimativa 2018. Incidência do Câncer no Brasil. http://www.inca.gov.br/estimativa/2018. Accessed 8 Oct 2018.
Blanchard P, Baujat B, Holostenco V, et al. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): a comprehensive analysis by tumour site. Radiot Oncol. 2011;100:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2011.05.036.
Vermoken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1116–27.
Agrawal N, Frederick MJ, Pickering CR, et al. Exome sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma reveals inactivating mutations in NOTCH1. Science. 2011;333:1154–7. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206923.
The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature. 2015;517:576–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14129.
Chung CH, Guthrie VB, Masica DL, et al. Genomic alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma determined by cancer gene-targeted sequencing. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1216–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv109.
Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:24–35. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0912217).
Castellsagué X, Alemany L, Quer M, et al. HPV Involvement in head and neck cancers: comprehensive assessment of biomarkers in 3680 patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016;108:djv403–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv403.
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J, et al. Nivolumab for recurrent squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1856–67. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1602252.
Yokota T. Is biomarker research advancing in the era of personalized medicine for head and neck cancer? Int J Clin Oncol. 2014;19:211–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-013-0660-4.
Licitra L, Störkel S, Kerr KM, et al. Predictive value of epidermal growth factor receptor expression for first-line chemotherapy plus cetuximab in patients with head and neck and colorectal cancer: analysis of data from the EXTREME and CRYSTAL studies. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:1161–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.11.018.
Lui VWY, Hedberg ML, Li H, et al. Frequent mutation of the pi3k pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:761–9. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0103.
Chiosea SI, Grandis JR, Lui VWY, et al. PIK3CA, HRAS and PTEN in human papillomavirus positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:602.
Leemans CR, Snijders PJF, Brakenhoff RH. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nature. 2018;18:269–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2018.11.
Pattje WJ, Schuuring E, Mastik MF, et al. The phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 mediates radiosensitivity in head and neck cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:1778–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605707.
Snietura M, Jaworska M, Mlynarczyk-Liszka J, et al. PTEN as a prognostic and predictive marker in postoperative radiotherapy for squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e33396–8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033396.
da Costa AABA, D’Almeida Costa F, Ribeiro AR, et al. Low PTEN expression is associated with worse overall survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with chemotherapy and cetuximab. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014;20:282–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-014-0707-1.
Rothenberger N, Stabile L. Hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling in head and neck cancer and implications for treatment. Cancers. 2017;9:39–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9040039.
Choe J-Y, Yun JY, Nam S-J, Kim JE. Expression of c-Met is different along the location and associated with lymph node metastasis of head and neck carcinoma. Korean J Pathol. 2012;46:515–8. https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.6.515.
Baschnagel AM, Williams L, Hanna A, et al. c-Met expression is a marker of poor prognosis in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with chemoradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88:701–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.11.013.
Madoz-Gúrpide J, Zazo S, Chamizo C, et al. Activation of MET pathway predicts poor outcome to cetuximab in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. J Transl Med. 2015;13:11–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0633-7.
Argiris A, Li S, Ghebremichael M, et al. Prognostic significance of human papillomavirus in recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer: an analysis of eastern cooperative oncology group trials. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1410–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu167.
Spreafico A, Amir E, Siu LL. Demystifying the role of tumor HPV status in recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:760–2. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu095.
Stransky N, Egloff AM, Tward AD, et al. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science. 2011;333:1157–60. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1206923.
Lee JI, Soria J-C, Hassan KA, et al. Loss of PTEN expression as a prognostic marker for tongue cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127:1441–5.
Cai Y, Dodhia S, Su GH. Dysregulations in the PI3K pathway and targeted therapies for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:22203–17.
Okutur K, Bassulu N, Dalar L, et al. Predictive and prognostic significance of p27, Akt, PTEN and PI3K expression in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16:2645–51. https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.7.2645.
Therkildsen C, Bergmann TK, Henrichsen-Schnack T, Ladelund S, Nilbert M. The predictive value of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and PTEN for anti-EGFR treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2014;53:852–64. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186X.2014.895036.
Cohen EEW, Licitra LF, Burtness B, et al. Biomarkers predict enhanced clinical outcomes with afatinib versus methotrexate in patients with second-line recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck cancer. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:2526–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx344.
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim D-W, et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2167–77. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1408440.
Choueiri TK, Halabi S, Sanford BL, et al. Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma of poor or intermediate risk: the alliance A031203 CABOSUN trial. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:591–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.70.7398.
Gibson MK, Li Y, Murphy B, et al. Randomized phase III evaluation of cisplatin plus fluorouracil versus cisplatin plus paclitaxel in advanced head and neck cancer (E1395): an intergroup trial of the eastern cooperative oncology group. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3562–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.01.057.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ricardo Brentani Award, A.C. Camargo Cancer Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

12032_2018_1234_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival according to ECOG performance status (A), smoking history (B), and type of recurrent disease (C). Progression-free survival according to age at diagnosis (D). Supplementary material 1 (JPG 423 KB)

12032_2018_1234_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival and progression-free survival according to CMET expression (A and C) and p16 expression (B and D) are presented, respectively in each case. Supplementary material 2 (JPG 413 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Costa, A.A.B.A., Costa, F.D., Araújo, D.V. et al. The roles of PTEN, cMET, and p16 in resistance to cetuximab in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol 36, 8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-018-1234-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-018-1234-0