Abstract
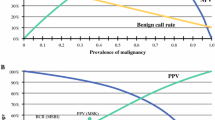
Prior studies demonstrate that a novel genomic test, the gene expression classifier (GEC), could identify a benign gene expression signature in those nodules with indeterminate cytology with a negative predictive value of greater than 95 %. Examine the performance of the AFIRMA gene expression classifier in predicting benign and malignant nodules in patients with cytologically indeterminate nodules. MEDLINE and EMBASE search for studies meeting eligibility criteria between January 1, 2005, and August 30, 2015. A total of 58 studies identified. After excluding duplicates, case reports, reviews, commentary, insufficient data, a total of seven studies selected for analysis. We combined individual patient data from seven studies that examined the GEC test for indeterminate thyroid nodules. The reference standard for determination of benign or malignant nodules was the histopathology of the thyroidectomy specimen. A QUADAS-2 report for all studies included in the final analysis was tabulated for risk of bias and applicability. The pooled sensitivity of the GEC was 95.7 % (95 % CI 92.2–97.9, I 2 value 45.4 %, p = 0.09), and the pooled specificity was 30.5 % (95 % CI 26.0–35.3, I 2 value 92.1 %, p < 0.01). Overall, the diagnostic odds ratio was 7.9 (95 % CI 4.1–15.1). Patients with benign GEC were not followed long enough to ascertain the actual false-negative rates of the index test. Our meta-analysis revealed a high pooled sensitivity and a low specificity for the AFIRMA-GEC test for indeterminate thyroid nodules. This makes it an excellent tool to rule out malignancy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jarzab B, Wiench M, Fujarewicz K, Simek K, Jarzab M, Oczko-Wojciechowska M, et al. Gene expression profile of papillary thyroid cancer: sources of variability and diagnostic implications. Cancer Res. 2005;65(4):1587–97. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-3078.
Bernet V, Hupart KH, Parangi S, Woeber KA. AACE/ACE disease state commentary: molecular diagnostic testing of thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytopathology. Endocr Pract. 2014;20(4):360–3. doi:10.4158/ep14066.ps.
Hirsch D, Robenshtok E, Bachar G, Braslavsky D, Benbassat C. The implementation of the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology improves malignancy detection despite lower rate of thyroidectomy in indeterminate nodules. World J Surg. 2015;. doi:10.1007/s00268-015-3032-6.
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):529–36. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clin Res Ed). 1997;315(7109):629–34.
George BJ, Aban IB. An application of meta-analysis based on DerSimonian and Laird method. J Nucl Cardiol. 2015;. doi:10.1007/s12350-015-0249-6.
Fleiss JL, Gross AJ. Meta-analysis in epidemiology, with special reference to studies of the association between exposure to environmental tobacco smoke and lung cancer: a critique. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991;44(2):127–39.
Ades AE, Lu G, Higgins JP. The interpretation of random-effects meta-analysis in decision models. Med Decis Mak. 2005;25(6):646–54. doi:10.1177/0272989x05282643.
Welton NJ, White IR, Lu G, Higgins JP, Hilden J, Ades AE. Correction: interpretation of random effects meta-analysis in decision models. Med Decis Mak. 2007;27(2):212–4. doi:10.1177/0272989x07300428.
Deeks JJ. Systematic reviews in health care: systematic reviews of evaluations of diagnostic and screening tests. BMJ (Clin Res Ed). 2001;323(7305):157–62.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58. doi:10.1002/sim.1186.
Moses LE, Shapiro D, Littenberg B. Combining independent studies of a diagnostic test into a summary ROC curve: data-analytic approaches and some additional considerations. Stat Med. 1993;12(14):1293–316.
Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta-analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006;59(12):1331–2. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.06.011 (author reply 2–3).
Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(10):982–90. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.02.022.
Alexander EK, Kennedy GC, Baloch ZW, Cibas ES, Chudova D, Diggans J, et al. Preoperative diagnosis of benign thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(8):705–15. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1203208.
Alexander EK, Schorr M, Klopper J, Kim C, Sipos J, Nabhan F, et al. Multicenter clinical experience with the Afirma gene expression classifier. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(1):119–25. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-2482.
Aragon Han P, Olson MT, Fazeli R, Prescott JD, Pai SI, Schneider EB, et al. The impact of molecular testing on the surgical management of patients with thyroid nodules. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(6):1862–9. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-3508-x.
Harrell RM, Bimston DN. Surgical utility of Afirma: effects of high cancer prevalence and oncocytic cell types in patients with indeterminate thyroid cytology. Endocr Pract. 2014;20(4):364–9. doi:10.4158/ep13330.or.
Lastra RR, Pramick MR, Crammer CJ, LiVolsi VA, Baloch ZW. Implications of a suspicious afirma test result in thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology: an institutional experience. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014;122(10):737–44. doi:10.1002/cncy.21455.
Marti JL, Avadhani V, Donatelli LA, Niyogi S, Wang B, Wong RJ, et al. Wide inter-institutional variation in performance of a molecular classifier for indeterminate thyroid nodules. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;. doi:10.1245/s10434-015-4486-3.
McIver B, Castro MR, Morris JC, Bernet V, Smallridge R, Henry M, et al. An independent study of a gene expression classifier (Afirma) in the evaluation of cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(11):4069–77. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-3584.
Bhatia P, Deniwar A, Friedlander P, Aslam R, Kandil E. Diagnostic potential of ancillary molecular testing in differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Anticancer Res. 2015;35(3):1237–41.
Nayar R, Ivanovic M. The indeterminate thyroid fine-needle aspiration: experience from an academic center using terminology similar to that proposed in the 2007 National Cancer Institute Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration State of the Science Conference. Cancer. 2009;117(3):195–202. doi:10.1002/cncy.20029.
Choi WJ, Baek JH. Role of core needle biopsy for patients with indeterminate, fine-needle aspiration cytology. Endocrine. 2014;45(1):1–2. doi:10.1007/s12020-013-0071-3.
Macias CA, Arumugam D, Arlow RL, Eng OS, Lu SE, Javidian P, et al. A risk model to determine surgical treatment in patients with thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(5):1527–32. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-4190-8.
Weber F, Shen L, Aldred MA, Morrison CD, Frilling A, Saji M, et al. Genetic classification of benign and malignant thyroid follicular neoplasia based on a three-gene combination. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(5):2512–21. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-2028.
Kamaya A, Lewis GH, Liu Y, Akatsu H, Kong C, Desser TS. Atypia of undetermined significance and follicular lesions of undetermined significance: sonographic assessment for prediction of the final diagnosis. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34(5):767–74. doi:10.7863/ultra.34.5.767.
Garino F, Deandrea M, Motta M, Mormile A, Ragazzoni F, Palestini N, et al. Diagnostic performance of elastography in cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. Endocrine. 2015;49(1):175–83. doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0438-0.
Trimboli P, Treglia G, Sadeghi R, Romanelli F, Giovanella L. Reliability of real-time elastography to diagnose thyroid nodules previously read at FNAC as indeterminate: a meta-analysis. Endocrine. 2014;. doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0510-9.
Ohori NP, Nikiforova MN, Schoedel KE, LeBeau SO, Hodak SP, Seethala RR, et al. Contribution of molecular testing to thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology of “follicular lesion of undetermined significance/atypia of undetermined significance”. Cancer Cytopathol. 2010;118(1):17–23. doi:10.1002/cncy.20063.
Nikiforov YE, Ohori NP, Hodak SP, Carty SE, LeBeau SO, Ferris RL, et al. Impact of mutational testing on the diagnosis and management of patients with cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules: a prospective analysis of 1056 FNA samples. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(11):3390–7. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-1469.
Howlader NA, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA. SEER cancer statistics factsheets: thyroid cancer. National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/thyro.html. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2012, National Cancer Institute Bethesda, MD. 2012.
Trimboli P, Bongiovanni M, Rossi F, Guidobaldi L, Crescenzi A, Ceriani L, et al. Differentiated thyroid cancer patients with a previous indeterminate (Thy 3) cytology have a better prognosis than those with suspicious or malignant FNAC reports. Endocrine. 2015;49(1):191–5. doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0453-1.
Li H, Robinson KA, Anton B, Saldanha IJ, Ladenson PW. Cost-effectiveness of a novel molecular test for cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(11):E1719–26. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0459.
Brauner E, Holmes BJ, Krane J, Nishino M, Zurakowski D, Hennessey JV, et al. Performance of the afirma gene expression classifier in Hurthle cell thyroid nodules differs from other indeterminate thyroid nodules. Thyroid. 2015;. doi:10.1089/thy.2015.0049.
Labourier E, Shifrin A, Busseniers AE, Lupo MA, Manganelli ML, Andruss B, et al. Molecular testing for miRNA, mRNA and DNA on fine needle aspiration improves the preoperative diagnosis of thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-1158.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Larry Dial MD, Chairman of Department on Internal Medicine, Marshall University, for his help in giving us resources to complete this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santhanam, P., Khthir, R., Gress, T. et al. Gene expression classifier for the diagnosis of indeterminate thyroid nodules: a meta-analysis. Med Oncol 33, 14 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0727-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0727-3