Abstract
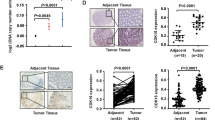
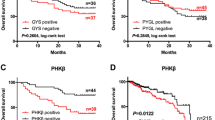
3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) is centrally involved in cancer progression, including proliferation, apoptosis and invasion. However, its expression pattern and possible cellular functions in human colorectal cancer remain unclear. In the present study, we show that PDK1 expression is up-regulated at both mRNA and protein levels in colorectal cancer clinical specimens and cell lines. Transient knockdown of PDK1 suppresses cellular growth, induces cellular apoptosis and causes abnormal cell cycle distribution. Meanwhile, decreased PDK1 level is closely associated with reduced Akt/cyclin D1 activity. Activating AKT activity and reintroducing cyclin D1 expression significantly compromised the oncogenic activity induced by PDK1. Together, our findings elucidate a key role for PDK1 in colorectal cellular functions trigged by the Akt/cyclin D1 pathway, thus providing a novel insight of PDK1 in colorectal carcinogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21208.
Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(2):104–17. doi:10.3322/caac.21220.
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J, Sjoblom T, Leary RJ, et al. The genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science. 2007;318(5853):1108–13. doi:10.1126/science.1145720.
Mora A, Komander D, van Aalten DM, Alessi DR. PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004;15(2):161–70.
Biondi RM. Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1, a sensor of protein conformation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29(3):136–42. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2004.01.005.
Bayascas JR. Dissecting the role of the 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) signalling pathways. Cell Cycle. 2008;7(19):2978–82.
Bayascas JR. PDK1: the major transducer of PI 3-kinase actions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;346:9–29. doi:10.1007/82_2010_43.
Lin HJ, Hsieh FC, Song H, Lin J. Elevated phosphorylation and activation of PDK-1/AKT pathway in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005;93(12):1372–81. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602862.
Maurer M, Su T, Saal LH, Koujak S, Hopkins BD, Barkley CR, et al. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 potentiates upstream lesions on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009;69(15):6299–306. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0820.
Zeng X, Xu H, Glazer RI. Transformation of mammary epithelial cells by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) is associated with the induction of protein kinase Calpha. Cancer Res. 2002;62(12):3538–43.
Pearn L, Fisher J, Burnett AK, Darley RL. The role of PKC and PDK1 in monocyte lineage specification by Ras. Blood. 2007;109(10):4461–9. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-09-047217.
Han L, Zhang G, Zhang N, Li H, Liu Y, Fu A, et al. Prognostic potential of microRNA-138 and its target mRNA PDK1 in sera for patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31(9):129. doi:10.1007/s12032-014-0129-y.
Ahmed N, Riley C, Quinn MA. An immunohistochemical perspective of PPAR beta and one of its putative targets PDK1 in normal ovaries, benign and malignant ovarian tumours. Br J Cancer. 2008;98(8):1415–24. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604306.
Osaki M, Oshimura M, Ito H. PI3K-Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis Int J Program Cell Death. 2004;9(6):667–76. doi:10.1023/B:APPT.0000045801.15585.dd.
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM. Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2007;12(1):9–22. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.05.008.
Manning BD, Cantley LC. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 2007;129(7):1261–74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009.
Nakamura K, Sakaue H, Nishizawa A, Matsuki Y, Gomi H, Watanabe E, et al. PDK1 regulates cell proliferation and cell cycle progression through control of cyclin D1 and p27Kip1 expression. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(25):17702–11. doi:10.1074/jbc.M802589200.
Nawa M, Kanekura K, Hashimoto Y, Aiso S, Matsuoka M. A novel Akt/PKB-interacting protein promotes cell adhesion and inhibits familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutant SOD1-induced neuronal death via inhibition of PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of Akt/PKB. Cell Signal. 2008;20(3):493–505. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.11.004.
Sharma RA, Dalgleish AG, Steward WP, O’Byrne KJ. Angiogenesis and the immune response as targets for the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 2003;10(5):1625–31.
Russo MW, Wei JT, Thiny MT, Gangarosa LM, Brown A, Ringel Y, et al. Digestive and liver diseases statistics, 2004. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(5):1448–53.
Littlejohns P, Tamber S, Ranson P, Campbell B. Treatment for liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6(2):73.
Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Hohler T, Galle PR, Buchler MW. Colorectal Cancer. Lancet. 2005;365(9454):153–65. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17706-X.
Pearce LR, Komander D, Alessi DR. The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(1):9–22. doi:10.1038/nrm2822.
Wick MJ, Ramos FJ, Chen H, Quon MJ, Dong LQ, Liu F. Mouse 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 undergoes dimerization and trans-phosphorylation in the activation loop. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(44):42913–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304172200.
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Current Biol. 1997;7(4):261–9.
Leslie NR, Yang X, Downes CP, Weijer CJ. The regulation of cell migration by PTEN. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005;33(Pt 6):1507–8. doi:10.1042/BST20051507.
Lim MA, Yang L, Zheng Y, Wu H, Dong LQ, Liu F. Roles of PDK-1 and PKN in regulating cell migration and cortical actin formation of PTEN-knockout cells. Oncogene. 2004;23(58):9348–58. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208147.
Rodriguez OC, Lai EW, Vissapragada S, Cromelin C, Avetian M, Salinas P, et al. A reduction in Pten tumor suppressor activity promotes ErbB-2-induced mouse prostate adenocarcinoma formation through the activation of signaling cascades downstream of PDK1. Am J Pathol. 2009;174(6):2051–60. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080859.
Nagashima K, Shumway SD, Sathyanarayanan S, Chen AH, Dolinski B, Xu Y, et al. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of PDK1 in cancer cells: characterization of a selective allosteric kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(8):6433–48. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.156463.
Liu Y, Wang J, Wu M, Wan W, Sun R, Yang D, et al. Down-regulation of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 levels inhibits migration and experimental metastasis of human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7(6):944–54. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0368.
Finlay DK, Sinclair LV, Feijoo C, Waugh CM, Hagenbeek TJ, Spits H, et al. Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 controls migration and malignant transformation but not cell growth and proliferation in PTEN-null lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 2009;206(11):2441–54. doi:10.1084/jem.20090219.
Pinner S, Sahai E. PDK1 regulates cancer cell motility by antagonising inhibition of ROCK1 by RhoE. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(2):127–37. doi:10.1038/ncb1675.
Currie RA, Walker KS, Gray A, Deak M, Casamayor A, Downes CP, et al. Role of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in regulating the activity and localization of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1. Biochem J. 1999;337(Pt 3):575–83.
Milburn CC, Deak M, Kelly SM, Price NC, Alessi DR, Van Aalten DM. Binding of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate to the pleckstrin homology domain of protein kinase B induces a conformational change. Biochem J. 2003;375(Pt 3):531–8. doi:10.1042/BJ20031229.
Calleja V, Ameer-Beg SM, Vojnovic B, Woscholski R, Downward J, Larijani B. Monitoring conformational changes of proteins in cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Biochem J. 2003;372(Pt 1):33–40. doi:10.1042/BJ20030358.
Stacey DW. Cyclin D1 serves as a cell cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15(2):158–63.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhenglei Xu and Bihong Liao have contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Liao, B., Zhang, R. et al. Expression of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in colorectal cancer as a potential therapeutic target. Med Oncol 32, 198 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0645-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0645-4