Abstract
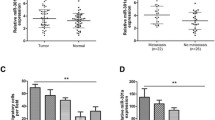
MicroRNAs have been suggested to play a vital role in regulate tumor progression and invasion. However, the expression of miR-335 in colorectal cancer (CRC) and its clinical significance are not known. Here, we report that miR-335 is a tumor suppressor by regulating expression of ZEB2. In this study, we showed that downregulated miR-335 levels in highly invasive CRC cell lines and tissues. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis indicated that patients with reduced miR-335 had a poor overall survival. Furthermore, enhancing the expression of miR-335 inhibited CRC cell migration and invasion in vitro and lung and liver metastasis in vivo, while silencing its expression resulted in increased migration and invasion. Additionally, we identified a novel miR-335 target, ZEB2, and the direct interaction between them was verified by 3′-untranslated region dual-luciferase reporter assay. In conclusion, our results demonstrate that miR-335 functions as a tumor suppressor and play a role in inhibiting metastasis of CRC cells through targeting ZEB2. These findings suggest that miR-335 may be useful as a new potential therapeutic target for CRC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz HJ, Lynch HT, Minsky B, Nordlinger B, et al. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2010;375(9719):1030–47. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60353-4.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56(2):106–30.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97.
Garzon R, Marcucci G, Croce CM. Targeting microRNAs in cancer: rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9(10):775–89. doi:10.1038/nrd3179.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(4):259–69. doi:10.1038/nrc1840.
Ebert MS, Sharp PA. Roles for microRNAs in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell. 2012;149(3):515–24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.005.
Brewster BL, Rossiello F, French JD, Edwards SL, Wong M, Wronski A, et al. Identification of fifteen novel germline variants in the BRCA1 3’UTR reveals a variant in a breast cancer case that introduces a functional miR-103 target site. Hum Mutat. 2012;33(12):1665–75. doi:10.1002/humu.22159.
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27(15):2128–36. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210856.
Yan Z, Xiong Y, Xu W, Gao J, Cheng Y, Wang Z, et al. Identification of hsa-miR-335 as a prognostic signature in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(7):e40037. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040037.
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang X, et al. MicroRNA-335 acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and specificity protein 1. Oncogene. 2012;31(11):1398–407. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.340.
Liu J, Mao Q, Liu Y, Hao X, Zhang S, Zhang J. Analysis of miR-205 and miR-155 expression in the blood of breast cancer patients. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013;25(1):46–54. doi:10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2012.11.04.
Cao J, Cai J, Huang D, Han Q, Chen Y, Yang Q, et al. miR-335 represents an independent prognostic marker in epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 2014;141(3):437–42. doi:10.1309/AJCPLYTZGB54ISZC.
Gadducci A, Sergiampietri C, Lanfredini N, Guiggi I. Micro-RNAs and ovarian cancer: the state of art and perspectives of clinical research. Gynecol Endocrinol Off J Int Soc Gynecol Endocrinol. 2014;. doi:10.3109/09513590.2013.871525.
Gong M, Ma J, Guillemette R, Zhou M, Yang Y, Yang Y, et al. miR-335 inhibits small cell lung cancer bone metastases via IGF-IR and RANKL pathways. Mol Cancer Res. 2014;12(1):101–10. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0136.
Zu Y, Ban J, Xia Z, Wang J, Cai Y, Ping W, et al. Genetic variation in a miR-335 binding site in BIRC5 alters susceptibility to lung cancer in Chinese Han populations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;430(2):529–34. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.001.
Xiong SW, Lin TX, Xu KW, Dong W, Ling XH, Jiang FN, et al. MicroRNA-335 acts as a candidate tumor suppressor in prostate cancer. Pathol Oncol Res POR. 2013;19(3):529–37. doi:10.1007/s12253-013-9613-5.
Hurst DR, Edmonds MD, Welch DR. Metastamir: the field of metastasis-regulatory microRNA is spreading. Cancer Res. 2009;69(19):7495–8. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2111.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–66. doi:10.1038/nrc1997.
Wang Y, Zhao W, Fu Q. miR-335 suppresses migration and invasion by targeting ROCK1 in osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;384(1–2):105–11. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1786-4.
Wang H, Li M, Zhang R, Wang Y, Zang W, Ma Y, et al. Effect of miR-335 upregulation on the apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer cell A549 and H1299. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodevelop Biol Med. 2013;34(5):3101–9. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-0878-9.
Cao J, Cai J, Huang D, Han Q, Yang Q, Li T, et al. miR-335 represents an invasion suppressor gene in ovarian cancer by targeting Bcl-w. Oncol Rep. 2013;30(2):701–6. doi:10.3892/or.2013.2482.
Png KJ, Yoshida M, Zhang XH, Shu W, Lee H, Rimner A, et al. MicroRNA-335 inhibits tumor reinitiation and is silenced through genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in human breast cancer. Genes Dev. 2011;25(3):226–31. doi:10.1101/gad.1974211.
Scarola M, Schoeftner S, Schneider C, Benetti R. miR-335 directly targets Rb1 (pRb/p105) in a proximal connection to p53-dependent stress response. Cancer Res. 2010;70(17):6925–33. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0141.
Bindels S, Mestdagt M, Vandewalle C, Jacobs N, Volders L, Noel A, et al. Regulation of vimentin by SIP1 in human epithelial breast tumor cells. Oncogene. 2006;25(36):4975–85. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209511.
Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M, Hiyoshi Y, Iwatsuki M, Tanaka Y, et al. MicroRNA-200b regulates cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by directly targeting ZEB2 in gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(Suppl 3):S656–64. doi:10.1245/s10434-012-2217-6.
Chu PY, Hu FW, Yu CC, Tsai LL, Yu CH, Wu BC, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factor ZEB1/ZEB2 co-expression predicts poor prognosis and maintains tumor-initiating properties in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2013;49(1):34–41. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.07.012.
Qi S, Song Y, Peng Y, Wang H, Long H, Yu X, et al. ZEB2 mediates multiple pathways regulating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis in glioma. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(6):e38842. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038842.
Cai MY, Luo RZ, Chen JW, Pei XQ, Lu JB, Hou JH, et al. Overexpression of ZEB2 in peritumoral liver tissue correlates with favorable survival after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(2):e32838. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032838.
Wu Q, Guo R, Lin M, Zhou B, Wang Y. MicroRNA-200a inhibits CD133/1 + ovarian cancer stem cells migration and invasion by targeting E-cadherin repressor ZEB2. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;122(1):149–54. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.03.026.
Gemmill RM, Roche J, Potiron VA, Nasarre P, Mitas M, Coldren CD, et al. ZEB1-responsive genes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2011;300(1):66–78. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.09.007.
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(6):415–28. doi:10.1038/nrc2131.
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, et al. The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell. 2001;7(6):1267–78.
Vandewalle C, Comijn J, De Craene B, Vermassen P, Bruyneel E, Andersen H, et al. SIP1/ZEB2 induces EMT by repressing genes of different epithelial cell–cell junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(20):6566–78. doi:10.1093/nar/gki965.
Ethical standards
The use of tissues for this study has been approved by the ethics committee of Tang Du Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University. All of the patients signed the informed consent before use of these clinical materials for research purposes. This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. The protocol was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of Fourth Military Medical University.
Acknowledgments
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81171984.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ZhiFeng Sun, Zhang Zhang and Zidong Liu have contributed equally to this study, and all should be considered first author.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Zhang, Z., Liu, Z. et al. MicroRNA-335 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting ZEB2. Med Oncol 31, 982 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0982-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0982-8