Abstract
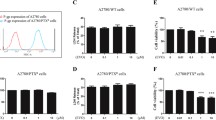
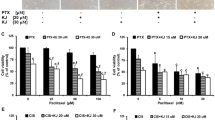
β-Elemene is a new anticancer compound extracted from the Chinese medicinal herb Rhizoma zedoariae. We have shown previously that β-elemene increases cisplatin cytotoxicity and enhances cisplatin sensitivity via blocking cell cycle progression at G2/M phase in resistant ovarian tumor cells. In the current study, we asked whether β-elemene-augmented cisplatin activity in ovarian carcinoma cells is mediated through the induction of apoptosis. Here, we show that β-elemene triggered apoptotic cell death in chemoresistant human ovarian cancer A2780/CP and MCAS cells in a dose- and time-dependent fashion, as assessed by six different apoptosis assays. Intriguingly, β-elemene was a stronger inducer of apoptosis than cisplatin in this model system, and a synergistic effect on induction of cell death was observed when the tumor cells were treated with both agents. Furthermore, β-elemene plus cisplatin exposure significantly disrupted the mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔΨ m) and increased the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytoplasm. The combination treatment with both compounds also induced increases in caspase-3/8/9 activities and caspase-9 cleavage, enhanced protein expression of Bax and phosphorylation of Bcl-2 at Ser-70, and reduced the protein levels of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL in the platinum-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Taken together, these data indicate that β-elemene sensitizes chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis and that the augmented effect of β-elemene on cisplatin cytotoxicity and sensitivity in resistant ovarian tumor cells is mediated through a mitochondria- and caspase-dependent cell death pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sfakianos GP, Havrilesky LJ. A review of cost-effectiveness studies in ovarian cancer. Cancer Control. 2010;18:59–64.
Murphy G. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2000;50:7–33.
Wang D, Lippard SJ. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:307–20.
Kelland L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:573–84.
Li X, Wang G, Zhao J, Ding H, Cunningham C, Chen F, Flynn DC, Reed E, Li QQ. Antiproliferative effect of beta-elemene in chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells is mediated through arrest of the cell cycle at the G2-M phase. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62:894–904.
Li QQ, Wang G, Zhang M, Cuff CF, Huang L, Reed E. beta-Elemene, a novel plant-derived antineoplastic agent, increases cisplatin chemosensitivity of lung tumor cells by triggering apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2009;22:161–70.
Li QQ, Wang G, Huang F, Banda M, Reed E. Antineoplastic effect of beta-elemene on prostate cancer cells and other types of solid tumour cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010;62:1018–27.
Li QQ, Wang G, Reed E, Huang L, Cuff CF. Evaluation of Cisplatin in Combination with beta-Elemene as a Regimen for Prostate Cancer Chemotherapy. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;107:868–76.
Zhao J, Li QQ, Zou B, Wang G, Li X, Kim JE, Cuff CF, Huang L, Reed E, Gardner K. In vitro combination characterization of the new anticancer plant drug beta-elemene with taxanes against human lung carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2007;31:241–52.
Wang G, Li X, Huang F, Zhao J, Ding H, Cunningham C, Coad JE, Flynn DC, Reed E, Li QQ. Antitumor effect of beta-elemene in non-small-cell lung cancer cells is mediated via induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62:881–93.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ. Cell death: critical control points. Cell. 2004;116:205–19.
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P. Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:552–65.
Ellis M, Yuan J, Horvitz H. Mechanisms and function of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–98.
Thompson C. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267:1456–62.
Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science. 1995;267:1445–9.
Li J, Feng Q, Kim J-M, Li M, Fung FK, Tsang BK. Human ovarian cancer and cisplatin resistance: possible role of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Endocrinology. 2001;142:370–80.
MacFarlane M. Cell death pathways–potential therapeutic targets. Xenobiotica. 2009;39:616–24.
Wyllie A. Apoptosis and carcinogenesis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1997;73:189–97.
Selzner M, Bielawska A, Morse M, Rudiger H, Sindram D, Hannun Y, Clavien P. Induction of apoptotic cell death and prevention of tumor growth by ceramide analogues in metastatic human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1233–40.
Serrano M, Sanchez-Rovira P, Algarra I, Jaen A, Lozano A, Gaforio J. Evaluation of a gemcitabine-doxorubicin-paclitaxel combination schedule through flow cytometry assessment of apoptosis extent induced in human breast cancer cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2002;93:559–66.
Pathania D, Millard M, Neamati N. Opportunities in discovery and delivery of anticancer drugs targeting mitochondria and cancer cell metabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61:1250–75.
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Vitale I, Rigoni A, Vacchelli E, Michaud M, Zischka H, Castedo M, Kroemer G. Mitochondrial gateways to cancer. Mol Aspects Med. 2010;31:1–20.
Xu CX, Jin H, Cho MH Apoptosis and apoptosis-based therapy in lung cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2009;9:952–7.
Wang C, Youle RJ. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:95–118.
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR. Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:537–49.
Fraser M, Leung B, Jahani-Asl A, Yan X, Thompson W, Tsang B. Chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer: the role of apoptotic regulators. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003;1:66.
Behrens BC, Hamilton TC, Masuda H, Grotzinger KR, Whang-Peng J, Louie KG, Knutsen T, McKoy WM, Young RC, Ozols RF. Characterization of a cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II)-resistant human ovarian cancer cell line and its use in evaluation of platinum analogues. Cancer Res. 1987;47:414–8.
Parker RJ, Eastman A, Bostick-Bruton F, Reed E. Acquired cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells is associated with enhanced DNA repair of cisplatin-DNA lesions and reduced drug accumulation. J Clin Invest. 1991;87:773–7.
Kitabayashi A, Hirokawa M, Hatano Y, Lee M, Kuroki J, Miura A. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor down-regulates allogeneic immune responses by post-transcriptional inhibition of tumor necrosis factor- production. Blood. 1995;86:2220.
Sasaki H, Sheng Y, Kotsuji F, Tsang B. Down-regulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein induces apoptosis in chemoresistant human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5659–66.
Ho YS, Duh JS, Jeng JH, Wang YJ, Liang YC, Lin CH, Tseng CJ, Yu CF, Chen RJ, Lin JK. Griseofulvin potentiates antitumorigenesis effects of nocodazole through induction of apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2001;91:393–401.
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B, Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ, Los M. Apoptosis and cancer: mutations within caspase genes. J Med Genet. 2009;46:497–510.
Ledgerwood EC, Morison IM. Targeting the apoptosome for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:420–4.
Ashkenazi A, Dixit V. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–8.
Nunez G, Benedict M, Hu Y, Inohara N. Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene. 1998;17:3237–45.
Stennicke H, Jurgensmeier J, Shin H, Deveraux Q, Wolf B, Yang X, Zhou Q, Ellerby H, Ellerby L, Bredesen D, Green D, Reed J, Froelich C, Salvesen G. Pro-caspase-3 is a major physiologic target of caspase-8. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:27084–90.
Deng Y, Lin Y, Wu X. TRAIL-induced apoptosis requires Bax-dependent mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO. Genes Dev. 2002;16:33–45.
Grunewald S, Sharma R, Paasch U, Glander HJ, Agarwal A. Impact of caspase activation in human spermatozoa. Microsc Res Tech, 2009;72:878–88.
Suen DF, Norris KL, Youle RJ. Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1577–90.
Colin J, Gaumer S, Guenal I, Mignotte B. Mitochondria, Bcl-2 family proteins and apoptosomes: of worms, flies and men. Front Biosci. 2009;14:4127–37.
Jourdain A, Martinou JC. Mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization and remodelling in apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:1884–9.
Zamzami N, Susin S, Marchetti P, et al. Mitochondrial control of nuclear apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1996;183:1533–44.
Green D, Reed J. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science. 1998;281:1309–12.
Liu X, Kim C, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 1996;86:147–57.
Zoratti M, Szabo I. The mitochondrial permeability transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1241:139–76.
Jacobson M, Weil M, Raff M. Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell. 1997;88:347–54.
Mandlekar S. Y. R., Tan TH, Kong AN. Activation of caspase-3 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-1 signaling pathways in tamoxifen-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5995–6000.
Fulda S. Caspase-8 in cancer biology and therapy. Cancer Lett. 2009;281:128–33.
Sun S, Yue P, Hong W, Lotan R. Augmentation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by the synthetic retinoid 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]-2-naphthalene carboxylic acid (CD437) through up-regulation of TRAIL receptors in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:7149–55.
Thornberry N, Lazebnik Y. Caspases. Enemies within. Science. 1998;281:1312–6.
Petronilli V, Costantini P, Scorrano L, Colonna R, Passamonti S, Bernardi P. The voltage sensor of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore is tuned by the oxidation-reduction state of vicinal thiols: increase of the gating potential by oxidants and its reversal by reducing agents. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:16638–42.
Kuo HM, Tsai HC, Lin YL, Yang JS, Huang AC, Yang MD, Hsu SC, Chung MC, Gibson Wood W, Chung JG. Mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway is involved in baicalein-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma J5 cells. Int J Oncol. 2009;35:717–24.
Kang MH, Reynolds CP. Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:1126–32.
Szegezdi E, Macdonald DC, Ni Chonghaile T, Gupta S, Samali A. Bcl-2 family on guard at the ER. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;296:C941–53.
Srivastava R, Mi Q, Hardwick J, Longo D. Deletion of the loop region of Bcl-2 completely blocks paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:3775–80.
Acknowledgments
This publication was made possible by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Guangxi Province (No. 0991294) and the Guangxi Scientific Research and Technological Development Program (No. 200901059), and by grants from the National Institutes of Health (Nos. P20RR16440-010003, P20RR16440-020003, P20RR16440-030003, P20RR16440-040003) and West Virginia University School of Medicine Research Grant (to Q. Q. Li).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Qingdi Li, Rebecca Lee, and Huasheng Liang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q.Q., Lee, R.X., Liang, H. et al. Enhancement of cisplatin-induced apoptosis by β-elemene in resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Med Oncol 30, 424 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0424-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0424-4