Abstract
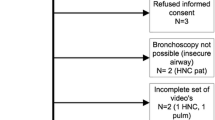
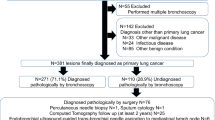
Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) videobronchoscopy is a new technique for visualization of microvascular changes in bronchial mucosa. The primary aim of this study was to evaluate relation between vascular patterns visualized by NBI and histology of lung cancer. We prospectively evaluated 65 patients with suspected lung cancer scheduled for bronchoscopy. NBI followed conventional WL videobronchoscopy. After identification of endoscopically visible tumor, NBI was used to determine predominant type of pathological vascular pattern (dotted, tortuous, abrupt-ending blood vessels—Shibuya descriptors). All the lesions were biopsied and histologically confirmed. There were 81.5 % male and 18.5 % female patients evaluated in the study. Lung cancer was confirmed in all patients; 63.1 % were diagnosed with squamous cell lung cancer (SCC), 24.6 % had adenocarcinoma, 9.2 % had small-cell (SCLC) and 3.1 % large-cell lung cancer (LC). Dotted blood vessels were significantly (p < 0.000) associated with adenocarcinoma, identified in 68.4 % adenocarcinoma and 31.6 % SCC. Tortuous blood vessels were identified in 72 % SCC, 8 % adenocarcinoma, 12 % SCLC and 8 % of LC. Tortuous blood vessels were significantly (p < 0.000) associated with SCC. Abrupt-ending vessels were identified in 81 % SCC, 14.3 % SCLC and 4.8 % adenocarcinoma and were significantly associated (p < 0.000) with SCC. Dotted visual pattern of blood vessels identified during NBI videobronchoscopy is highly suggesting adenocarcinoma histology of lung cancer. Tortuous and abrupt-ending blood vessels visualized under NBI videobronchoscopy significantly suggest squamous cell histology of lung cancer. Large-scale studies should be designed in order to determine true relation between visual appearance and histology in lung cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colt HG, Murgu SD. Interventional bronchoscopy from bench to bedside: new techniques for early lung cancer detection. Clin Chest Med. 2010;31(1):29–37.
Gono K, Obi T, Yamaguchi M, et al. Appearance of enhanced tissue features in narrow-band endoscopic imaging. J Biomed Opt. 2004;9(3):568–77.
Yarmus L, Feller-Kopman D. Bronchoscopes of the twenty-first century. Clin Chest Med. 2010;31(1):19–27.
Yasufuku K. Early diagnosis of lung cancer. Clin Chest Med. 2010;31(1):39–47.
Herth F. Playing with the wavelengths: endoscopic early lung cancer detection. Lung Cancer. 2010;69(2):131–2.
Zaric B, Perin B. The use of narrow band imaging bronchoscopy in detection of lung cancer. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2010;7(3):395–406.
Miyazu Y, Ishida A, Nakamura M, et al. Possible clinical applications of high magnification bronchoscopy combined with narrow band imaging. Chest. 2006;130(4):146s.
Yamada G, Kitamura Y, Kitada J, Yamada Y, Takahashi M, Fujii M, Takahashi H. Increased microcirculation in subepithelial invasion of lung cancer. Intern Med. 2011;50(8):839–43.
Herth FJF, Eberhardt R, Anantham D, Gompelmann D, Zakaria MW, Ernst A. Narrow-band imaging bronchoscopy increases the specificity of bronchoscopic early lung cancer detection. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4:1060–5.
Herth F, Eberhardt R, Ernst A. Narrow band imagining (NBI) for early lung cancer detection. Chest. 2006;130(4):146s.
Zaric B, Perin B, Becker HD, Herth FJ, Eberhardt R, Jovanovic S, Orlic T, Panjkovic M, Zvezdin B, Jovelic A, Bijelovic M, Jurisic V, Antonic M. Combination of narrow band imaging (NBI) and autofluorescence imaging (AFI) videobronchoscopy in endoscopic assessment of lung cancer extension. Med Oncol. 2012;29(3):1638–42.
Vincent BD, Fraig M, Silvestri GA. A pilot study of narrow-band imaging compared to white light bronchoscopy for evaluation of normal airways and premalignant and malignant airways disease. Chest. 2007;131:1794–9.
Park JK, Jo YS, Jang S, Park YS, Choi CM. Clinical benefits of narrow band imaging bronchoscopy in central lung cancer. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2010;68(1):16–21.
Shibuya K, Hoshino H, Chiyo M, Yasufuku K, Iizasa T, Saitoh Y, et al. Subepithelial vascular patterns in bronchial dysplasias using a high magnification bronchovideoscope. Thorax. 2002;57(10):902–7.
Shibuya K, Hoshino H, Chiyo M, Iyoda A, Yoshida S, Sekine Y, et al. High magnification bronchovideoscopy combined with narrow band imaging could detect capillary loops of angiogenic squamous dysplasia in heavy smokers at high risk for lung cancer. Thorax. 2003;58:989–95.
Shibuya K, Nakajima T, Fujiwara T, Chiyo M, Hoshino H, Moriya Y, et al. Narrow band imaging with high-resolution bronchovideoscopy: a new approach for visualizing angiogenesis in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer. 2010;69(2):194–202.
Yamada G, Shijubo N, Kitada J, Takahashi M, Otsuka M, Fujii M, et al. Narrow band imaging yields clear images of subepithelial microvessels in large airways in combination with high magnification bronchovideoscopy. J Bronchol. 2007;14:75–8.
Miyazu Y, Ishida A, Nakamura M, et al. Clinical utility of narrow band imaging for centrally located lesions in the lung. Chest. 2007;132(4):516s.
Zaric B, Perin B, Jovelic A, Stojanovic G, Ilic MD, Andrijevic I, et al. Influence of Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) Videobronchoscopy on the Assessment of Central Lung Cancer Extension and Therapeutic Decision. Cancer Invest. 2009;27:918–23.
Zaric B, Becker HD, Perin B, Jovelic A, Stojanovic G, Ilic MD, et al. Narrow band imaging (NBI) videobronchoscopy improves assessment of lung cancer extension and influences therapeutic strategy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2009;39:657–63.
Yasufuku K, Shibuya K, Fujisawa T. Narrow band imaging in the airway: where do we stand? J Bronchol. 2007;14(2):71–2.
Irani S, Thuer I, Seifert B, Speich R, Boehler A. Endoscopic narrow-band imaging-quantitative assessment of airway vascularity after lung transplantation. J Biomed Opt. 2009;14(1):014010.
East JE, Tan EK, Bergman JJ, Saunders BP, Tekkis PP. Meta-analysis: narrow band imaging for lesion characterization in the colon, oesophagus, duodenal ampulla and lung. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28(7):854–67.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the grant of the Serbian Ministry for Science and Technology, grant number 175056.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaric, B., Perin, B., Stojsic, V. et al. Relation between vascular patterns visualized by narrow band imaging (NBI) videobronchoscopy and histological type of lung cancer. Med Oncol 30, 374 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0374-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0374-x