Abstract
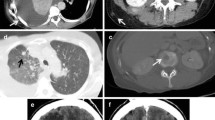
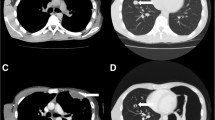
Spontaneous pyopneumothorax is a very rare occurrence, even in cancer treated patients. Here we present two consecutive cases of spontaneous pyopneumothorax that occurred early after initiation of mTOR inhibitors for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma with subpleural pulmonary metastasis. In these two cases, necrosis and excavation of lung metastasis were observed, suggesting their involvement in the pathogenic mechanism of pyopneumothorax. This report extends the available experience of the pulmonary side effects of these novel targeted therapies.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
References
Abraham RT, Gibbons JJ. The mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway: twists and turns in the road to cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:3109–14.
Vignot S, Faivre S, Aguirre D, Raymond E. mTOR-targeted therapy of cancer with rapamycin derivatives. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:525–37.
Hidalgo M, Rowinsky EK. The rapamycin-sensitive signal transduction pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2000;19:6680–6.
Del Bufalo D, et al. Antiangiogenic potential of the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor temsirolimus. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5549–54.
Hudes G, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2271–81.
Motzer RJ, et al. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372:449–56.
Mekhail TM, et al. Validation and extension of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering prognostic factors model for survival in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:832–41.
Klugo RC, Detmers M, Stiles RE, Talley RW, Cerny JC. Aggressive versus conservative management of stage IV renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1977;118:244–6.
McNichols DW, Segura JW, DeWeerd JH. Renal cell carcinoma: long-term survival and late recurrence. J Urol. 1981;126:17–23.
Mahalati K. Bronchiolitis obliterans and organizing pneumonia in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2000;69:1581.
Pham PT, et al. Sirolimus-associated pulmonary toxicity. Transplantation. 2004;77:1215–20.
Morelon E, Mamzer-Bruneel MF, Peraldi MN, Kreis H. Sirolimus: a new promising immunosuppressive drug. Towards a rationale for its use in renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16:18–20.
Duran I, et al. Characterisation of the lung toxicity of the cell cycle inhibitor temsirolimus. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:1875–80.
Atkins MB, et al. Randomized phase II study of multiple dose levels of CCI-779, a novel mammalian target of rapamycin kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced refractory renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:909–18.
Chan S, et al. Phase II study of temsirolimus (CCI-779), a novel inhibitor of mTOR, in heavily pretreated patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5314–22.
Galanis E, et al. Phase II trial of temsirolimus (CCI-779) in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5294–304.
Hudson CC, et al. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:7004–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ladoire, S., Beynat, C., Diaz, P. et al. Spontaneous pyopneumothorax in patients treated with mTOR inhibitors for subpleural pulmonary metastases. Med Oncol 27, 938–941 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9311-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9311-z