Abstract
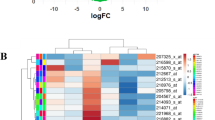
Multidrug resistance remains a major clinical obstacle to successful treatment of breast cancer and leads to poor prognosis for the patients. Recently studies have shown that microRNAs play an important role in breast cancer cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. In this study, microRNA expression profiles of MCF-7/AdrVp and MCF-7 were analyzed using microarray and the results were confirmed by real-time RT-polymerase chain reaction. Gene Ontology (GO) and pathways mapping tools were employed to analyse systemically the biological processes and signaling pathways affected by differential expression microRNAs. Here, we showed that 181 human microRNAs were differentially expressed between two cell lines. Compared to MCF-7 cells, there were 16 microRNAs down-regulated and 165 microRNAs up-regulated in MCF-7/AdrVp. Western blot confirmed the correlation between specific microRNA expression and corresponding changes in protein levels of their targets, specifically those that have a documented role in cancer drug resistance. Furthermore, we validated that signaling pathway highlighted in the study was involved in drug resistance. These results indicated that breast cancer cell resistant to chemotherapy was associated with a group of microRNAs. GO and pathway mapping are valid and effective approach to analyse the function of microRNAs and the results could be a guideline for further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fojo T. Multiple paths to a drug resistance phenotype: mutations, translocations, deletions and amplification of coding genes or promoter regions, epigenetic changes and microRNAs. Drug Resist Updat. 2007;10(1–2):59–67. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2007.02.002.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5.
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 2005;433(7027):769–73. doi:10.1038/nature03315.
Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122(1):6–7. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.036.
O’Rourke JR, Swanson MS, Harfe BD. MicroRNAs in mammalian development and tumorigenesis. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2006;78(2):172–9. doi:10.1002/bdrc.20071.
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007;302(1):1–12. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.028.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–66. doi:10.1038/nrc1997.
Chen CZ. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(17):1768–71. doi:10.1056/NEJMp058190.
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26(19):2799–803. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210083.
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, et al. Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(7):2113–29. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.057.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(2):647–58. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.022.
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, et al. MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(1):1–9. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0573.
Weidhaas JB, Babar I, Nallur SM, et al. MicroRNAs as potential agents to alter resistance to cytotoxic anticancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2007;67(23):11111–6. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2858.
Rossi L, Bonmassar E, Faraoni I. Modification of miR gene expression pattern in human colon cancer cells following exposure to 5-fluorouracil in vitro. Pharmacol Res. 2007;56(3):248–53. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2007.07.001.
Nakajima G, Hayashi K, Xi Y, et al. Non-coding microRNAs hsa-let-7g and hsa-miR-181b are associated with chemoresponse to S-1 in colon cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2006;3(5):317–24.
Chen YN, Mickley LA, Schwartz AM, et al. Characterization of doxorubicin-resistant human breast cancer cells which display overexpression of a novel resistance-related membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(17):10073–80.
Schmittgen TD, Lee EJ, Jiang J, et al. Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA. Methods. 2008;44(1):31–8. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.09.006.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Gusev Y. Computational methods for analysis of cellular functions and pathways collectively targeted by differentially expressed microRNA. Methods. 2008;44(1):61–72. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.10.005.
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Tan Q, et al. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Web Server issue):W169–75.
Draghici S, Khatri P, Tarca AL, et al. A systems biology approach for pathway level analysis. Genome Res. 2007;17(10):1537–45. doi:10.1101/gr.6202607.
Nam S, Kim B, Shin S, Lee S. miRGator: an integrated system for functional annotation of microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(Database issue):D159–64.
Welch C, Chen Y, Stallings RL. MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 2007;26(34):5017–22. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210293.
Takagi S, Nakajima M, Mohri T, Yokoi T. Post-transcriptional regulation of human pregnane X receptor by micro-RNA affects the expression of cytochrome P450 3A4. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(15):9674–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709382200.
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, et al. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell. 2005;120(5):635–47. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.014.
Doyle LA, Yang W, Abruzzo LV, et al. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95(26):15665–70. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.26.15665.
Bandrés E, Cubedo E, Agirre X, et al. Identification by real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral tissues. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:29. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-5-29.
Woods K, Thomson JM, Hammond SM. Direct regulation of an oncogenic micro-RNA cluster by E2F transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(4):2130–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.C600252200.
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, et al. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17–92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65(21):9628–32. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2352.
Michael MZ, O’ Connor SM, van Holst Pellekaan NG, et al. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1(12):882–91.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(16):7065–70. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1783.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(7):2257–61. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510565103.
Adams BD, Furneaux H, White BA. The micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and represses ERalpha messenger RNA and protein expression in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(5):1132–47. doi:10.1210/me.2007-0022.
Chédotal A, Kerjan G, Moreau-Fauvarque C. The brain within the tumor: new roles for axon guidance molecules in cancers. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12(8):1044–56. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401707.
Chédotal A. Chemotropic axon guidance molecules in tumorigenesis. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 2007;39:78–90. doi:10.1159/000100048.
Yoo YA, Kim YH, Kim JS, Seo JH. The functional implications of Akt activity and TGF-beta signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1783(3):438–47. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.12.001.
Normanno N, Campiglio M, Maiello MR, et al. Breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib show persistent activation of MAPK signaling. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;112(1):25–33. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9830-2.
Nahta R, Yuan LX, Zhang B, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterodimerization contributes to trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(23):11118–28. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3841.
Bender LM, Nahta R. Her2 cross talk and therapeutic resistance in breast cancer. Front Biosci. 2008;13:3906–12. doi:10.2741/2978.
Tsuruo T, Naito M, Tomida A, et al. Molecular targeting therapy of cancer: drug resistance, apoptosis and survival signal. Cancer Sci. 2003;94(1):15–21. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01345.x.
Wendel HG, Malina A, Zhao Z, et al. Determinants of sensitivity and resistance to rapamycin-chemotherapy drug combinations in vivo. Cancer Res. 2006;66(15):7639–46. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Display of targets gene of differential expressed microRNAs (shown in orange) in MCF-7/AdrVp and MCF-7 cells mapped on the axon guidance signaling pathway (A) and MAPK Signaling Pathway (B) (JPG 1808 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, GQ., Zhao, ZW., Zhou, HY. et al. Systematic analysis of microRNA involved in resistance of the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell to doxorubicin. Med Oncol 27, 406–415 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9225-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9225-9