Abstract
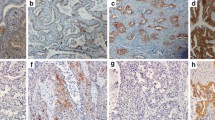
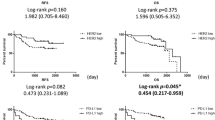
Purpose The prognostic significance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression remains unestablished, although EGFR and COX-2 are frequently overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Considering the importance of EGFR activation after ligand binding, however, the expression of phosphorylated EGFR (p-EGFR) may have more significance in predicting tumor aggressiveness in NSCLC than either EGFR or COX-2 expression. Patients and methods We studied the relationships between p-EGFR, EGFR, and COX-2 overexpression and examined their association with prognosis in localized NSCLC. The expression of p-EGFR, EGFR, and COX-2 was studied by immunohistochemistry in 77 surgically-resected stage I/II NSCLC cases. EGFR mutational status was determined by sequencing exons 18–21. Correlation of expression with clinical outcome and other biomarkers, including Ki-67 and microvessel density (MVD), was also examined. Results Out of the 77 patients, EGFR overexpression was observed in 37 (48.1%), p-EGFR expression was found in 22 (28.6%), and COX-2 overexpression was seen in 45 (58.4%). Expression of p-EGFR was associated with COX-2 overexpression (P = 0.047), but not EGFR overexpression or high Ki-67 (P = 0.087 and P = 0.092, respectively). COX-2 overexpression was significantly associated with high Ki-67 (P = 0.011). Expression of p-EGFR correlated with lower disease-free survival (P = 0.045), but not overall survival. Neither EGFR nor COX-2 overexpression was associated with prognosis. Conclusion p-EGFR appears to be a better indicator for lower disease-free survival than EGFR overexpression itself in localized NSCLC. Pathways other than EGFR activation may influence COX-2 overexpression.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:127–37. doi:10.1038/35052073.
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2787–99. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.01.504.
Brabender J, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2-neu mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer is correlated with survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:1850–5.
Lai WW, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor family members in stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72:1868–76. doi:10.1016/S0003-4975(01)03207-6.
Tateishi M, et al. Immunohistochemical evidence of autocrine growth factors in adenocarcinoma of the human lung. Cancer Res. 1990;50:7077–80.
Rusch V, et al. Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligand transforming growth factor alpha is frequent in resectable non-small cell lung cancer but does not predict tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:515–22.
Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Harper ME. EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(suppl 4):9–15. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00231-3.
Vadlamudi R, et al. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 pathway by HER2 receptor. Oncogene. 1999;18:305–14. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202307.
Kim HS, et al. Correlation between cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2003;42:163–70. doi:10.1016/S0169-5002(03)00290-3.
Richardson CM, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 protein levels are independent of epidermal growth factor receptor expression or activation in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2005;48:47–57. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.09.007.
Kanematsu T, et al. Phosphorylation, but not overexpression, of epidermal growth factor receptor is associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncol Res. 2003;13:289–98.
Fry WA, Phillips JL, Menck HR. Ten-year survey of lung cancer treatment and survival in hospitals in the United States: a national cancer data base report. Cancer. 1999;86:1867–76. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19991101)86:9<1867::AID-CNCR31>3.0.CO;2-9.
Kim SJ, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7925–33. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0636.
Paez JG, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1458–61.
Yarden Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer: signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(suppl 4):3–8. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(01)00230-1.
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1995;19:183–232. doi:10.1016/1040-8428(94)00144-I.
Mendelsohn J. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1S–13S.
Prenzel N, et al. EGF receptor transactivation by G-protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage of proHB-EGF. Nature. 1999;402:884–8.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:489–501. doi:10.1038/nrc839.
Weinstein-Oppenheimer CR, et al. The Raf signal transduction cascade as a target for chemotherapeutic intervention in growth factor-responsive tumors. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;88:229–79. doi:10.1016/S0163-7258(00)00085-1.
Calo V, et al. STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2003;197:157–68. doi:10.1002/jcp.10364.
Jorissen RN, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:31–53. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(02)00098-8.
O’Byrne KJ, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor and angiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2000;82:1427–32. doi:10.1054/bjoc.1999.1115.
Cox G, Jones JL, O’Byrne KJ. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 and the epidermal growth factor signal pathway in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2349–55.
Khuri FR, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression is a marker of poor prognosis in stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:861–7.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NCI grants R21-CA91565 and U01-CA96123 and a VA merit review award (to MJK). We thank Marguerite Adkins for secretarial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.J., Rabbani, Z.N., Dong, F. et al. Phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in localized non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol 27, 91–97 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9178-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-009-9178-z