Abstract
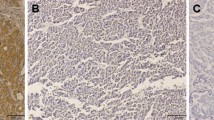
The objective of this study was to investigate the expressions of angiogenic factors and elucidate their angiogenic and prognostic roles in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with background of hepatitis B virus (HBV). We evaluated microvessel density (MVD) of HCC, and investigated immunohistochemical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), angiopoietins (Ang-1 and Ang-2), and matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9) in 67 specimens of surgically resected HCC, which were all positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. We investigated the relationship between their expressions and clinicopathological factors or prognosis. The microvessel density (MVD) of tumor tissue and surrounding normal liver tissue was 93.1 ± 43.8/mm2 and 30.4 ± 14.8/mm2, respectively. The MVD of well-differentiated HCC was significantly less than that of poorly differentiated HCC. MVD was positively correlated with VEGF and Ang-2 expression (P = 0.0023 and 0.0265, respectively). There was less tumor recurrence in low Ang-2 and low MMP-9 group than high Ang-2 and/or high MMP-9 group (P = 0.002). In Cox regression model, portal vein thrombus and intrahepatic metastasis was the risk factors of tumor recurrence (P = 0.003 and 0.001, respectively). Our study showed that the expression of VEGF and Ang-2 were positively correlated with MVD. Ang-2 expression and/or MMP-9 expression might be a significant predictive factor for recurrence after resection in HCC patients with the background of HBV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mise M, Arii S, Higashituji H, et al. Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor gene expression in liver tumor. Hepatology. 1996;23:455–64. doi:10.1002/hep.510230309.
Mitsuhashi N, Shimizu H, Ohtsuka M, et al. Angiopoietins and Tie-2 expression in angiogenesis and proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2003;37:1105–13. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50204.
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Noguchi R, et al. Angiopoietin 2 displays a vascular endothelial growth factor dependent synergistic effect in hepatocellular carcinoma development in mice. Gut. 2005;54:1768–75. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.067900.
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, et al. Synergistic effect of basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002;35:834–42. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.32541.
Sun MH, Han XC, Jia MK, et al. Expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and their effects on angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:5931–7.
Ishii Y, Nakasato Y, Kobayashi S, et al. A study on angiogenesis-related matrix metalloproteinase networks in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2003;22:461–70.
El-Assal ON, Yamanoi A, Soda Y, et al. Clinical significance of microvessel density and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding liver: possible involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor in the angiogenesis of cirrhotic liver. Hepatology. 1998;27:1554–62. doi:10.1002/hep.510270613.
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor tightly regulates in vivo development of murine hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 1998;28:1489–96. doi:10.1002/hep.510280607.
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and receptor interaction is a prerequisite for murine hepatic fibrogenesis. Gut. 2003;52:1347–54. doi:10.1136/gut.52.9.1347.
Young PP, Hofling AA, Sands MS. VEGF increases engraftment of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) into vasculature of newborn murine recipients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:11951–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.182215799.
Yau T, Chan P, Wong H, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of low-dose thalidomide as first-line systemic treatment of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2007;72(Suppl 1):67–71. doi:10.1159/000111709.
Sugimachi K, Tanaka S, Taguchi K, et al. Angiopoietin switching regulates angiogenesis and progression of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2003;56:854–60. doi:10.1136/jcp.56.11.854.
Furuse J, Ishii H, Nakachi K, et al. Phase I study of sorafenib in Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:159–65.
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, et al. Expression pattern of angiogenic factors and prognosis after hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma: importance of angiopoietin-2 and hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha. Liver Int. 2006;26:414–23. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01243.x.
Sun HC, Tang ZY, Li XM, et al. Microvessel density of hepatocellular carcinoma: its relationship with prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1999;125:419–26. doi:10.1007/s004320050296.
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis–correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1–8.
Ng IO, Poon RT, Lee JM, et al. Microvessel density, vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1/KDR in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2001;116:838–45. doi:10.1309/FXNL-QTN1-94FH-AB3A.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Arai I, Nagano H, Kondo M, et al. Overexpression of MT3-MMP in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with capsular invasion. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54:167–71.
Moon WS, Park HS, Yu KH, et al. Expression of betacellulin and epidermal growth factor receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for angiogenesis. Hum Pathol. 2006;37:1324–32. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2006.04.022.
Khoury T, Chadha K, Javle M, et al. Expression of intestinal trefoil factor (TFF-3) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2005;35:171–7. doi:10.1385/IJGC:35:3:171.
Poon RT, Chung KK, Cheung ST, et al. Clinical significance of thrombospondin 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4150–7. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0435.
Poon RT, Ng IO, Lau C, et al. Correlation of serum basic fibroblast growth factor levels with clinicopathologic features and postoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2001;182:298–304. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(01)00708-5.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the contributions of Dr. Dong-Ying Chen (Department of pathology, Sun-Yat-Sen Medical College, Sun-Yat-Sen University) for pathological support during the experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, ZB., Shen, SQ., Ding, YM. et al. The angiogenic and prognostic implications of VEGF, Ang-1, Ang-2, and MMP-9 for hepatocellular carcinoma with background of hepatitis B virus. Med Oncol 26, 365–371 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-008-9130-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-008-9130-7