Abstract
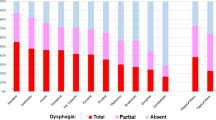
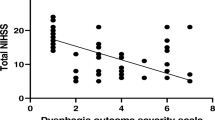
Dysphagia is often a long-term problem after ischemic stroke, which are often accompanied by complications and results in poor outcome. This study aimed to investigate the influencing factors associated with the prognosis of dysphagia after senile ischemic stroke and evaluate the diagnostic performance of crucial factors. A total of 192 elderly ischemic stroke patients (96 patients without dysphagia with average age of 69.81 ± 4.61 years and 96 patients with dysphagia with average of 70.00 ± 6.66 years) were enrolled in the retrospective study. The clinical factors of the patients were collected and recorded for chi-square analysis and logistic analysis. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was performed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of international normalized ratio (INR) and homocysteine (Hcy) in senile ischemic stroke patients. The age, cough reflex, history of stroke, mechanical ventilation, eating posture, insufficient elevation of the larynx, standard swallowing assessment (SSA) score, Hcy value, and INR were closely related to endpoint events of patients with dysphagia. The joint model (combined INR and Hcy value) can increase the area under the curve (AUC) value (0.948) with higher sensitivity and specificity for predicting patients with dysphagia occurred endpoint events. The influencing factors for older ischemic stroke patients with dysphagia include age, cough reflex, history of stroke, mechanical ventilation, eating posture, insufficient elevation of the larynx, SSA score, Hcy value, and INR. INR and Hcy were independent risk factors for prognosis and diagnostic markers for patients with dysphagia after senile ischemic stroke.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Andrade PA, Santos CAD, Firmino HH, Rosa COB (2018) The importance of dysphagia screening and nutritional assessment in hospitalized patients. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 16(2):eAO4189. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1679-45082018ao4189
Ashjazadeh N, Fathi M, Shariat A (2013) Evaluation of Homocysteine Level as a Risk Factor among Patients with Ischemic Stroke and Its Subtypes. Iran J Med Sci 38(3):233–239
Branco LL, Trentin S, Augustin Schwanke CH, Gomes I, Loureiro F (2019) The Swallowing Clinical Assessment Score in Parkinson’s Disease (SCAS-PD) Is a Valid and Low-Cost Tool for Evaluation of Dysphagia: A Gold-Standard Comparison Study. J Aging Res 2019:7984635. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7984635
Chalos V, van der Ende NAM, Lingsma HF, Mulder M, Venema E, Dijkland SA, Berkhemer OA, Yoo AJ, Broderick JP, Palesch YY, Yeatts SD, Roos Y, van Oostenbrugge RJ, van Zwam WH, Majoie C, van der Lugt A, Roozenbeek B, Dippel DWJ (2020) National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale: An Alternative Primary Outcome Measure for Trials of Acute Treatment for Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 51(1):282–290. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.119.026791
Chang MC, Kwak SG, Chun MH (2018) Dysphagia in patients with isolated pontine infarction. Neural Regen Res 13(12):2156–2159. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.241466
Chen CJ, Yang TC, Chang C, Lu SC, Chang PY (2018) Homocysteine is a bystander for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a case-control study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 18(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-018-0774-8
Feng MC, Lin YC, Chang YH, Chen CH, Chiang HC, Huang LC, Yang YH, Hung CH (2019) The Mortality and the Risk of Aspiration Pneumonia Related with Dysphagia in Stroke Patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 28(5):1381–1387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.02.011
Galli J, Marchese MR, Di Cesare T, Tricarico L, Almadori G, Tempesta V, Valenza V, Paludetti G (2021) Impact of Tracheal Tube on Swallowing in Post-Operative Head and Neck Cancer Patients: Scintigraphic Analysis. Dysphagia 36(6):953–958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10222-y
He K, Wu L, Ni F, Li X, Liang K, Ma R (2022) Efficacy and Safety of Mirror Therapy for Post-stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Neurol 13:874994. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.874994
Holdiman A, Rogus-Pulia N, Pulia MS, Stalter L, Thibeault SL (2023) Risk Factors for Dysphagia in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19. Dysphagia 38(3):933–942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-022-10518-1
Kim YK, Cha JH, Lee KY (2019) Comparison of Dysphagia Between Infratentorial and Supratentorial Stroke Patients. Ann Rehabil Med 43(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.149
Li J, Jiang S, Zhang Y, Tang G, Wang Y, Mao G, Li Z, Xu X, Wang B, Huo Y (2015) H-type hypertension and risk of stroke in chinese adults: A prospective, nested case-control study. J Transl Int Med 3(4):171–178. https://doi.org/10.1515/jtim-2015-0027
Liang J, Yin Z, Li Z, Gu H, Yang K, Xiong Y, Wang Y, Wang C (2022) Predictors of dysphagia screening and pneumonia among patients with acute ischaemic stroke in China: findings from the Chinese Stroke Center Alliance (CSCA). Stroke Vasc Neurol 7(4):294–301. https://doi.org/10.1136/svn-2020-000746
Nawaz S, Tulunay-Ugur OE (2018) Dysphagia in the Older Patient. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 51(4):769–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2018.03.006
Nunes MC, Jurkiewicz AL, Santos RS, Furkim AM, Massi G, Pinto GS, Lange MC (2012) Correlation between brain injury and dysphagia in adult patients with stroke. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 16(3):313–321. https://doi.org/10.7162/s1809-97772012000300003
Parlak MM, Bizpinar O, Saylam G (2022) Dysphagia in patients in acute period of ischemic stroke: What is the relationship of dysphagia with infarct localization, cognition, malnutrition, and independence level? [Article]. Neurology Asia 27(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.54029/2022kmw
Quyet D, Hien NM, Khan MX, Dai PD, Thuan DD, Duc DM, Hai ND, Nam BV, Huy PQ, Ton MD, Truong DT, Nga VT, Duc DP (2019) Risk Factors for Stroke Associated Pneumonia. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 7(24):4416–4419. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2019.873
Savcı C, Acaroğlu R (2021) Effects of Swallowing Training and Follow-up on the Problems Associated with Dysphagia in Patients with Stroke. Florence Nightingale J Nurs 29(2):137–149. https://doi.org/10.5152/fnjn.2021.19007
Shem K, Wong J, Dirlikov B, Castillo K (2019) Pharyngeal Dysphagia in Individuals With Cervical Spinal Cord Injury: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil 25(4):322–330. https://doi.org/10.1310/sci2504-322
Song H, Bharadwaj PK, Raichlen DA, Habeck CG, Huentelman MJ, Hishaw GA, Trouard TP, Alexander GE (2023) Association of homocysteine-related subcortical brain atrophy with white matter lesion volume and cognition in healthy aging. Neurobiol Aging 121:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2022.10.011
Sun J, Li Z (2018) Study on the Correlation between Barium Radiography and Pulmonary Infection rate in the Evaluation of Swallowing Function. Clinics (sao Paulo) 73:e182. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2018/e182
Tay SY, Ampil ER, Chen CP, Auchus AP (2006) The relationship between homocysteine, cognition and stroke subtypes in acute stroke. J Neurol Sci 250(1–2):58–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2006.06.028
Tsao JW, Hemphill JC 3rd, Johnston SC, Smith WS, Bonovich DC (2005) Initial Glasgow Coma Scale score predicts outcome following thrombolysis for posterior circulation stroke. Arch Neurol 62(7):1126–1129. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.62.7.1126
Umay E, Eyigor S, Bahat G, Halil M, Giray E, Unsal P, Unlu Z, Tikiz C, Vural M, Cincin AT, Bengisu S, Gurcay E, Keseroglu K, Aydeniz B, Karaca EC, Karaca B, Yalcin A, Ozsurekci C, Seyidoglu D, Yilmaz O, Alicura S, Tokgoz S, Selcuk B, Sen EI, Karahan AY, Yaliman A, Ozkok S, Ilhan B, Oytun MG, Ozturk ZA, Akin S, Yavuz B, Akaltun MS, Sari A, Inanir M, Bilgilisoy M, Çaliskan Z, Saylam G, Ozer T, Eren Y, Bicakli DH, Keskin D, Ulger Z, Demirhan A, Calik Y, Saka B, Yigman ZA, Ozturk EA (2022) Best Practice Recommendations for Geriatric Dysphagia Management with 5 Ws and 1H. Ann Geriatr Med Res 26(2):94–124. https://doi.org/10.4235/agmr.21.0145
Wang ZZ, Sun Z, Zhang ML, Xiong K, Zhou F (2022) Systematic review and meta-analysis of acupuncture in the treatment of cognitive impairment after stroke. Medicine (baltimore) 101(41):e30461. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000030461
Wen X, Liu Z, Zhong L, Peng Y, Wang J, Liu H, Gong X (2022) The Effectiveness of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Post-stroke Dysphagia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Hum Neurosci 16:841781. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2022.841781
Xu H, Zheng H, Huang J, Shen Y, Luo M (2017) T-cell subsets are associated with serum homocysteine concentration in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens 39(4):377–381. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641963.2016.1267189
Yagi N, Oku Y, Nagami S, Yamagata Y, Kayashita J, Ishikawa A, Domen K, Takahashi R (2017) Inappropriate Timing of Swallow in the Respiratory Cycle Causes Breathing-Swallowing Discoordination. Front Physiol 8:676. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00676
Yew AY, Nguyen MT, Hsu WK, Patel AA (2019) Quantitative Risk Factor Analysis of Postoperative Dysphagia After Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) Using the Eating Assessment Tool-10 (EAT-10). Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 44(2):E82-e88. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000002770
Yu-Lei X, Shan W, Ju Y, Yu-Han X, Wu Q, Yin-Xu W (2022) Theta burst stimulation versus high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for poststroke dysphagia: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Medicine (baltimore) 101(2):e28576. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000028576
Zhang M, Li C, Zhang F, Han X, Yang Q, Lin T, Zhou H, Tang M, Zhou J, Shi H, Hui Y, Xiong M, Pang L, Wang B, Feng Z, Li Z, Cao C, Lu X, Ding Y, Shen S, Xu Z, Yu F, Chen C, Meng L, Liao G, Zhang J, Sasegbon A, Dou Z (2021) Prevalence of Dysphagia in China: An Epidemiological Survey of 5943 Participants. Dysphagia 36(3):339–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10138-7
Zuercher P, Schenk NV, Moret C, Berger D, Abegglen R, Schefold JC (2020) Risk Factors for Dysphagia in ICU Patients After Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Chest 158(5):1983–1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2020.05.576
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.X. F, J.R. Z, Y.E. W and S.Q. Z designed the research study. Q.P. H, Y. G and J.Q. W performed the research. J.R. Z, Y.E. W and C.Q. G analyzed the data. J.R. Z and Y.E. W wrote the manuscript. Q.X. F and S.Q. Z contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The study protocol was approved by The Ethics Committee of Houjie Hospital of Dongguan and followed the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. In addition, informed consent has been obtained from the participants involved.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Q., Zhao, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Factors Influencing Early Diagnosis and Poor Prognosis of Dysphagia After Senile Ischemic Stroke. J Mol Neurosci 74, 31 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02210-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-024-02210-w