Abstract
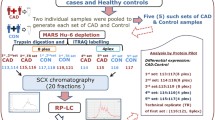
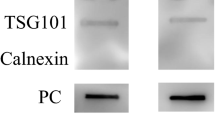
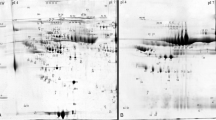
Moyamoya disease (MMD) is a chronic cerebrovascular disease with unknown etiology. The pathogenesis of vascular changes remains unclear. Ischemic and hemorrhagic adult MMD patients and healthy volunteers were enrolled to collect serum for data-independent acquisition (DIA)-based proteomic analysis and ELISA validation. DIA serum proteomic revealed that apolipoprotein C-I (APOC1), apolipoprotein D (APOD), and apolipoprotein A-IV (APOA4) were decreased. The reductases glutathione S-transferase omega-1 (GSTO1) and peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase A (PPIA) were upregulated, and ADAMTS-like protein 4 (ADAMTSL4) was downregulated in both ischemic and hemorrhagic MMD. Afamin (AFM) and transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 (TGFBI) increased in ischemic patients but decreased in hemorrhagic patients. Serum ELISA results confirmed that APOA4, APOC1, and APOD were decreased compared to controls. Then, we retrospectively analyzed biochemical indexes of 200 MMD patients. A total of 54 enrolled MMD patients showed decreased total cholesterol (TC) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c). APOA4, APOC1, and APOD were vital factors in the HDL decrease in MMD patients. Lipoprotein dysfunction in MMD patients is involved in MMD. Intimal thickening by enhanced adhesion, middle layer vascular smooth muscle cell migration, and decreased lipid antioxidant function represented by HDL are potential pathogeneses of vascular changes in MMD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Datasets of proteomics analyses and other material related to the current study are readily available upon request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- MMD:
-
Moyamoya disease
- MMS:
-
Moyamoya syndrome
- DIA:
-
Data-independent acquisition
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- APOC1:
-
Apolipoprotein C-I
- APOD:
-
Apolipoprotein D
- APOA4:
-
Apolipoprotein A-IV
- GSTO1:
-
Glutathione S-transferase omega-1
- PPIA:
-
Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase A
- ADAMTSL4:
-
ADAMTS-like protein 4
- AFM:
-
Afamin
- TGFBI:
-
Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- VHDL:
-
Very-low-density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- VLDL:
-
Very-low-density lipoprotein
- LCAT:
-
Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase
- LFA-1:
-
Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1
- VSMCs:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells
- ICAM:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule
References
Araki Y, Yoshikawa K, Okamoto S, Sumitomo M, Maruwaka M, Wakabayashi T (2010) Identification of novel biomarker candidates by proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with moyamoya disease using SELDI-TOF-MS. BMC Neurol 10:112
Aviram R, Zaffryar-Eilot S, Hubmacher D, Grunwald H, Maki JM, Myllyharju J, Apte SS, Hasson P (2019) Interactions between lysyl oxidases and ADAMTS proteins suggest a novel crosstalk between two extracellular matrix families. Matrix Biol 75–76:114–125
Bang OY, Fujimura M, Kim SK (2016) The pathophysiology of moyamoya disease: an update. J Stroke 18(1):12–20
Buga AM, Margaritescu C, Scholz CJ, Radu E, Zelenak C, Popa-Wagner A (2014) Transcriptomics of post-stroke angiogenesis in the aged brain. Front Aging Neurosci 6:44
Cao Y, Kobayashi H, Morimoto T, Kabata R, Harada KH, Koizumi A (2016) Frequency of RNF213 p.R4810K, a susceptibility variant for moyamoya disease, and health characteristics of carriers in the Japanese population. Environ Health Prev Med 21(5):387–390
Christoffersen C (2021) Apolipoprotein M-A marker or an active player in type II diabetes? Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 12:665393
Colombo GI, Bianconi V, Bonomi A, Simonelli S, Amato M, Frigerio B, Ravani A, Vitali C, Sansaro D, Coggi D, Mannarino MR, Savonen KP, Kurl S, Gigante B, Smit AJ, Giral P, Tremoli E, Calabresi L, Veglia F, Pirro M, Baldassarre D, On behalf of the improve study (2021) The association between HDL-C and subclinical atherosclerosis depends on CETP plasma concentration: insights from the IMPROVE study. Biomedicines 9(3)
Dassati S, Waldner A, Schweigreiter R (2014) Apolipoprotein D takes center stage in the stress response of the aging and degenerative brain. Neurobiol Aging 35(7):1632–1642
DeLaney K, Li L (2020) Neuropeptidomic profiling and localization in the Crustacean cardiac ganglion using mass spectrometry imaging with multiple platforms. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 31(12):2469–2478
Ducroux C, Desilles JP, Mawhin MA, Delbosc S, Ho-Tin-Noe B, Ollivier V, Di Meglio L, Lapergue B, Michel JB, Amarenco P (2020) Protective effect of ApoA1 (Apolipoprotein A1)-Milano in a rat model of large vessel occlusion stroke. Stroke 51(6):1886–1890
Ge P, Zhang Q, Ye X, Liu X, Deng X, Wang J, Wang R, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Zhao J (2020) Modifiable risk factors associated with moyamoya disease: a case-control study. Stroke 51(8):2472–2479
Ge P, Zhao Y, Zhai Y, Zhang Q, Ye X, Wang J, Wang R, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Zhao J (2022) Circulating choline pathway nutrients and risk of moyamoya disease. Front Nutr 9:953426
Hosoda Y, Ikeda E, Hirose S (1997) Histopathological studies on spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis (cerebrovascular moyamoya disease). Clin Neurol Neurosurg 99(Suppl 2):S203-208
Hubmacher D, Apte SS (2015) ADAMTS proteins as modulators of microfibril formation and function. Matrix Biol 47:34–43
Jiang Q, Qin D, Yang L, Lin Y, Zhai L, Zhang Y, Yang G, Wang K, Tong D, Li X, Chen Z, Huang K, Yu T, Xiang X, Cui C, Cai C, Shi J, Li M, Chen M (2021) Causal effects of plasma lipids on the risk of atrial fibrillation: a multivariable mendelian randomization study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 31(5):1569–1578
Jolugbo P, Ariens RAS (2021) Thrombus composition and efficacy of thrombolysis and thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 52(3):1131–1142
Kan P, Srinivasan VM, Srivatsan A, Kaufmann AB, Cherian J, Burkhardt JK, Johnson J, Duckworth EA (2021) Double-barrel STA-MCA bypass for cerebral revascularization: lessons learned from a 10-year experience. J Neurosurg 1–9
Karamanos NK (2019) Extracellular matrix: key structural and functional meshwork in health and disease. FEBS J 286(15):2826–2829
Kim HJ, Choi EH, Chung JW, Kim JH, Kim YS, Seo WK, Kim GM, Bang OY (2020) Luminal and wall changes in intracranial arterial lesions for predicting stroke occurrence. Stroke 51(8):2495–2504
Kitamura Y, Usami R, Ichihara S, Kida H, Satoh M, Tomimoto H, Murata M, Oikawa S (2017) Plasma protein profiling for potential biomarkers in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Res 39(3):231–238
Kolsch H, Linnebank M, Lutjohann D, Jessen F, Wullner U, Harbrecht U, Thelen KM, Kreis M, Hentschel F, Schulz A, von Bergmann K, Maier W, Heun R (2004) Polymorphisms in glutathione S-transferase omega-1 and AD, vascular dementia, and stroke. Neurology 63(12):2255–2260
Lee JH, Youn TJ, Yoon YE, Park JJ, Hong SJ, Chun EJ, Choi SI, Cho YS, Cho GY, Chae IH, Choi DJ (2013) Coronary artery stenosis in moyamoya disease: tissue characterization by 256-slice multi-detector CT and virtual histology. Circulation 127(20):2063–2065
Liu Z, Chang AN, Grinnell F, Trybus KM, Milewicz DM, Stull JT, Kamm KE (2017) Vascular disease-causing mutation, smooth muscle alpha-actin R258C, dominantly suppresses functions of alpha-actin in human patient fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(28):E5569–E5578
Messner CB, Demichev V, Bloomfield N, Yu JS, White M, Kreidl M, Egger AS, Freiwald A, Ivosev G, Wasim F, Zelezniak A, Jurgens L, Suttorp N, Sander LE, Kurth F, Lilley KS, Mulleder M, Tate S, Ralser M (2021) Ultra-fast proteomics with scanning SWATH. Nat Biotechnol
Mikami T, Suzuki H, Komatsu K, Mikuni N (2019) Influence of inflammatory disease on the pathophysiology of moyamoya disease and quasi-moyamoya disease. Neurol Med Chir (tokyo) 59(10):361–370
Nishihara H, Gastfriend BD, Soldati S, Perriot S, Mathias A, Sano Y, Shimizu F, Gosselet F, Kanda T, Palecek SP, Du Pasquier R, Shusta EV, Engelhardt B (2020) Advancing human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived blood-brain barrier models for studying immune cell interactions. FASEB J 34(12):16693–16715
Petkovic F, Lazzarino GP, Engblom D, Blomqvist A (2020) IL-6R expressed on CNS vascular endothelial cells contributes to the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. J Neuroimmunol 342:577211
Raso A, Biassoni R, Mascelli S, Nozza P, Ugolotti E, Di Marco E, De Marco P, Merello E, Cama A, Pavanello M, Capra V (2020) Moyamoya vasculopathy shows a genetic mutational gradient decreasing from East to West. J Neurosurg Sci 64(2):165–172
Ren X, Yao LL, Pan JX, Zhang JS, Mei L, Wang YG, Xiong WC (2021) Linking cortical astrocytic neogenin deficiency to the development of moyamoya disease-like vasculopathy. Neurobiol Dis 154:105339
Research Committee on the, P., W. Treatment of spontaneous occlusion of the circle of and D. health labour sciences research grant for research on measures for infractable (2012) Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis). Neurol Med Chir (tokyo) 52(5):245–266
Ritzel RM, Lai YJ, Crapser JD, Patel AR, Schrecengost A, Grenier JM, Mancini NS, Patrizz A, Jellison ER, Morales-Scheihing D, Venna VR, Kofler JK, Liu F, Verma R, McCullough LD (2018) Aging alters the immunological response to ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol 136(1):89–110
Saw J, Yang ML, Trinder M, Tcheandjieu C, Xu C, Starovoytov A, Birt I, Mathis MR, Hunker KL, Schmidt EM, Jackson L, Fendrikova-Mahlay N, Zawistowski M, Brummett CM, Zoellner S, Katz A, Coleman DM, Swan K, O'Donnell CJ, Million Veteran P, Zhou X, Li JZ, Gornik HL, Assimes TL, Stanley JC, Brunham LR, Ganesh SK (2020) Chromosome 1q21.2 and additional loci influence risk of spontaneous coronary artery dissection and myocardial infarction. Nat Commun 11(1):4432
Steinlin M (2017) Neuroinflammation in ischemic pediatric stroke. Semin Pediatr Neurol 24(3):201–206
Suzuki J, Takaku A (1969) Cerebrovascular “moyamoya” disease. Disease showing abnormal net-like vessels in base of brain. Arch Neurol 20(3):288–299
Togao O, Hiwatashi A, Obara M, Yamashita K, Kikuchi K, Kamei R, Nishimura A, Arimura K, Yoshimoto K, Iihara K, Van Cauteren M, Honda H (2018) Acceleration-selective arterial spin-labeling MR angiography used to visualize distal cerebral arteries and collateral vessels in moyamoya disease. Radiology 286(2):611–621
Trujillo-Viera J, El-Merahbi R, Schmidt V, Karwen T, Loza-Valdes A, Strohmeyer A, Reuter S, Noh M, Wit M, Hawro I, Mocek S, Fey C, Mayer AE, Loffler MC, Wilhelmi I, Metzger M, Ishikawa E, Yamasaki S, Rau M, Geier A, Hankir M, Seyfried F, Klingenspor M, Sumara G (2021) Protein Kinase D2 drives chylomicron-mediated lipid transport in the intestine and promotes obesity. EMBO Mol Med 13(5):e13548
Varga VE, Lorincz H, Szentpeteri A, Juhasz L, Seres I, Paragh G Jr, Balla J, Paragh G, Harangi M (2018) Changes in serum afamin and vitamin E levels after selective LDL apheresis. J Clin Apher 33(5):569–575
Wang X, Han C, Jia Y, Wang J, Ge W, Duan L (2021a) Proteomic profiling of exosomes from hemorrhagic moyamoya disease and dysfunction of mitochondria in endothelial cells. Stroke: STROKEAHA120032297
Wang X, Han C, Jia Y, Wang J, Ge W, Duan L (2021b) Proteomic profiling of exosomes from hemorrhagic moyamoya disease and dysfunction of mitochondria in endothelial cells. Stroke 52(10):3351–3361
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Wei L, Zhang Q, Zou Z, Yang L, Li D, Shang M, Han C, Mambiya M, Bao X, Li Q, Hao F, Zhang K, Wang H, Liu S, Liu M, Zeng F, Nie F, Wang K, Liu W, Duan L (2020) Predictive role of heterozygous p.R4810K of RNF213 in the phenotype of Chinese moyamoya disease. Neurology 94(7):e678-e686
Yang Y, Wang J, Liang Q, Wang Y, Chen X, Zhang Q, Na S, Liu Y, Yan T, Hang C, Zhu Y (2020) PHACTR1 is associated with disease progression in Chinese moyamoya disease. PeerJ 8:e8841
Zhao L, Sun W, Liang H, Gao T, Liu Y, Sun Y, Zhang S, Li C (2020) Therapeutic effect of autologous bone marrow stem cell mobilization combined with anti-infective therapy on moyamoya disease. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(2):676–681
Zhao TJ, Zhu N, Shi YN, Wang YX, Zhang CJ, Deng CF, Liao DF, Qin L (2021) Targeting HDL in tumor microenvironment: new hope for cancer therapy. J Cell Physiol
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant (82002643), Postdoctoral Research Foundation of China grant (2019M651954), and Gusu Health Personal Training Project (GSWS2019002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Zongqi Wang, Chengyuan Ji, and Qingdong Han. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Zongqi Wang. Writing—review and editing by Qingdong Han and Yabo Huang. Funding acquisition: Zongqi Wang and Zhong Wang. Supervision: Zhong Wang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All individual participants enrolled in this study were informed of the trial and signed an informed consent form. This study was performed following the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to the publication of the manuscript in Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, should the article be accepted by the Editor-in-chief.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Ji, C., Han, Q. et al. Data-Independent Acquisition-Based Serum Proteomic Profiling of Adult Moyamoya Disease Patients Reveals the Potential Pathogenesis of Vascular Changes. J Mol Neurosci 72, 2473–2485 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02092-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02092-w