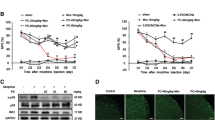
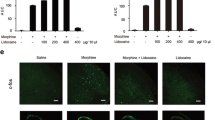
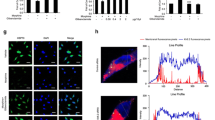
Abstract
Morphine is generally used to treat chronic pain in clinic. But long-term use of morphine can inevitably induce analgesic tolerance and hyperalgesia. Caveolin-1 is reported to affect morphine-mediated signaling transduction. However, the action mechanism of morphine-induced analgesic tolerance is still unknown. In this study, morphine-induced analgesic tolerance model was established in Sprague–Dawley rats. The effects of Caveolin-1 blocking on neuroinflammation and ERK/c-JUN pathway were then explored. Morphine can remarkably elevate the expression level of Caveolin-1. Based on paw withdrawal latency behavior test, we found that Caveolin-1 blocking can effectively attenuate morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and neuroinflammation. Activation of ERK/c-JUN significantly reversed the above influences caused by Caveolin-1 blocking. Taken together, blocking of Caveolin-1 can attenuate morphine-induced inflammation and analgesic tolerance through inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and ERK/c-JUN pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Almela P, Garcia-Nogales P, Romero A, Milanes MV, Laorden ML, Puig MM (2009) Effects of chronic inflammation and morphine tolerance on the expression of phospho-ERK 1/2 and phospho-P38 in the injured tissue. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 379(3):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0356-x
Cai Y, Kong H, Pan YB, Jiang L, Pan XX, Hu L et al (2016) Procyanidins alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0520-z
Chakrabarti S, Chang AY, Liu NJ, Gintzler AR (2016) Chronic opioid treatment augments caveolin-1 scaffolding: relevance to stimulatory -opioid receptor adenylyl cyclase signaling. J Neurochem 139(5):737–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13852
Chen R, Yin C, Fang J, Liu B (2021) The NLRP3 inflammasome: an emerging therapeutic target for chronic pain. J Neuroinflammation 18(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-021-02131-0
de Freitas BG, Pereira LM, Santa-Cecilia FV, Hosch NG, Picolo G, Cury Y et al (2019) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling mediates morphine induced-delayed hyperalgesia. Front Neurosci 13:1018. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01018
Doyle TM, Largent-Milnes TM, Chen Z, Staikopoulos V, Esposito E, Dalgarno R et al (2020) Chronic morphine-induced changes in signaling at the A3 adenosine receptor contribute to morphine-induced hyperalgesia, tolerance, and withdrawal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 374(2):331–341. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.120.000004
Eidson LN, Inoue K, Young LJ, Tansey MG, Murphy AZ (2017) Toll-like receptor 4 mediates morphine-induced neuroinflammation and tolerance via soluble tumor necrosis factor signaling. Neuropsychopharmacology 42(3):661–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2016.131
Fields H (2004) State-dependent opioid control of pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(7):565–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1431
Fields HL (2011) The doctor’s dilemma: opiate analgesics and chronic pain. Neuron 69(4):591–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.001
Gao F, Shen J, Zhao L, Hao Q, Yang Y (2019) Curcumin alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated neuroinflammation via modulation of miR-199b-5p/IkappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta)/Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kappaB) Pathway in Microglia. Med Sci Monit 25:9801–9810. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.918237
Gao F, Xiang HC, Li HP, Jia M, Pan XL, Pan HL et al (2018) Electroacupuncture inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation through CB2 receptors in inflammatory pain. Brain Behav Immun 67:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.004
Geng S, Wang S, Zhu W, Xie C, Li X, Wu J et al (2018) Curcumin suppresses JNK pathway to attenuate BPA-induced insulin resistance in LO2 cells. Biomed Pharmacother 97:1538–1543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.069
Grace PM, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2015) Opioid-induced central immune signaling: implications for opioid analgesia. Headache 55(4):475–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12552
Grace PM, Strand KA, Galer EL, Urban DJ, Watkins LR (2016) Morphine paradoxically prolongs neuropathic pain in rats by amplifying spinal NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Pro Nat Acad Sci U S a. 113(24):3441–3450. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1602070113
Kalso E, Edwards JE, Moore RA, Mcquay HJ (2004) Opioids in chronic non-cancer pain: systematic review of efficacy and safety. Pain 112(3):372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2004.09.019
Kim JH, Park JM, Kim EK, Lee JO, Lee SK, Jung JH et al (2010) Curcumin stimulates glucose uptake through AMPK-p38 MAPK pathways in L6 myotube cells. J Cell Physiol 223(3):771–778. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22093
Lin X, Bai D, Wei Z, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Deng H et al (2019) Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. PLoS One 14(5):e0216711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216711
Liu Q, Su LY, Sun C, Jiao L, Miao Y, Xu M et al (2020) Melatonin alleviates morphine analgesic tolerance in mice by decreasing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol 34:101560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101560
Macey TA, Bobeck EN, Suchland KL, Morgan MM, Ingram SL (2015) Change in functional selectivity of morphine with the development of antinociceptive tolerance. Br J Pharmacol 172(2):549–561. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12703
Marcus DJ, Zee M, Hughes A, Yuill MB, Hohmann AG, Mackie K et al (2015) Tolerance to the antinociceptive effects of chronic morphine requires c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Mol Pain 11:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12990-015-0031-4
Mo Y, Yue E, Shi N, Liu K (2021) The protective effects of curcumin in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury through PKC-theta signaling. Cell Cycle 20(5–6):550–560. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2021.1889188
Mohankumar K, Francis AP, Pajaniradje S, Rajagopalan R (2021) Synthetic curcumin analog: inhibiting the invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis in human laryngeal carcinoma cells via NF-kB pathway. Mol Biol Rep 48(8):6065–6074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06610-8
Muscoli C, Doyle T, Dagostino C, Bryant L, Chen Z, Watkins LR et al (2010) Counter-regulation of opioid analgesia by glial-derived bioactive sphingolipids. J Neurosci 30(46):15400–15408. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2391-10.2010
Okamoto T, Schlegel A, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (1998) Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing “preassembled signaling complexes” at the Plasma Membrane. J Bio Chem 273(10):5419–5422. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.10.5419
Okerman T, Jurgenson T, Moore M, Klein AH (2021) Inhibition of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT-cyclic GMP-c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway attenuates the development of morphine tolerance in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 17:17448069211003376. https://doi.org/10.1177/17448069211003375
Pan Z, Shan Q, Gu P, Wang XM, Tai LW, Sun M et al (2018) miRNA-23a/CXCR4 regulates neuropathic pain via directly targeting TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1073-0
Parsadaniantz SM, Rivat C, Rostène W, Goazigo RL (2015) Opioid and chemokine receptor crosstalk: a promising target for pain therapy? Nat Rev Neurosci 16(2):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3858
Patel HH, Murray F, Insel PA (2008) Caveolae as organizers of pharmacologically relevant signal transduction molecules. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:359–391. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.121506.124841
Petiti J, Rosso V, Lo Iacono M, Panuzzo C, Calabrese C, Signorino E et al (2019) Curcumin induces apoptosis in JAK2-mutated cells by the inhibition of JAK2/STAT and mTORC1 pathways. J Cell Mol Med 23(6):4349–4357. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14326
Qu J, Tao XY, Teng P, Zhang Y, Guo CL, Hu L et al (2017) Blocking ATP-sensitive potassium channel alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting HSP70-TLR4-NLRP3-mediated neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 14(1):228. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0997-0
Roeckel LA, Coz G, Gavériaux-Ruff C, Simonin F (2016) Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Neuroscience 338:160–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.06.029
Sanna MD, Ghelardini C, Galeotti N (2014) Regionally selective activation of ERK and JNK in morphine paradoxical hyperalgesia: a step toward improving opioid pain therapy. Neuropharmacology 86:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.06.007 S0028-3908(14)00229-9[pii]
Sanna MD, Mello T, Ghelardini C, Galeotti N (2015) Inhibition of spinal ERK1/2-c-JUN signaling pathway counteracts the development of low doses morphine-induced hyperalgesia. Eur J Pharmacol 764:271–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.07.022 S0014-2999(15)30151-5[pii]
Shrestha S, Zhu J, Wang Q, Du X, Liu F, Jiang J et al (2017) Melatonin potentiates the antitumor effect of curcumin by inhibiting IKKbeta/NF-kappaB/COX-2 signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 51(4):1249–1260. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.4097
Sommer C (2017) Peripheral neuropathies: long-term opioid therapy in neuropathy: benefit or harm? Nat Rev Neurol 13(9):516–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.101
SoukhakLari R, Moezi L, Pirsalami F, Moosavi M (2018) The effect of BSA-based curcumin nanoparticles on memory and hippocampal MMP-2, MMP-9, and MAPKs in adult mice. J Mol Neurosci 65(3):319–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1104-4
Vanjani R, Trimbur MC (2019) Opioid tolerance in critical illness. N Eng J Med 380(16):e26. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1902646
Volkow ND, Mclellan AT (2016) Opioid abuse in chronic pain–misconceptions and mitigation strategies. N Engl J Med 374(13):1253–1263. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1507771
Wang J, Zhao Q, Zhou Y, Sun W, Han S, Peng Y et al (2020) Subanesthetic dose of ketamine improved cfa-induced inflammatory pain and depression-like behaviors via caveolin-1 in mice. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 32(4):359–366. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0000000000000610
Wang S, Zeng M, Ren Y, Han S, Cui W (2021) In vivo reduction of hippocampal caveolin-1 by RNA interference alters morphine addiction and neuroplasticity changes in male mice. Neurosci Lett 749(6):135742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135742
Wang X, Loram LC, Ramos K, de Jesus AJ, Thomas J, Cheng K et al (2012) Morphine activates neuroinflammation in a manner parallel to endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(16):6325–6330. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1200130109
Weng P, Zhang XT, Sheng Q, Tian WF, Chen JL, Yuan JJ et al (2017) Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptides enhance anti-inflammatory effect of heme oxygenase-1 through interrupting its interact with caveolin-1. Oncotarget 8(25):40104–401014. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16676
Wu LY, Chen CW, Chen LK, Chou HY, Chang CL, Juan CC (2019) Curcumin attenuates adipogenesis by inducing preadipocyte apoptosis and inhibiting adipocyte differentiation. Nutrients 11(10):2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102307
Xu L, Ding L, Su Y, Shao R, Liu J, Huang Y (2019) Neuroprotective effects of curcumin against rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Med 43(4):1879–1887. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2019.4094
Yang JX, Hua L, Li YQ, Jiang YY, Han D, Liu H et al (2015) Caveolin-1 in the anterior cingulate cortex modulates chronic neuropathic pain via regulation of NMDA receptor 2B subunit. J Neurosci 35(1):36–52. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1161-14.2015
Yu T, Ji J, Guo YL (2013) MST1 activation by curcumin mediates JNK activation, Foxo3a nuclear translocation and apoptosis in melanoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 441(1):53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.008
Zhao W, Zhou X, Qi G, Guo Y (2018) Curcumin suppressed the prostate cancer by inhibiting JNK pathways via epigenetic regulation. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 32(5):e22049. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22049
Zhong W, Huang Q, Zeng L, Hu Z, Tang X (2019) Caveolin-1 and MLRs: a potential target for neuronal growth and neuroplasticity after ischemic stroke. Int J Med Sci 16(11):1492–1503. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.35158
Zhou K, Shi L, Wang Y, Chen S, Zhang J (2016) Recent advances of the NLRP3 inflammasome in central nervous system disorders. J Immunol Res 2016:9238290. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9238290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LWL made main contributions that are as follows: Writing — original draft, funding acquisition, conceptualization, formal analysis, project administration; PJ WAS mainly responsible for the following work: Resources, writing — review and editing; Data curation, Investigation; LJQ was in charge of methodology, supervision, validation writing — review and editing; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All animal experiments in this study were performed in strict accordance with the protocols stated in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the ethical committee of HuiZhou Municipal Central Hospital.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Jiang, P. & Qiu, L. Blocking of Caveolin-1 Attenuates Morphine-Induced Inflammation, Hyperalgesia, and Analgesic Tolerance via Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome and ERK/c-JUN Pathway. J Mol Neurosci 72, 1047–1057 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-01989-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-01989-w